Indonesia - ID - IDN - INA - East and Southeast Asia
Last updated: January 21, 2026

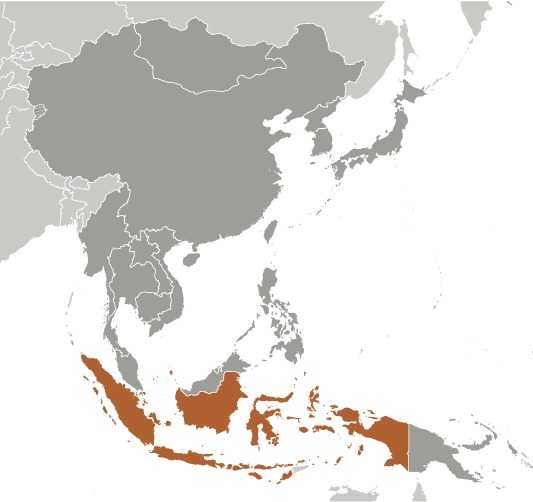
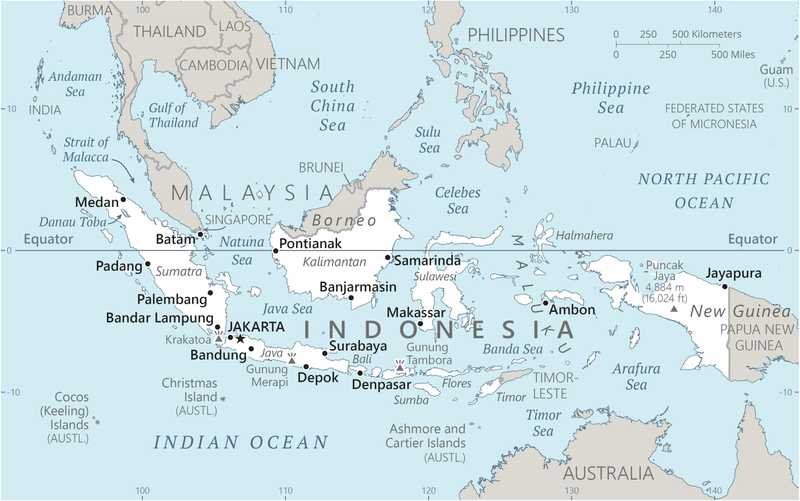
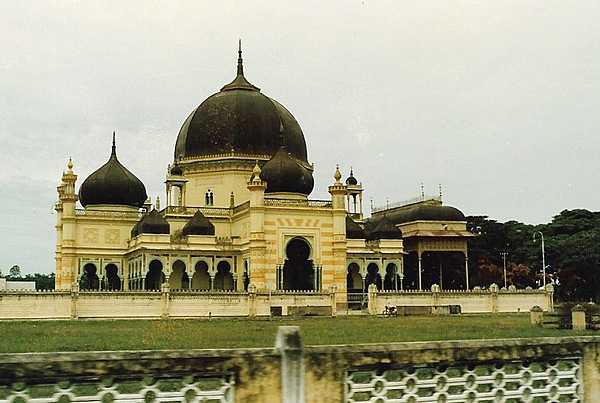
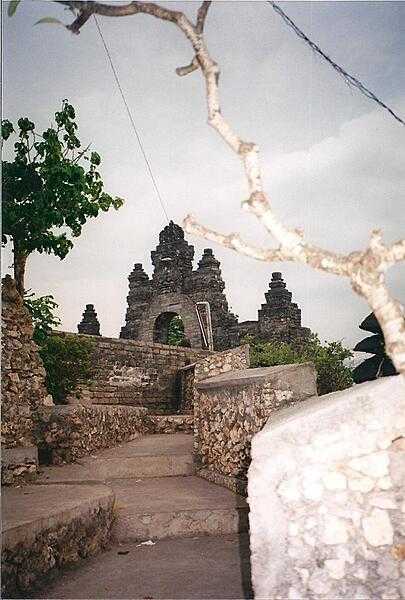
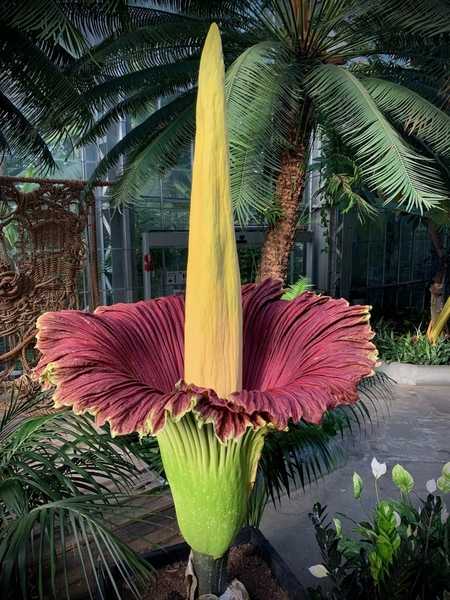
Indonesia Images
Indonesia Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Chargé d’Affaires Peter M. HAYMOND (since 15 June 2025)
embassy: Jl. Medan Merdeka Selatan No. 3-5, Jakarta 10110
mailing address: 8200 Jakarta Place, Washington DC 20521-8200
telephone: [62] (21) 5083-1000
FAX: [62] (21) 385-7189
email address and website:
jakartaacs@state.gov
https://id.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Surabaya
consulate(s): Medan
embassy: Jl. Medan Merdeka Selatan No. 3-5, Jakarta 10110
mailing address: 8200 Jakarta Place, Washington DC 20521-8200
telephone: [62] (21) 5083-1000
FAX: [62] (21) 385-7189
email address and website:
jakartaacs@state.gov
https://id.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Surabaya
consulate(s): Medan
Age structure
0-14 years: 23.8% (male 34,247,218/female 32,701,367)
15-64 years: 68.3% (male 96,268,201/female 95,961,293)
65 years and over: 8% (2024 est.) (male 10,284,628/female 12,099,758)
15-64 years: 68.3% (male 96,268,201/female 95,961,293)
65 years and over: 8% (2024 est.) (male 10,284,628/female 12,099,758)
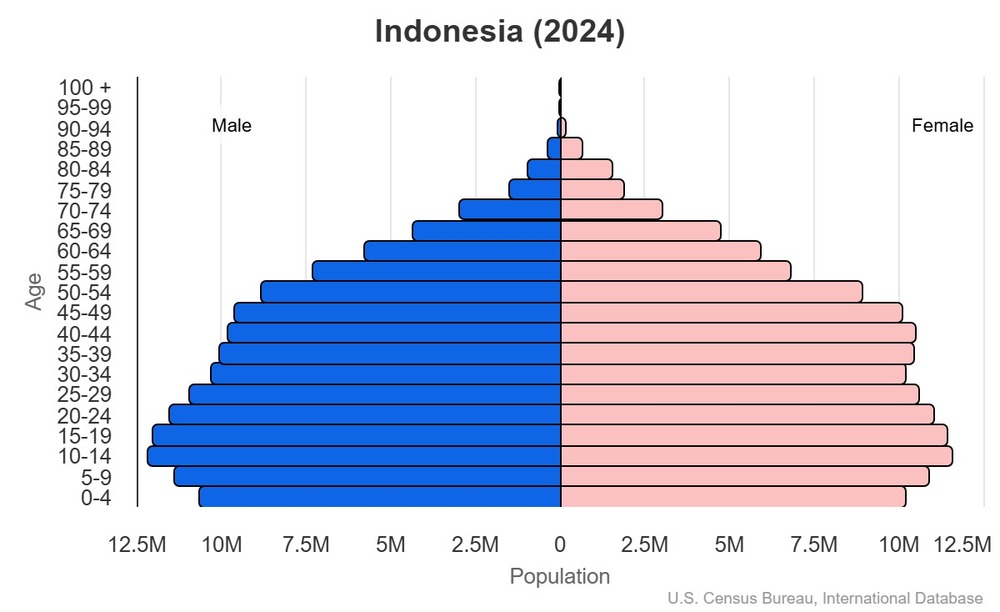
This is the population pyramid for Indonesia. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
5 00 S, 120 00 E
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
occasional floods; severe droughts; tsunamis; earthquakes; volcanoes; forest fires
volcanism: Indonesia contains the most volcanoes of any country in the world, with over 75 historically active; significant volcanic activity occurs on Java, Sumatra, the Sunda Islands, Halmahera Island, Sulawesi Island, Sangihe Island, and in the Banda Sea; Merapi (2,968 m), Indonesia's most active volcano, has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; in 2018, a large explosion and flank collapse destroyed most of the island of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) and generated a deadly tsunami that left more than 400 dead; other notable historically active volcanoes include Agung, Awu, Karangetang, Krakatau (Krakatoa), Makian, Raung, Sinabung, and Tambora; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
