Madagascar - MG - MDG - MAD - Africa
Last updated: January 21, 2026

Madagascar Images
Madagascar Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Claire PIERANGELO (since 2 May 2022)
embassy: Lot 207A, Andranoro, Antehiroka, 105 Antananarivo - Madagascar
mailing address: 2040 Antananarivo Place, Washington DC 20521-2040
telephone: [261] 33-44-320-00
FAX: [261] 33-44-320-35
email address and website:
antanACS@state.gov
https://mg.usembassy.gov/
embassy: Lot 207A, Andranoro, Antehiroka, 105 Antananarivo - Madagascar
mailing address: 2040 Antananarivo Place, Washington DC 20521-2040
telephone: [261] 33-44-320-00
FAX: [261] 33-44-320-35
email address and website:
antanACS@state.gov
https://mg.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
0-14 years: 37% (male 5,507,847/female 5,400,551)
15-64 years: 59.1% (male 8,720,012/female 8,673,880)
65 years and over: 3.9% (2024 est.) (male 532,642/female 617,782)
15-64 years: 59.1% (male 8,720,012/female 8,673,880)
65 years and over: 3.9% (2024 est.) (male 532,642/female 617,782)
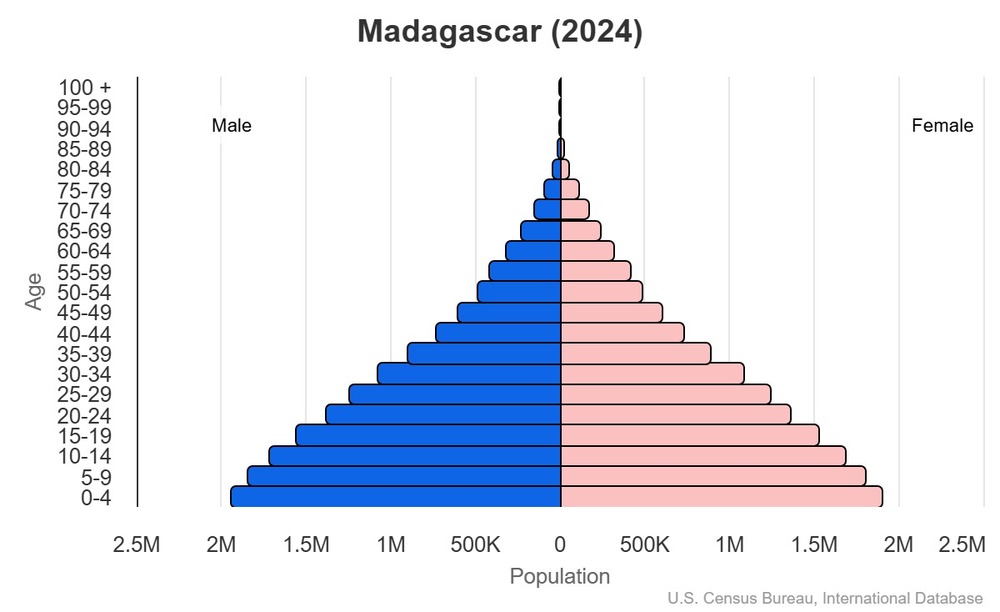
This is the population pyramid for Madagascar. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
20 00 S, 47 00 E
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
periodic cyclones; drought; and locust infestation
volcanism: Madagascar's volcanoes have not erupted in recorded history
volcanism: Madagascar's volcanoes have not erupted in recorded history
Area - comparative
almost four times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Arizona
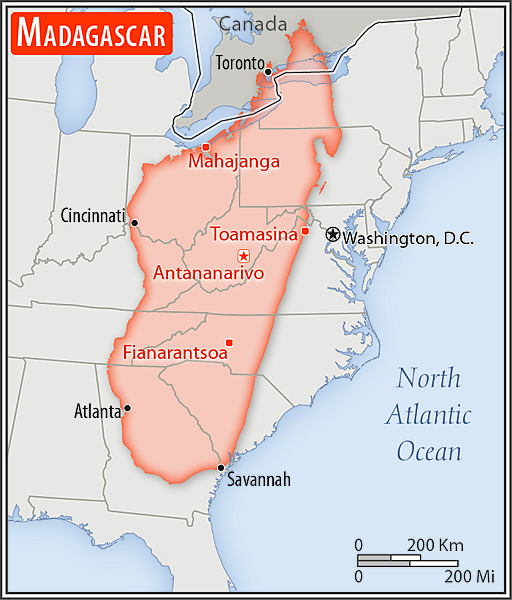
almost four times the size of Georgia; slightly less than twice the size of Arizona
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service for men and women; service obligation 18 months; conscription available in times of national emergency or war (2025)
Background
Madagascar was one of the last major habitable landmasses on earth to be settled by humans. While there is some evidence of human presence on the island in the millennia B.C., large-scale settlement began between A.D. 350 and 550 with settlers from present-day Indonesia. The island attracted Arab and Persian traders as early as the 7th century, and migrants from Africa arrived around A.D. 1000. Madagascar was a pirate stronghold during the late 17th and early 18th centuries and served as a slave trading center into the 19th century. From the 16th to the late 19th century, a native Merina Kingdom dominated much of Madagascar. The French conquered the island in 1896 and made it a colony; independence was regained in 1960.
