South Korea - KR - KOR - KOR - East and Southeast Asia

Korea, South Images
Korea, South Factbook Data
Age structure
15-64 years: 69.4% (male 18,653,915/female 17,465,817)
65 years and over: 19.3% (2024 est.) (male 4,440,688/female 5,623,348)
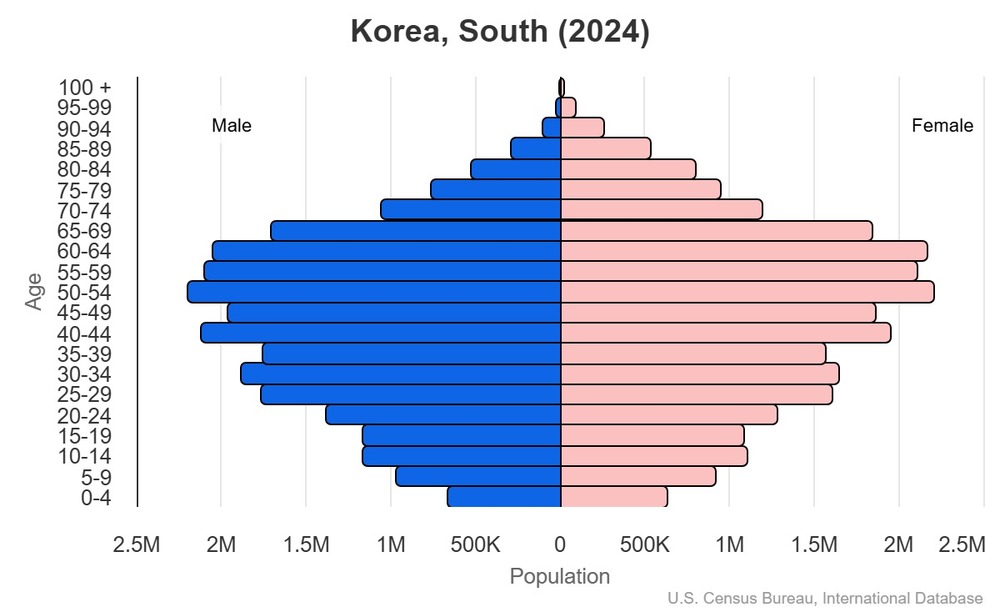
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.79 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
volcanism: Halla (1,950 m) is considered historically active; it has not erupted in many centuries
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Indiana
Military service age and obligation
note: women, in service since 1950, are able to serve in all branches and as of 2024 more than 15,000 served in the armed forces
Background
The first recorded kingdom (Choson) on the Korean Peninsula dates from approximately 2300 B.C. Over the subsequent centuries, three main kingdoms -- Kogoryo, Baekche, and Silla -- were established on the Peninsula. By the 5th century A.D., Kogoryo emerged as the most powerful, with control over much of the Peninsula and part of Manchuria (modern-day northeast China). However, Silla allied with the Chinese to create the first unified Korean state in 688. Following the collapse of Silla in the 9th century, Korea was unified under the Koryo (Goryeo; 918-1392) and the Chosen (Joseon; 1392-1910) dynasties.
Korea became the object of intense imperialistic rivalry among the Chinese (its traditional benefactor), Japanese, and Russian empires in the latter half of the 19th and early 20th centuries. After the Sino-Japanese War (1894-95) and the Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905), Korea was occupied by Imperial Japan. In 1910, Japan formally annexed the entire Peninsula. Korea regained its independence after Japan's surrender to the US and its allies in 1945. A US-supported democratic government (Republic of Korea, ROK) was set up in the southern half of the Korean Peninsula, while a communist-style government backed by the Soviet Union was installed in the north (North Korea; aka Democratic People's Republic of Korea, DPRK). During the Korean War (1950-53), US troops and UN forces fought alongside ROK soldiers to defend South Korea from a North Korean invasion supported by communist China and the Soviet Union. After the 1953 armistice, the two Koreas were separated by a demilitarized zone.