volcanism: Indonesia contains the most volcanoes of any country in the world, with over 75 historically active; significant volcanic activity occurs on Java, Sumatra, the Sunda Islands, Halmahera Island, Sulawesi Island, Sangihe Island, and in the Banda Sea; Merapi (2,968 m), Indonesia's most active volcano, has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; in 2018, a large explosion and flank collapse destroyed most of the island of Anak Krakatau (Child of Krakatau) and generated a deadly tsunami that left more than 400 dead; other notable historically active volcanoes include Agung, Awu, Karangetang, Krakatau (Krakatoa), Makian, Raung, Sinabung, and Tambora; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Area - comparative
slightly less than three times the size of Texas
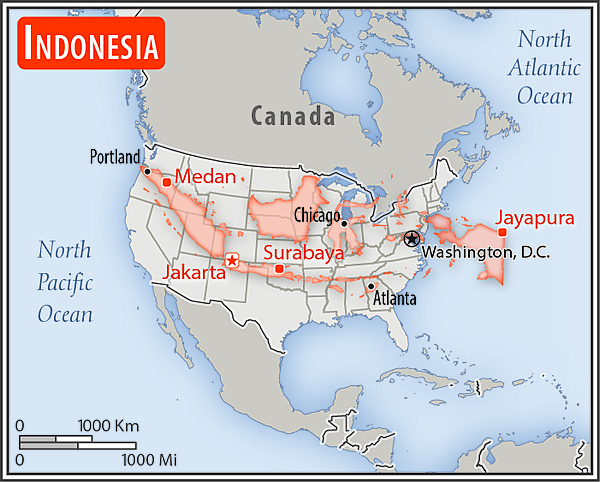
slightly less than three times the size of Texas
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary service for men and women; upper age limits vary by military service, position, specialty; compulsory service authorized but not utilized (2025)
Background
The archipelago was once largely under the control of Buddhist and Hindu rulers. By around the 7th century, a Buddhist kingdom arose on Sumatra and expanded into Java and the Malay Peninsula until it was conquered in the late 13th century by the Hindu Majapahit Empire from Java. Majapahit (1290-1527) united most of modern-day Indonesia and Malaysia. Traders introduced Islam around the 11th century, and the religion gradually expanded over the next 500 years. The Portuguese conquered parts of Indonesia in the 16th century, but the Dutch ousted them (except in East Timor) and began colonizing the islands in the early 17th century. It would be the early 20th century before Dutch colonial rule was established across the entirety of what would become the boundaries of the modern Indonesian state.