Free presidential and National Assembly elections were held in 1992-93, ending 17 years of single-party rule. In 1997, in the second presidential race, Didier RATSIRAKA, the leader during the 1970s and 1980s, returned to the presidency. The 2001 presidential election was contested between the followers of RATSIRAKA and Marc RAVALOMANANA, nearly causing half the country to secede. In 2002, the High Constitutional Court announced RAVALOMANANA the winner. He won a second term in 2006 but, following protests in 2009, handed over power to the military, which then conferred the presidency on the mayor of Antananarivo, Andry RAJOELINA, in what amounted to a coup d'etat. After a lengthy mediation process, Madagascar held UN-supported presidential and parliamentary elections in 2013. Former de facto finance minister Hery RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA won in a runoff and was inaugurated in 2014. In 2019, RAJOELINA was declared the winner against RAVALOMANANA. In 2023, RAJOELINA won another term in an election that most of the opposition boycotted, including RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA and RAVALOMANANA, who claimed it was rigged in favor of RAJOELINA. International observers, however, saw no evidence of systemic fraud, leading the international community to accept the election results.
Free presidential and National Assembly elections were held in 1992-93, ending 17 years of single-party rule. In 1997, in the second presidential race, Didier RATSIRAKA, the leader during the 1970s and 1980s, returned to the presidency. The 2001 presidential election was contested between the followers of RATSIRAKA and Marc RAVALOMANANA, nearly causing half the country to secede. In 2002, the High Constitutional Court announced RAVALOMANANA the winner. He won a second term in 2006 but, following protests in 2009, handed over power to the military, which then conferred the presidency on the mayor of Antananarivo, Andry RAJOELINA, in what amounted to a coup d'etat. After a lengthy mediation process, Madagascar held UN-supported presidential and parliamentary elections in 2013. Former de facto finance minister Hery RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA won in a runoff and was inaugurated in 2014. In 2019, RAJOELINA was declared the winner against RAVALOMANANA. In 2023, RAJOELINA won another term in an election that most of the opposition boycotted, including RAJAONARIMAMPIANINA and RAVALOMANANA, who claimed it was rigged in favor of RAJOELINA. International observers, however, saw no evidence of systemic fraud, leading the international community to accept the election results.
Environmental issues
erosion and soil degradation from deforestation and overgrazing; desertification; agricultural fires; water pollution from raw sewage and other organic wastes; wildlife preservation
International environmental agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping-London Protocol, Marine Life Conservation, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 2006, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
0.7% of GDP (2024 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2022 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2021 est.)