Syngman RHEE led the country as its first president from 1948 to 1960. PARK Chung-hee took over leadership of the country in a 1961 coup. During his controversial rule (1961-79), South Korea achieved rapid economic growth, with per capita income rising to roughly 17 times the level of North Korea by 1979. PARK was assassinated in 1979, and subsequent years were marked by political turmoil and continued military rule as the country's pro-democracy movement grew. South Korea held its first free presidential election under a revised democratic constitution in 1987, with former South Korean Army general ROH Tae-woo winning a close race. In 1993, KIM Young-sam became the first civilian president of South Korea's new democratic era. President KIM Dae-jung (1998-2003) won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2000 for his contributions to South Korean democracy and his "Sunshine Policy" of engagement with North Korea. President PARK Geun-hye, daughter of former South Korean President PARK Chung-hee, took office in 2013 as South Korea's first female leader. In 2016, the National Assembly passed an impeachment motion against PARK over her alleged involvement in a corruption and influence-peddling scandal, triggering an early presidential election in 2017 won by MOON Jae-in. In 2022, longtime prosecutor and political newcomer YOON Suk Yeol won the presidency by the slimmest margin in South Korean history.
Discord and tensions with North Korea, punctuated by North Korean military provocations, missile launches, and nuclear tests, have permeated inter-Korean relations for years. Relations remained strained, despite a period of respite in 2018-2019 ushered in by North Korea's participation in the 2018 Winter Olympic and Paralympic Games in South Korea and high-level diplomatic meetings, including historic US-North Korea summits. In 2024, Pyongyang announced it was ending all economic cooperation with South Korea, a move that followed earlier proclamations that it was scrapping a 2018 military pact to de-escalate tensions along their militarized border, abandoning the country’s decades-long pursuit of peaceful unification with South Korea, and designating the South as North Korea’s “principal enemy.”
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
2.4% of GDP (2024 est.)
2.4% of GDP (2023 est.)
2.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
2.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 24.6% (2021 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
provinces: Chungcheongbuk-do (North Chungcheong), Chungcheongnam-do (South Chungcheong), Gangwon-do, Gyeongsangbuk-do (North Gyeongsang), Gyeonggi-do, Gyeongsangnam-do (South Gyeongsang), Jeju-do (Jeju), Jeollabuk-do (North Jeolla), Jeollanam-do (South Jeolla)
metropolitan cities: Busan (Pusan), Daegu (Taegu), Daejeon (Taejon), Gwangju (Kwangju), Incheon (Inch'on), Ulsan
special city: Seoul
special self-governing city: Sejong
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries: Korea Coast Guard; Ministry of Interior and Safety: Korean National Police Agency (2025)
Budget
expenditures: $532.023 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 37 33 N, 126 59 E
time difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name originates from the Korean word meaning "capital city;" it was the capital of the unified Korea from 1392 to 1910
note: Sejong, located some 120 km (75 mi) south of Seoul, serves as an administrative capital for segments of the South Korean government
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the president or by majority support of the National Assembly membership; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly membership, approval in a referendum by more than one half of the votes by more than one half of eligible voters, and promulgation by the president
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
1,363.375 (2024 est.)
1,305.662 (2023 est.)
1,291.447 (2022 est.)
1,143.952 (2021 est.)
1,180.266 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister KIM Min-seok (since 3 July 2025)
cabinet: State Council appointed by the president on the prime minister's recommendation
election/appointment process: president directly elected by simple-majority popular vote for a single 5-year term; prime minister appointed by president with consent of the National Assembly
most recent election date: 3 June 2025 (special snap election in the wake of the impeachment of former President YOON Suk-yeol)
election results: 2025: LEE Jae-myung elected president; LEE Jae-myung (DPK) 49.4%, KIM Moon-soo (PPP) 41.2%, LEE Jun-seok (New Reform Party) 8.3%
2022: YOON Suk-yeol elected president; YOON Suk-yeol (PPP) 48.6%, LEE Jae-myung (DPK) 47.8%; other 3.6%
expected date of next election: 2030
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government; the prime minister serves as the principal executive assistant to the president, similar to the role of a vice president
Flag
meaning: the flag is called Taegukki; white is a traditional Korean color and represents peace and purity; blue stands for the negative cosmic forces of the yin, and red for the opposite positive forces of the yang; each trigram represents one of the universal elements, which together express the principle of movement and harmony
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court chief justice appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly; other justices appointed by the president on the recommendation of the chief justice and consent of the National Assembly; position of the chief justice is a 6-year nonrenewable term; other justices serve 6-year renewable terms; Constitutional Court justices appointed - 3 by the president, 3 by the National Assembly, and 3 by the Supreme Court chief justice; court head serves until retirement at age 70, while other justices serve 6-year renewable terms with mandatory retirement at age 65
subordinate courts: High Courts; District Courts; Branch Courts (organized under the District Courts); specialized courts for family and administrative issues
Land boundaries
border countries (1): North Korea 237 km
Land use
arable land: 14.9% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 2.1% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 0.6% (2023 est.)