Japan occupied the islands from 1942 to 1945. Indonesia declared its independence shortly before Japan's surrender, but it required four years of sometimes brutal fighting, intermittent negotiations, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to transfer sovereignty in 1949. A period of sometimes unruly parliamentary democracy ended in 1957 when President SOEKARNO declared martial law and instituted "Guided Democracy." After an abortive coup in 1965 by alleged communist sympathizers, SOEKARNO was gradually eased from power. From 1967 until 1998, President SUHARTO ruled Indonesia with his "New Order" government. After street protests toppled SUHARTO in 1998, free and fair legislative elections took place in 1999 while the country's first direct presidential election occurred in 2004. Indonesia has since become a robust democracy, holding four direct presidential elections, each considered by international observers to have been largely free and fair.
Indonesia is now the world's third-most-populous democracy and the world's largest Muslim-majority nation. It has had strong economic growth since overcoming the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s. By the 2020s, it had the largest economy in Southeast Asia, and its economy ranked in the world's top 10 in terms of purchasing power parity. It has also made considerable gains in reducing poverty. Although relations amongst its diverse population--there are more than 300 ethnic groups--have been harmonious in the 2000s, there have been areas of sectarian discontent and violence, as well as instances of religious extremism and terrorism. A political settlement to an armed separatist conflict in Aceh was achieved in 2005, but a separatist group in Papua continued to conduct a low-intensity conflict as of 2024.
Japan occupied the islands from 1942 to 1945. Indonesia declared its independence shortly before Japan's surrender, but it required four years of sometimes brutal fighting, intermittent negotiations, and UN mediation before the Netherlands agreed to transfer sovereignty in 1949. A period of sometimes unruly parliamentary democracy ended in 1957 when President SOEKARNO declared martial law and instituted "Guided Democracy." After an abortive coup in 1965 by alleged communist sympathizers, SOEKARNO was gradually eased from power. From 1967 until 1998, President SUHARTO ruled Indonesia with his "New Order" government. After street protests toppled SUHARTO in 1998, free and fair legislative elections took place in 1999 while the country's first direct presidential election occurred in 2004. Indonesia has since become a robust democracy, holding four direct presidential elections, each considered by international observers to have been largely free and fair.
Indonesia is now the world's third-most-populous democracy and the world's largest Muslim-majority nation. It has had strong economic growth since overcoming the Asian financial crisis of the late 1990s. By the 2020s, it had the largest economy in Southeast Asia, and its economy ranked in the world's top 10 in terms of purchasing power parity. It has also made considerable gains in reducing poverty. Although relations amongst its diverse population--there are more than 300 ethnic groups--have been harmonious in the 2000s, there have been areas of sectarian discontent and violence, as well as instances of religious extremism and terrorism. A political settlement to an armed separatist conflict in Aceh was achieved in 2005, but a separatist group in Papua continued to conduct a low-intensity conflict as of 2024.
Environmental issues
large-scale deforestation (much of it illegal) and related wildfires cause heavy smog; over-exploitation of marine resources; air pollution from vehicle emissions; waste disposal; water pollution from industrial wastes, sewage
International environmental agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation
signed, but not ratified: Marine Life Conservation
Military expenditures
0.8% of GDP (2024 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.8% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
9% (2024 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3.5% (2024 est.)
highest 10%: 28.8% (2024 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
highest 10%: 28.8% (2024 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
coal, palm oil, iron alloys, lignite, garments (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
China 24%, USA 9%, India 8%, Japan 8%, Singapore 5% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
35 provinces (provinsi-provinsi, singular - provinsi), 1 autonomous province*, 1 special region** (daerah istimewa), and 1 national capital district*** (daerah khusus ibukota); Aceh*, Bali, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Jakarta***, Jambi, Jawa Barat (West Java), Jawa Tengah (Central Java), Jawa Timur (East Java), Kalimantan Barat (West Kalimantan), Kalimantan Selatan (South Kalimantan), Kalimantan Tengah (Central Kalimantan), Kalimantan Timur (East Kalimantan), Kalimantan Utara (North Kalimantan), Kepulauan Bangka Belitung (Bangka Belitung Islands), Kepulauan Riau (Riau Islands), Lampung, Maluku, Maluku Utara (North Maluku), Nusa Tenggara Barat (West Nusa Tenggara), Nusa Tenggara Timur (East Nusa Tenggara), Papua, Papua Barat (West Papua), Papua Barat Daya (Southwest Papua), Papua Pegunungan (Papua Highlands), Papua Selatan (South Papua), Papua Tengah (Central Papua), Riau, Sulawesi Barat (West Sulawesi), Sulawesi Selatan (South Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tengah (Central Sulawesi), Sulawesi Tenggara (Southeast Sulawesi), Sulawesi Utara (North Sulawesi), Sumatera Barat (West Sumatra), Sumatera Selatan (South Sumatra), Sumatera Utara (North Sumatra), Yogyakarta**
Agricultural products
oil palm fruit, rice, sugarcane, maize, coconuts, cassava, bananas, eggs, chicken, mangoes/guavas (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Indonesian National Armed Forces (Tentara Nasional Indonesia, TNI): Army (TNI-Angkatan Darat, TNI-AD), Navy (TNI-Angkatan Laut, TNI-AL; includes Marine Corps (Korps Marinir or KorMar)), Air Force (TNI-Angkatan Udara, TNI-AU)
Indonesian National Police (aka The State Police of the Republic of Indonesia or POLRI)
Ministry of Transportation: Indonesia Sea and Coast Guard (Kesatuan Penjagaan Laut dan Pantai Republik Indonesia, KPLP); Coordinating Ministry for Political, Legal, and Security Affairs: Maritime Security Agency of the Republic of Indonesia (Badan Keamanan Laut Republik Indonesia, Bakamla) (2025)
note 1: the National Police are an independent organization reporting directly to the president of Indonesia
note 2: the KPLP ensures the safety of shipping inside the Indonesian Maritime Zone; the Bakamla conducts security and safety patrols in the territorial waters of Indonesia
Indonesian National Police (aka The State Police of the Republic of Indonesia or POLRI)
Ministry of Transportation: Indonesia Sea and Coast Guard (Kesatuan Penjagaan Laut dan Pantai Republik Indonesia, KPLP); Coordinating Ministry for Political, Legal, and Security Affairs: Maritime Security Agency of the Republic of Indonesia (Badan Keamanan Laut Republik Indonesia, Bakamla) (2025)
note 1: the National Police are an independent organization reporting directly to the president of Indonesia
note 2: the KPLP ensures the safety of shipping inside the Indonesian Maritime Zone; the Bakamla conducts security and safety patrols in the territorial waters of Indonesia
Budget
revenues: $182.658 billion (2023 est.)