0.7% of GDP (2020 est.)
Exports - commodities
garments, nickel, vanilla, cloves, gold (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
USA 16%, France 15%, Japan 8%, China 6%, S. Korea 6% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
6 provinces (faritany); Antananarivo, Antsiranana, Fianarantsoa, Mahajanga, Toamasina, Toliara
Agricultural products
rice, sugarcane, cassava, sweet potatoes, milk, bananas, vegetables, mangoes/guavas, maize, potatoes (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Madagascar Armed Forces (aka Armed forces of the Republic of Madagascar); Malagasy Army, Naval Forces (or National Navy), Air Force; Malagasy National Gendarmerie (2025)
note: the National Gendarmerie is under the Ministry of Defense but separate from the PAF and is responsible for maintaining law and order in rural areas at the village level, protecting government facilities, and operating a maritime police contingent; the National Police under the Ministry of Security is responsible for maintaining law and order in urban areas
note: the National Gendarmerie is under the Ministry of Defense but separate from the PAF and is responsible for maintaining law and order in rural areas at the village level, protecting government facilities, and operating a maritime police contingent; the National Police under the Ministry of Security is responsible for maintaining law and order in urban areas
Budget
revenues: $2.066 billion (2023 est.)
expenditures: $2.876 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
expenditures: $2.876 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
name: Antananarivo
geographic coordinates: 18 55 S, 47 31 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name means "City of the Thousand," from the Malagasy an- (a prefix denoting a place name), tanana (town), and arivo (thousand); in the 17th century, King ADRIANJAKA named the original fortress after the 1,000 soldiers stationed there
geographic coordinates: 18 55 S, 47 31 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name means "City of the Thousand," from the Malagasy an- (a prefix denoting a place name), tanana (town), and arivo (thousand); in the 17th century, King ADRIANJAKA named the original fortress after the 1,000 soldiers stationed there
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, rice, fabric, cotton fabric, wheat (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
tropical along coast, temperate inland, arid in south
Coastline
4,828 km
Constitution
history: previous 1992; latest passed by referendum 17 November 2010, promulgated 11 December 2010
amendment process: proposed by the president of the republic in consultation with the cabinet or supported by a least two thirds of both the Senate and National Assembly membership; passage requires at least three-fourths approval of both the Senate and National Assembly and approval in a referendum; constitutional articles, including the form and powers of government, the sovereignty of the state, and the autonomy of Madagascar’s collectivities, cannot be amended
amendment process: proposed by the president of the republic in consultation with the cabinet or supported by a least two thirds of both the Senate and National Assembly membership; passage requires at least three-fourths approval of both the Senate and National Assembly and approval in a referendum; constitutional articles, including the form and powers of government, the sovereignty of the state, and the autonomy of Madagascar’s collectivities, cannot be amended
Exchange rates
Malagasy ariary (MGA) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
4,525.425 (2024 est.)
4,429.579 (2023 est.)
4,096.116 (2022 est.)
3,829.978 (2021 est.)
3,787.754 (2020 est.)
Exchange rates:
4,525.425 (2024 est.)
4,429.579 (2023 est.)
4,096.116 (2022 est.)
3,829.978 (2021 est.)
3,787.754 (2020 est.)