forest: 64.4% (2023 est.)
other: 19.5% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 300 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 4 years
most recent election date: 4/10/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Democratic Party of Korea (161); People Power Party (90); People Future Party (18); Other (31)
percentage of women in chamber: 20.3%
expected date of next election: April 2028
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: not specified
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Korean
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
high-income, export- and technology-oriented East Asian economy; manufacturing led by semiconductor and automotive industries; slow growth amid declining construction investment, export risks, and recent political instability; aging workforce; increased restraint in fiscal policy while maintaining industry support initiatives
Political parties
Democratic Party of Korea or DPK
New Future Party
New Reform Party
Open Democratic Party or ODP
People Power Party or PPP
Progressive Party or Jinbo Party
Rebuilding Korea Party
Social Democratic Party
note: the Democratic Alliance coalition consists of the DPK and the smaller Basic Income, Jinbo, Open Democratic, and Social Democratic parties, as well as two independents; for the 2024 election, the Basic Income Party, the ODP, and the Social Democratic Party formed the New Progressive Alliance
Railways
standard gauge: 3,979 km (2016) 1.435-m gauge (2,727 km electrified)
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: South Korea
local long form: Taehan-min'guk
local short form: Han'guk
abbreviation: ROK
etymology: derived from the Chinese name for Goryeo, which was the Korean dynasty that united the peninsula in the 10th century A.D.; the South Korean name "Han'guk" derives from the long form, "Taehan-min'guk," which is itself a derivation from "Daehan-je'guk," which means "the Great Han Empire"
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 2450 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 939-5600
FAX: [1] (202) 797-0595
email address and website:
generalusa@mofa.go.kr
https://overseas.mofa.go.kr/us-en/index.do
consulate(s) general: Anchorage (AK), Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Hagatna (Guam), Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Seattle, Philadelphia
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
stateless persons: 248 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 17 years (2022 est.)
female: 16 years (2022 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.31% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: YUN Ch'i-Ho or AN Ch'ang-Ho/AHN Eaktay
history: adopted 1948, well-known by 1910; North Korea's and South Korea's anthems have the same name and a similar melody, but different lyrics
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 18.9% (2023 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 32.2% (2023 est.)
investment in inventories: -0.1% (2023 est.)
exports of goods and services: 44% (2023 est.)
imports of goods and services: -43.9% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of South Korea
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
total: 99.8% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
total: 0.2% of population (2022 est.)
Religions
note: many people also carry on at least some Confucian traditions and practices
Languages
major-language sample(s):
월드 팩트북, 필수적인 기본 정보 제공처 (Korean)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Sea of Japan 0 m
mean elevation: 282 m
Health expenditure
14.1% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
South Korea's primary defense partner is the US, and the 1953 US-South Korea Mutual Defense Treaty is a cornerstone of the country's national security; the Treaty committed the US to provide assistance in the event of an attack and gave the US permission to station land, air, and sea forces in and about the territory of South Korea as determined by mutual agreement; South Korea hosts approximately 28,000 US military troops and regularly conducts bilateral exercises with the US military; South Korea has Major Non-NATO Ally (MNNA) status with the US, a designation under US law that provides foreign partners with certain benefits in the areas of defense trade and security cooperation; the South Korean military has assisted the US in conflicts in Afghanistan (5,000 troops; 2001-2014), Iraq (20,000 troops; 2003-2008), and Vietnam (325,000 troops; 1964-1973)
in 2016, South Korea concluded an agreement with the EU for participation in EU Common Security and Defense Policy (CSDP) missions and operations, such as EU counter-piracy operations off the coast of East Africa; South Korea has had a relationship with NATO since 2005, and in 2022 established a mission to the NATO headquarters to further cooperation; it has participated in NATO-led missions and exercises, including in Afghanistan and the Gulf of Aden (2025)
Literacy
male: NA
female: NA
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 4.45 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 15.96 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 67.1% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Illicit drugs
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Jeju Volcanic Island and Lava Tubes (n); Changdeokgung Palace Complex (c); Jongmyo Shrine (c); Seokguram Grotto and Bulguksa Temple (c); Hwaseong Fortress (c); Gochang, Hwasun, and Ganghwa Dolmen Sites (c); Gyeongju Historic Areas (c); Namhansanseong (c); Baekje Historic Areas (c); Sansa, Buddhist Mountain Monasteries in Korea (c); Royal Tombs of the Joseon Dynasty (c); Petroglyphs along the Bangucheon Stream (c)
Coal
consumption: 136.817 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 500 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 122.845 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 326 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
nuclear: 30.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 5.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 0.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
tide and wave: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1.8% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 57.314 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 93.639 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
imports: 60.025 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 7.079 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 2.542 million bbl/day (2024 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Remittances
0.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors under construction: 2 (2025)
Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors: 25.57GW (2025 est.)