expenditures: $204.739 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenditures (excluding grants and social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
expenditures: $204.739 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenditures (excluding grants and social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
name: Jakarta
geographic coordinates: 6 10 S, 106 49 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
time zone note: Indonesia has three time zones
etymology: derives from the Sanscrit name Jayakarta, meaning "victory and prosperity;" Prince FATILLAH conquered and renamed the city, formerly known as Sunda Kelapa, in 1527
note: in 2022, the relocation of the country’s capital was approved, from Jakarta to a site on the island of Borneo between Samarinda City and the port city of Balikpapan; Nusantara ("archipelago"), the new capital, was in development as of 2024 and is expected to be completed in 2045
geographic coordinates: 6 10 S, 106 49 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
time zone note: Indonesia has three time zones
etymology: derives from the Sanscrit name Jayakarta, meaning "victory and prosperity;" Prince FATILLAH conquered and renamed the city, formerly known as Sunda Kelapa, in 1527
note: in 2022, the relocation of the country’s capital was approved, from Jakarta to a site on the island of Borneo between Samarinda City and the port city of Balikpapan; Nusantara ("archipelago"), the new capital, was in development as of 2024 and is expected to be completed in 2045
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, crude petroleum, plastics, vehicle parts/accessories, integrated circuits (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
tropical; hot, humid; more moderate in highlands
Coastline
54,716 km
Constitution
history: drafted July to August 1945, effective 18 August 1945, abrogated by 1949 and 1950 constitutions; 1945 constitution restored 5 July 1959
amendment process: proposed by the People’s Consultative Assembly, with at least two thirds of its members present; passage requires simple majority vote by the Assembly membership; constitutional articles on the unitary form of the state cannot be amended
amendment process: proposed by the People’s Consultative Assembly, with at least two thirds of its members present; passage requires simple majority vote by the Assembly membership; constitutional articles on the unitary form of the state cannot be amended
Exchange rates
Indonesian rupiah (IDR) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
15,855.448 (2024 est.)
15,236.885 (2023 est.)
14,849.854 (2022 est.)
14,308.144 (2021 est.)
14,582.203 (2020 est.)
Exchange rates:
15,855.448 (2024 est.)
15,236.885 (2023 est.)
14,849.854 (2022 est.)
14,308.144 (2021 est.)
14,582.203 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: President PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo (since 20 October 2024)
head of government: President PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo (since 20 October 2024)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president and vice president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term)
most recent election date: 14 February 2024
election results:
2024: PRABOWO Subianto elected president (assumes office 20 October 2024); percent of vote - PRABOWO Subianto (GERINDRA) 58.6%, Anies Rasyid BASWEDAN (Independent) 24.9%, GANJAR Pranowo (PDI-P) 16.5%
2019: Joko WIDODO reelected president; percent of vote - Joko WIDODO (PDI-P) 55.5%, PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo (GERINDRA) 44.5%
expected date of next election: 2029
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
head of government: President PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo (since 20 October 2024)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president and vice president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term)
most recent election date: 14 February 2024
election results:
2024: PRABOWO Subianto elected president (assumes office 20 October 2024); percent of vote - PRABOWO Subianto (GERINDRA) 58.6%, Anies Rasyid BASWEDAN (Independent) 24.9%, GANJAR Pranowo (PDI-P) 16.5%
2019: Joko WIDODO reelected president; percent of vote - Joko WIDODO (PDI-P) 55.5%, PRABOWO Subianto Djojohadikusumo (GERINDRA) 44.5%
expected date of next election: 2029
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
description: two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and white
meaning: red stands for courage and white for purity
history: the colors derive from the banner of the Majapahit Empire of the 13th-15th centuries
note: similar to the flags of Monaco, which is shorter, and Poland, which is white (top) and red
meaning: red stands for courage and white for purity
history: the colors derive from the banner of the Majapahit Empire of the 13th-15th centuries
note: similar to the flags of Monaco, which is shorter, and Poland, which is white (top) and red
Independence
17 August 1945 (declared independence from the Netherlands)
Industries
petroleum and natural gas, textiles, automotive, electrical appliances, apparel, footwear, mining, cement, medical instruments and appliances, handicrafts, chemical fertilizers, plywood, rubber, processed food, jewelry, and tourism
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Mahkamah Agung (51 judges divided into 8 chambers); Constitutional Court or Mahkamah Konstitusi (consists of 9 judges)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by Judicial Commission, appointed by president with concurrence of parliament; judges serve until retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court judges - 3 nominated by president, 3 by Supreme Court, and 3 by parliament; judges appointed by the president; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: High Courts of Appeal, district courts, religious courts
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by Judicial Commission, appointed by president with concurrence of parliament; judges serve until retirement at age 65; Constitutional Court judges - 3 nominated by president, 3 by Supreme Court, and 3 by parliament; judges appointed by the president; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: High Courts of Appeal, district courts, religious courts
Land boundaries
total: 2,958 km
border countries (3): Malaysia 1,881 km; Papua New Guinea 824 km; Timor-Leste 253 km
border countries (3): Malaysia 1,881 km; Papua New Guinea 824 km; Timor-Leste 253 km
Land use
agricultural land: 29.1% (2023 est.)