Flag
description: two equal horizontal bands of red (top) and green, with a vertical white band on the left side
meaning: red stands for sovereignty, green for hope, and white for purity
meaning: red stands for sovereignty, green for hope, and white for purity
Independence
26 June 1960 (from France)
Industries
meat processing, seafood, soap, beer, leather, sugar, textiles, glassware, cement, automobile assembly plant, paper, petroleum, tourism, mining
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Cour Suprême (consists of 11 members; addresses judicial administration issues only); High Constitutional Court or Haute Cour Constitutionnelle (consists of 9 members); High Court of Justice (consists of 11 members; addresses cases brought against the president of Madagascar and senior officials for high treason, grave violations of the Constitution, or breach of duties incompatible with the exercise of the presidential mandate)
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court heads elected by the president and judiciary officials to serve 3-year, single renewable terms; High Constitutional Court members appointed - 3 each by the president, by both legislative bodies, and by the Council of Magistrates; members serve single, 7-year terms; High Court of Justice members include: first president of the Supreme Court; 2 presidents from the Court of Cassation; 2 presidents from the Court of Appeal; 2 deputies from the National Assembly; 2 senators from the Senate; 2 members from the High Council for the Defense of Democracy and the State of law
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Court of Cassation; Courts of First Instance; military courts; traditional courts (dina); Trade Court
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court heads elected by the president and judiciary officials to serve 3-year, single renewable terms; High Constitutional Court members appointed - 3 each by the president, by both legislative bodies, and by the Council of Magistrates; members serve single, 7-year terms; High Court of Justice members include: first president of the Supreme Court; 2 presidents from the Court of Cassation; 2 presidents from the Court of Appeal; 2 deputies from the National Assembly; 2 senators from the Senate; 2 members from the High Council for the Defense of Democracy and the State of law
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal; Court of Cassation; Courts of First Instance; military courts; traditional courts (dina); Trade Court
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Land use
agricultural land: 70.3% (2023 est.)
arable land: 5.2% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 64.1% (2023 est.)
forest: 17.5% (2023 est.)
other: 12.2% (2023 est.)
arable land: 5.2% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 64.1% (2023 est.)
forest: 17.5% (2023 est.)
other: 12.2% (2023 est.)
Legal system
civil law system based on the old French civil code and customary law in matters of marriage, family, and obligation
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Literacy
total population: 74.7% (2021 est.)
male: 77.9% (2021 est.)
female: 71.8% (2021 est.)
male: 77.9% (2021 est.)
female: 71.8% (2021 est.)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or 100 nm from the 2,500-m isobath
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or 100 nm from the 2,500-m isobath
International organization participation
ACP, AfDB, AU, CD, COMESA, EITI (candidate country), FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (NGOs), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, InOC, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day, 26 June (1960)
Nationality
noun: Malagasy (singular and plural)
adjective: Malagasy
adjective: Malagasy
Natural resources
graphite, chromite, coal, bauxite, rare earth elements, salt, quartz, tar sands, semiprecious stones, mica, fish, hydropower
Geography - note
world's fourth-largest island; strategic location along Mozambique Channel; despite Madagascar’s close proximity to the African continent, ocean currents isolate the island, resulting in high rates of endemic plant and animal species; approximately 90% of the flora and fauna on the island are found nowhere else
Economic overview
low-income East African island economy; natural resource rich; extreme poverty; return of political stability has helped growth; sharp tax revenue drop due to COVID-19; leading vanilla producer; environmentally fragile
Political parties
Group of Young Malagasy Patriots (Groupe des Jeunes Malgaches Patriotes) or GJMP
I Love Madagascar (Tiako I Madagasikara) or TIM
Isika Rehetra Miaraka amin'i Andry Rajoelina coalition or IRD
Malagasy Aware (Malagasy Tonga Saina) or MTS
Malagasy Tia Tanindrazana or MATITA or ANGADY
Movement for Democracy in Madagascar (Mouvement pour la Démocratie à Madagascar) or MDM