Percent of total electricity production: 30.7% (2023 est.)
Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down: 2 (2025)
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
Geoparks
global geoparks and regional networks: Cheongsong; Danyang; Gyeongbuk Donghaean; Hantangang; Jeju Island; Jeonbuk West Coast; Mudeungsan (2025)
Ports
large: 2
medium: 5
small: 4
very small: 4
ports with oil terminals: 10
key ports: Busan, Gwangyang Hang, Inchon, Masan, Mokpo, Pyeongtaek Hang, Ulsan
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Methane emissions
agriculture: 500 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 478.6 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 27 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Key space-program milestones
1993-1998 - launched first single-stage sounding rocket (KSR-1) and first two-stage sounding rocket (KSR-2)
1999 - first domestically built multi-purpose satellite (KOMPSAT-1, aka Arirang-1) launched by US
2008 - first South Korean astronaut in space on International Space Station
2013 - first successful satellite launch of two-stage Korean Space Launch Vehicle-I (KSLV-I; aka Naro)
2021 - maiden launch of three-stage KSLV-II (aka Nuri); signed the US-led Artemis Accords for space and lunar exploration
2022 - first successful attempt to place satellites into orbit on the KSLV-II/Nuri; domestically made lunar orbiter (Danuri) reached Moon's orbit; began development of the Korea Positioning System (KPS) satellite navigational network
2024 - third successful launch of Nuri SLV placed eight small satellites in orbit, including a remote sensing satellite (NexSat-2) with radar imaging technology
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 6% (2024 est.)
female: 5.8% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 44 years
female: 47.3 years
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$420.93 billion (2023 est.)
$423.366 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
2.7% (2023 est.)
2.9% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 275.411 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 248.599 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 120.222 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 96,920 sq km
water: 2,800 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$2.572 trillion (2022 est.)
$2.507 trillion (2021 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.6 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
3.6% (2023 est.)
5.1% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$32.822 billion (2023 est.)
$25.829 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$49,800 (2022 est.)
$48,400 (2021 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 47 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 29.7% (2025 est.)
female: 5.2% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 575.359 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 19.688 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 93, container ship 115, general cargo 362, oil tanker 219, other 1,360
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$758.41 billion (2023 est.)
$817.594 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$769.243 billion (2023 est.)
$825.961 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 1.72 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.15 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.22 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 5.66 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 80.3 years
female: 86.6 years
Real GDP growth rate
2.6% (2022 est.)
4.3% (2021 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 31.6% (2023 est.)
services: 58.4% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
Population growth rate
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 173 (2024 est.)
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: 188 Sejong-daero, Jongno-gu, Seoul
mailing address: 9600 Seoul Place, Washington, DC 20521-9600
telephone: [82] (2) 397-4114
FAX: [82] (2) 397-4101
email address and website:
seoulinfoACS@state.gov
https://kr.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s): Busan
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 14.7 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 30.2 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 3.3 (2025 est.)
Ethnic groups
Population
male: 25,636,127
female: 25,850,216
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 41 (2024 est.)