arable land: 9.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 13.9% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 5.8% (2023 est.)
forest: 50.6% (2023 est.)
other: 20.3% (2023 est.)
arable land: 9.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 13.9% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 5.8% (2023 est.)
forest: 50.6% (2023 est.)
other: 20.3% (2023 est.)
Legal system
civil law system based on the Roman-Dutch model and influenced by customary law
Legislative branch
legislature name: House of Representatives (Dewan Perwakilan Rakyat)
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 580 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 2/14/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Indonesian Democratic Party - Struggle (PDI-P) (110); Party of Functional Groups (Golkar) (102); Great Indonesia Movement (Gerindra) (86); National Democratic Party (NasDem) (69); National Awakening Party (PKB) (68); Prosperous Justice Party (PKS) (53); National Mandate Party (PAN) (48); Democratic Party (PD) (44)
percentage of women in chamber: 21.9%
expected date of next election: April 2029
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 580 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 2/14/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Indonesian Democratic Party - Struggle (PDI-P) (110); Party of Functional Groups (Golkar) (102); Great Indonesia Movement (Gerindra) (86); National Democratic Party (NasDem) (69); National Awakening Party (PKB) (68); Prosperous Justice Party (PKS) (53); National Mandate Party (PAN) (48); Democratic Party (PD) (44)
percentage of women in chamber: 21.9%
expected date of next election: April 2029
Literacy
total population: 96% (2020 est.)
male: 97.4% (2020 est.)
female: 94.6% (2020 est.)
male: 97.4% (2020 est.)
female: 94.6% (2020 est.)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
note: measured from claimed archipelagic straight baselines
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
note: measured from claimed archipelagic straight baselines
International organization participation
ADB, APEC, ARF, ASEAN, BIS, CD, CICA (observer), CP, D-8, EAS, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-11, G-15, G-20, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IORA, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, MSG (associate member), NAM, OECD (enhanced engagement), OIC, OPCW, PIF (partner), UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHRC, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNOOSA, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day, 17 August (1945)
Nationality
noun: Indonesian(s)
adjective: Indonesian
adjective: Indonesian
Natural resources
petroleum, tin, natural gas, nickel, timber, bauxite, copper, fertile soils, coal, gold, silver
note: Indonesia is the World's leading producer of nickel with an output of 1.6 million mt in 2022
note: Indonesia is the World's leading producer of nickel with an output of 1.6 million mt in 2022
Geography - note
note 1: 13,466 islands are in the archipelago, of which 922 are permanently inhabited; Indonesia is the world's largest country composed solely of islands; the country straddles the equator and occupies a strategic location along major sea lanes from the Indian Ocean to the Pacific Ocean
note 2: Indonesia is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, which is a belt bordering the Pacific Ocean that contains about 75% of the world's volcanoes, up to 90% of the world's earthquakes, and 80% of tsunamis
note 3: despite having the fourth largest population in the world, Indonesia is the most heavily forested region on earth after the Amazon
note 2: Indonesia is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, which is a belt bordering the Pacific Ocean that contains about 75% of the world's volcanoes, up to 90% of the world's earthquakes, and 80% of tsunamis
note 3: despite having the fourth largest population in the world, Indonesia is the most heavily forested region on earth after the Amazon
Economic overview
one of the fastest growing economies and largest in Southeast Asia; upper middle-income country; human capital and competitiveness phase of its 20-year development plan; COVID-19 reversed poverty reduction trajectory; strengthening financial resilience
Political parties
Democrat Party or PD
Functional Groups Party or GOLKAR
Great Indonesia Movement Party or GERINDRA
Indonesia Democratic Party-Struggle or PDI-P
National Awakening Party or PKB
National Democratic Party or NasDem
National Mandate Party or PAN
Prosperous Justice Party or PKS
Functional Groups Party or GOLKAR
Great Indonesia Movement Party or GERINDRA
Indonesia Democratic Party-Struggle or PDI-P
National Awakening Party or PKB
National Democratic Party or NasDem
National Mandate Party or PAN
Prosperous Justice Party or PKS
Railways
total: 8,159 km (2014)
narrow gauge: 8,159 km (2014) 1.067-m gauge (565 km electrified)
note: 4,816 km operational
narrow gauge: 8,159 km (2014) 1.067-m gauge (565 km electrified)
note: 4,816 km operational
Suffrage
17 years of age; universal; married persons regardless of age
Terrain
mostly coastal lowlands; larger islands have interior mountains
Government type
presidential republic
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Indonesia
conventional short form: Indonesia
local long form: Republik Indonesia
local short form: Indonesia
former: Netherlands East Indies (Dutch East Indies), Netherlands New Guinea
etymology: the name is an 18th-century construct of two Greek words, "Indos" (India) and "nesoi" (islands), meaning "Indian islands"
conventional short form: Indonesia
local long form: Republik Indonesia
local short form: Indonesia
former: Netherlands East Indies (Dutch East Indies), Netherlands New Guinea
etymology: the name is an 18th-century construct of two Greek words, "Indos" (India) and "nesoi" (islands), meaning "Indian islands"
Location
Southeastern Asia, archipelago between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean
Map references
Southeast Asia
Irrigated land
67,220 sq km (2012)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador INDROYONO Soesilo (since 16 December 2025)
chancery: 2020 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 775-5200
FAX: [1] (202) 775-5236
email address and website:
washington.kbri@kemlu.go.id
Embassy of The Republic of Indonesia, in Washington D.C., The United States of America (kemlu.go.id)
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