Rally for Democratic Socialism (Rassemblement pour Socialisme Démocratique - Nouveau) or RPSD Vaovao
Young Malagasies Determined (Tanora Malagasy Vonona) or TGV
I Love Madagascar (Tiako I Madagasikara) or TIM
Isika Rehetra Miaraka amin'i Andry Rajoelina coalition or IRD
Malagasy Aware (Malagasy Tonga Saina) or MTS
Malagasy Tia Tanindrazana or MATITA or ANGADY
Movement for Democracy in Madagascar (Mouvement pour la Démocratie à Madagascar) or MDM
Rally for Democratic Socialism (Rassemblement pour Socialisme Démocratique - Nouveau) or RPSD Vaovao
Young Malagasies Determined (Tanora Malagasy Vonona) or TGV
Railways
total: 836 km (2018)
narrow gauge: 836 km (2018) 1.000-m gauge
narrow gauge: 836 km (2018) 1.000-m gauge
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Terrain
narrow coastal plain, high plateau and mountains in center
Government type
semi-presidential republic
Country name
conventional long form: Republic of Madagascar
conventional short form: Madagascar
local long form: République de Madagascar/Repoblikan'i Madagasikara
local short form: Madagascar/Madagasikara
former: Malagasy Republic
etymology: a variant of the name was first used by 13th-century Venetian explorer Marco POLO when he confused the island with the Somali port of Mogadishu; the transliteration was later adopted as the official name
conventional short form: Madagascar
local long form: République de Madagascar/Repoblikan'i Madagasikara
local short form: Madagascar/Madagasikara
former: Malagasy Republic
etymology: a variant of the name was first used by 13th-century Venetian explorer Marco POLO when he confused the island with the Somali port of Mogadishu; the transliteration was later adopted as the official name
Location
Southern Africa, island in the Indian Ocean, east of Mozambique
Map references
Africa
Irrigated land
10,860 sq km (2012)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Lantosoa RAKOTOMALALA (since 13 January 2025)
chancery: 2374 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 265-5525
FAX: [1] (202) 265-3034
email address and website:
madagascar.embassy.dc@gmail.com
https://us-madagascar-embassy.org/
chancery: 2374 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 265-5525
FAX: [1] (202) 265-3034
email address and website:
madagascar.embassy.dc@gmail.com
https://us-madagascar-embassy.org/
Internet users
percent of population: 20% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.mg
Refugees and internally displaced persons
refugees: 1,256 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 9,868 (2024 est.)
IDPs: 9,868 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
$17.421 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
337 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years (2019 est.)
male: 9 years (2019 est.)
female: 9 years (2019 est.)
male: 9 years (2019 est.)
female: 9 years (2019 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 40.6% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 4.26% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
rate of urbanization: 4.26% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned Radio Nationale Malagasy (RNM) and Television Malagasy (TVM) have an extensive national network reach; privately owned radio and TV broadcasters in cities and major towns; state-run radio dominates in rural areas; relays of 2 international broadcasters are available in Antananarivo (2019)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 79.8% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 36% of population (2022 est.)
total: 53.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 20.2% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 64% of population (2022 est.)
total: 46.5% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 79.8% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 36% of population (2022 est.)
total: 53.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 20.2% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 64% of population (2022 est.)
total: 46.5% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "Ry Tanindraza nay malala o" (O Our Beloved Fatherland)
lyrics/music: Pasteur RAHAJASON/Norbert RAHARISOA
history: adopted 1959
lyrics/music: Pasteur RAHAJASON/Norbert RAHARISOA
history: adopted 1959
This is an audio of the National Anthem for Madagascar. The national anthem is generally a patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
Major urban areas - population
3.872 million ANTANANARIVO (capital) (2023)
International law organization participation
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Physician density
0.17 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
National symbol(s)
traveller's palm (ravenala), zebu
Mother's mean age at first birth
19.5 years (2021 est.)