chancery: 2020 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 775-5200
FAX: [1] (202) 775-5236
email address and website:
washington.kbri@kemlu.go.id
Embassy of The Republic of Indonesia, in Washington D.C., The United States of America (kemlu.go.id)
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco
Internet users
percent of population: 69% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.id
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees: 11,964 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 95,521 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 2,643 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 95,521 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 2,643 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$1.396 trillion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
2.019 trillion cubic meters (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 13 years (2023 est.)
male: 13 years (2023 est.)
female: 13 years (2023 est.)
male: 13 years (2023 est.)
female: 13 years (2023 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 58.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 1.99% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
rate of urbanization: 1.99% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
mix of about a dozen national TV networks, including 1 public broadcaster and the rest private; more than 100 local TV stations; widespread use of satellite and cable TV systems; public radio broadcaster operates 6 national networks, as well as regional and local stations; more than 700 radio stations, with over 650 privately operated (2019)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 98.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 88.3% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 1.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 11.7% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.9% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 98.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 88.3% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.1% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 1.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 11.7% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.9% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "Indonesia Raya" (Great Indonesia)
lyrics/music: Wage Rudolf SOEPRATMAN
history: adopted 1945
lyrics/music: Wage Rudolf SOEPRATMAN
history: adopted 1945
This is an audio of the National Anthem for Indonesia. The national anthem is generally a patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
Major urban areas - population
11.249 million JAKARTA (capital), 3.729 million Bekasi, 3.044 million Surabaya, 3.041 million Depok, 2.674 million Bandung, 2.514 million Tangerang (2023)
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Physician density
0.52 physicians/1,000 population (2023)
Hospital bed density
1.4 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
National symbol(s)
garuda (mythical bird)
Mother's mean age at first birth
22.4 years (2017 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 55.4% (2024 est.)
government consumption: 7.7% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 29.1% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 2.3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 22.2% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -20.4% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 7.7% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 29.1% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 2.3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 22.2% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -20.4% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Indonesia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 continuous years
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Indonesia
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 continuous years
Population distribution
major concentration on the island of Java, which is considered one of the most densely populated places on earth; of the outer islands, Sumatra contains some of the most significant clusters, particularly in the south near the Selat Sunda and along the northeastern coast near Medan; the cities of Makasar (Sulawesi), Banjarmasin (Kalimantan) are also heavily populated
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2022 est.)
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 98.2%
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 98.2%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
PK
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 97.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 91.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.7% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 8.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.3% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 97.4% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 91.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.7% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.6% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 8.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.3% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Javanese 40.1%, Sundanese 15.5%, Malay 3.7%, Batak 3.6%, Madurese 3%, Betawi 2.9%, Minangkabau 2.7%, Buginese 2.7%, Bantenese 2%, Banjarese 1.7%, Balinese 1.7%, Acehnese 1.4%, Dayak 1.4%, Sasak 1.3%, Chinese 1.2%, other 15% (2010 est.)
Religions
Muslim 87.4%, Protestant 7.5%, Roman Catholic 3.1%, Hindu 1.7%, other 0.8% (includes Buddhist and Confucian) (2022 est.)
Languages
Bahasa Indonesia (official, modified form of Malay), English, Dutch, local dialects (of which the most widely spoken is Javanese); note - more than 700 languages are used in Indonesia
major-language sample(s):
Fakta Dunia, sumber informasi dasar yang sangat diperlukan. (Indonesian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
major-language sample(s):
Fakta Dunia, sumber informasi dasar yang sangat diperlukan. (Indonesian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Imports - partners
China 29%, Singapore 8%, Japan 7%, USA 5%, Malaysia 5% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
highest point: Puncak Jaya 4,884 m
lowest point: Indian/Pacific Oceans 0 m
mean elevation: 367 m
lowest point: Indian/Pacific Oceans 0 m
mean elevation: 367 m
Health expenditure
3.7% of GDP (2021)
8% of national budget (2022 est.)
8% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the military is responsible for external defense, combatting separatism, and responding to national emergencies and natural disasters; in certain conditions it may provide operational support to police, such as for counterterrorism operations, maintaining public order, and addressing communal conflicts
key operational priorities include an insurgency on Papua and the security of Indonesia's vast maritime domain; the West Papua Liberation Army, the military wing of the Free Papua Organization, has been fighting a low-level insurgency in Papua since Indonesia annexed the former Dutch colony in the 1960s; maritime issues include piracy, transnational crime, illegal fishing, and incursions by People's Republic of China (PRC) vessels; Indonesia is not a formal claimant in the South China Sea, although some of its waters lie within the PRC's “nine-dash line” maritime claims, resulting in some stand offs in recent years; over the past decade, the Indonesian military has bolstered its presence on and around the strategically located Natuna Islands (2025)
key operational priorities include an insurgency on Papua and the security of Indonesia's vast maritime domain; the West Papua Liberation Army, the military wing of the Free Papua Organization, has been fighting a low-level insurgency in Papua since Indonesia annexed the former Dutch colony in the 1960s; maritime issues include piracy, transnational crime, illegal fishing, and incursions by People's Republic of China (PRC) vessels; Indonesia is not a formal claimant in the South China Sea, although some of its waters lie within the PRC's “nine-dash line” maritime claims, resulting in some stand offs in recent years; over the past decade, the Indonesian military has bolstered its presence on and around the strategically located Natuna Islands (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
approximately 400,000 active Armed Forces, including about 300,000 Army (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory is a mix of older and new weapons platforms from China, Russia, Europe, the US, and other countries; in recent years, major suppliers have included China, France, Germany, the Netherlands, South Korea, and the US; the TNI has been engaged in a modernization program for more than a decade; Indonesia has a growing defense industry fueled by technology transfers and cooperation agreements with several countries; it has jointly produced aircraft and naval vessels (2025)
Military deployments
250 (plus about 170 police) Central African Republic (MINUSCA); 1,025 Democratic Republic of the Congo (MONUSCO); 1,225 Lebanon (UNIFIL) (2025)
Terrorist group(s)
Terrorist group(s): Islamic State of Iraq and ash-Sham (aka Jemaah Anshorut Daulah); Jemaah Islamiyah
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 23.8 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 9.135 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 189.7 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 9.135 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 189.7 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 65.2 million tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 15.2% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 15.2% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on food: 33.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 7.3% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 7.3% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
fresh water lake(s): Danau Toba - 1,150 sq km
note - located in the caldera of a super volcano that erupted more than 70,000 years ago; it is the largest volcanic lake in the World
note - located in the caldera of a super volcano that erupted more than 70,000 years ago; it is the largest volcanic lake in the World
Major rivers (by length in km)
Sepik (shared with Papua New Guinea [s]) - 1,126 km; Fly (shared with Papua New Guinea [s]) - 1,050 km
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 10 (6 cultural, 4 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Borobudur Temple Compounds (c); Komodo National Park (n); Prambanan Temple Compounds (c); Ujung Kulon National Park (n); Sangiran Early Man Site (c); Lorentz National Park (n); Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra (n); Cultural Landscape of Bali Province (c); Ombilin Coal Mining Heritage of Sawahlunto (c); Cosmological Axis of Yogyakarta and its Historic Landmarks (c)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Borobudur Temple Compounds (c); Komodo National Park (n); Prambanan Temple Compounds (c); Ujung Kulon National Park (n); Sangiran Early Man Site (c); Lorentz National Park (n); Tropical Rainforest Heritage of Sumatra (n); Cultural Landscape of Bali Province (c); Ombilin Coal Mining Heritage of Sawahlunto (c); Cosmological Axis of Yogyakarta and its Historic Landmarks (c)
People - note
Indonesia is the fourth most populous nation in the World after China, India, and the United States; more than half of the Indonesian population - roughly 150 million people or 55% - live on the island of Java (about the size of California) making it the most crowded island on earth
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 2% (2017)
women married by age 18: 16.3% (2017)
women married by age 18: 16.3% (2017)
Coal
production: 783.453 million metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 281.159 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 519.23 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 16.935 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 35.055 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 281.159 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 519.23 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 16.935 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 35.055 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 82% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 6.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
geothermal: 4.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 6.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 6.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
geothermal: 4.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 6.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
production: 58.691 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
consumption: 38.378 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 20.989 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 727.056 million cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.408 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
consumption: 38.378 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 20.989 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 727.056 million cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.408 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
total petroleum production: 865,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 1.645 million bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 2.48 billion barrels (2021 est.)
refined petroleum consumption: 1.645 million bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 2.48 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
0.94 (2025 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
70.3% (2022 est.)
Remittances
1.1% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2023 est.)
1% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
1.1% of GDP (2023 est.)
1% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Space program overview
focuses largely on rocket development and satellite acquisition/operation; manufactures remote sensing (RS) satellites; has a sounding (research) rocket program to develop an orbital satellite launch vehicle (SLV); researching and developing a range of other space-related technologies related to satellite payloads, communications, RS, and astronomy; has relations with several foreign space agencies and industries, including those of France, Germany, India, Japan, Russia, South Korea, and the US; national space program includes building up the country's private space sector (2025)
Space agency/agencies
Indonesian Space Agency (INASA; formed 2022); National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN; established 2021); Research Organization for Aeronautics and Space (ORPA; formed 2021) (2025)
Geoparks
total global geoparks and regional networks: 12 (2025)
global geoparks and regional networks: Batur; Belitong; Ciletuh - Palabuhanratu; Gunung Sewu; Ijen; Kebumen; Maros Pangkep; Merangin Jambi; Meratus; Raja Ampat; Rinjani-Lombok; Toba Caldera (2025)
global geoparks and regional networks: Batur; Belitong; Ciletuh - Palabuhanratu; Gunung Sewu; Ijen; Kebumen; Maros Pangkep; Merangin Jambi; Meratus; Raja Ampat; Rinjani-Lombok; Toba Caldera (2025)
Ports
total ports: 123 (2024)
large: 3
medium: 6
small: 18
very small: 96
ports with oil terminals: 79
key ports: Belawan, Cilacap, Dumai, Jakarta, Kasim Terminal, Merak Mas Terminal, Palembang, Surabaya, Ujung Pandang
large: 3
medium: 6
small: 18
very small: 96
ports with oil terminals: 79
key ports: Belawan, Cilacap, Dumai, Jakarta, Kasim Terminal, Merak Mas Terminal, Palembang, Surabaya, Ujung Pandang
National color(s)
red, white
Particulate matter emissions
18.4 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Key space-program milestones
1964 - launched first sounding rocket (Kartika)
1976 - first communications satellite (Palapa A1) built and launched by US
2005 - re-started sounding rocket program with goal of producing a satellite launch vehicle (SLV)
2007 - first remote sensing (RS) satellite (LAPAN-A1) built by Germany and launched by India
2015 - first domestically produced RS satellite (LAPAN-A2) launched by India
2023-2024 - two communications satellites (SATRIA-1 and Merah Putih 2) to provide high-speed internet access across the Indonesian archipelago built by European company and launched by US
1976 - first communications satellite (Palapa A1) built and launched by US
2005 - re-started sounding rocket program with goal of producing a satellite launch vehicle (SLV)
2007 - first remote sensing (RS) satellite (LAPAN-A1) built by Germany and launched by India
2015 - first domestically produced RS satellite (LAPAN-A2) launched by India
2023-2024 - two communications satellites (SATRIA-1 and Merah Putih 2) to provide high-speed internet access across the Indonesian archipelago built by European company and launched by US
Methane emissions
energy: 3,621.7 kt (2022-2024 est.)
agriculture: 3,379.3 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 4,200.1 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 165.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
agriculture: 3,379.3 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 4,200.1 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 165.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
143.144 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 13.1% (2024 est.)
male: 13.2% (2024 est.)
female: 13% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 13.2% (2024 est.)
female: 13% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
-0.7 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 31.8 years (2025 est.)
male: 30.8 years
female: 32.3 years
male: 30.8 years
female: 32.3 years
Debt - external
$225.273 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
140 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$155.708 billion (2024 est.)
$146.359 billion (2023 est.)
$137.222 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$146.359 billion (2023 est.)
$137.222 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
45.34% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
1.93 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Unemployment rate
3.3% (2024 est.)
3.4% (2023 est.)
3.5% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
3.4% (2023 est.)
3.5% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
829.655 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 527.923 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 223.352 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 78.38 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 527.923 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 223.352 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 78.38 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 1,904,569 sq km
land: 1,811,569 sq km
water: 93,000 sq km
land: 1,811,569 sq km
water: 93,000 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
11.6% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$4.102 trillion (2024 est.)
$3.906 trillion (2023 est.)
$3.718 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$3.906 trillion (2023 est.)
$3.718 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
556 (2025)
Infant mortality rate
total: 18.5 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 21.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 16.4 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 21.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 16.4 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
34.9 (2024 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
3.7% (2023 est.)
4.2% (2022 est.)
1.6% (2021 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
4.2% (2022 est.)
1.6% (2021 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$8.47 billion (2024 est.)
-$2.042 billion (2023 est.)
$13.215 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
-$2.042 billion (2023 est.)
$13.215 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$14,500 (2024 est.)
$13,900 (2023 est.)
$13,300 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$13,900 (2023 est.)
$13,300 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 13.5 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 5 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 39% (2025 est.)
male: 74.9% (2025 est.)
female: 3.1% (2025 est.)
male: 74.9% (2025 est.)
female: 3.1% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
6.9% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
37.39 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Death rate
6.82 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
14.55 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 70.826 million kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 356.135 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 828.198 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 27.477 billion kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 356.135 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 828.198 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 27.477 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 11,422 (2023)
by type: bulk carrier 160, container ship 219, general cargo 2,347, oil tanker 714, other 7,982
by type: bulk carrier 160, container ship 219, general cargo 2,347, oil tanker 714, other 7,982
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
15.9% (2023 est.)
Imports
$279.419 billion (2024 est.)
$262.694 billion (2023 est.)
$273.031 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$262.694 billion (2023 est.)
$273.031 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$300.868 billion (2024 est.)
$291.287 billion (2023 est.)
$315.746 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$291.287 billion (2023 est.)
$315.746 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
53 (2025)
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 0.08 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.06 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.06 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 73.6 years (2024 est.)
male: 71.3 years
female: 76 years
male: 71.3 years
female: 76 years
Real GDP growth rate
5% (2024 est.)
5% (2023 est.)
5.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
5% (2023 est.)
5.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
5.2% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 12.6% (2024 est.)
industry: 39.3% (2024 est.)
services: 43.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 39.3% (2024 est.)
services: 43.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
1.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
10.6% national budget (2025 est.)
10.6% national budget (2025 est.)
Population growth rate
0.7% (2025 est.)
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 347 million (2024 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 123 (2024 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 123 (2024 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 46.1 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 34.1 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.3 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 34.1 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.3 (2025 est.)
Population
total: 283,587,097 (2025 est.)
male: 141,778,977
female: 141,808,120
male: 141,778,977
female: 141,808,120
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 9.16 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 3 (2023 est.)