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-29
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-29
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 69.8% (2024 est.)
government consumption: 15.3% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22.6% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 23.6% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -31.3% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 15.3% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 22.6% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 23.6% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -31.3% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Madagascar; in the case of a child born out of wedlock, the mother must be a citizen
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: unknown
citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Madagascar; in the case of a child born out of wedlock, the mother must be a citizen
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: unknown
Population distribution
most of population lives on the eastern half of the island; significant clustering is found in the central highlands and eastern coastline, as shown in this population distribution map
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 36.1% (2022 est.)
electrification - urban areas: 71.6%
electrification - rural areas: 10.9%
electrification - urban areas: 71.6%
electrification - rural areas: 10.9%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
5R
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 53.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 25.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 36.7% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 46.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 74.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 63.3% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 53.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 25.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 36.7% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 46.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 74.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 63.3% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Malayo-Indonesian (Merina and related Betsileo), Cotiers (mixed African, Malayo-Indonesian, and Arab ancestry - Betsimisaraka, Tsimihety, Antaisaka, Sakalava), French, Indian, Creole, Comoran
Religions
Church of Jesus Christ in Madagascar/Malagasy Lutheran Church/Anglican Church 34%, Roman Catholic 32.3%, other Christian 8.1%, traditional/Animist 1.7%, Muslim 1.4%, other 0.6%, none 21.9% (2021 est.)
Languages
Malagasy (official) 99.9%, French (official) 23.6%, English 8.2%, other 0.6% (2018 est.)
note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
note: shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
Imports - partners
China 19%, Oman 13%, France 10%, India 8%, South Africa 5% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
highest point: Maromokotro 2,876 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 615 m
lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 m
mean elevation: 615 m
Health expenditure
3.5% of GDP (2021)
5.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
5.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the military’s responsibilities include ensuring sovereignty and territorial integrity and protecting Madagascar’s maritime domain, particularly against piracy, drug trafficking, and smuggling; it also assists the Gendarmerie with maintaining law and order in rural areas, largely in areas affected by banditry, cattle rustling, and criminal groups; the military has a history of influence in domestic politics and seized control of the government in October 2025; security relationships have included France, India, and Russia; Madagascar's small Navy has traditionally looked to India for assistance with maritime security (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
estimated 13,000 Armed Forces; estimated 10,000 Gendarmerie (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the military's inventory consists mostly of older or secondhand armaments originating from countries such as France, South Africa, the former Soviet Union, the UAE, the UK, and the US (2025)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 395 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 161.9 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 13 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 161.9 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 13 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 3.769 million tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 9.2% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 9.2% (2022 est.)
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 3 (1 cultural, 2 natural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Tsingy de Bemaraha Strict Nature Reserve (n); Ambohimanga Royal Hill (c); Atsinanana Rainforests (n)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Tsingy de Bemaraha Strict Nature Reserve (n); Ambohimanga Royal Hill (c); Atsinanana Rainforests (n)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 12.7% (2021)
women married by age 18: 38.8% (2021)
men married by age 18: 11.2% (2021)
women married by age 18: 38.8% (2021)
men married by age 18: 11.2% (2021)
Coal
consumption: 472,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 472,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 150 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 472,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 150 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 64.8% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 3.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 31.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 3.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 31.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 20,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.71 (2025 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
62.3% (2021 est.)
Remittances
2.4% of GDP (2023 est.)
2.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
3.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
2.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
3.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Ports
total ports: 13 (2024)
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 2
very small: 11
ports with oil terminals: 5
key ports: Andoany, Antsiranana, Antsohim Bondrona, Iharana, Mahajanga, Maintirano, Manakara, Mananjary, Maroantsetra, Morondava, Toamasina, Tolanaro, Toliara
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 2
very small: 11
ports with oil terminals: 5
key ports: Andoany, Antsiranana, Antsohim Bondrona, Iharana, Mahajanga, Maintirano, Manakara, Mananjary, Maroantsetra, Morondava, Toamasina, Tolanaro, Toliara
Legislative branch - lower chamber
chamber name: National Assembly (Antenimierampirenena)
number of seats: 163 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 12/11/2020
parties elected and seats per party: Isika Rehetra Miaraka Amin’i Andry Rajoelina (IRMAR) (84); Firaisankina (22); Independents (50); Other (7)
percentage of women in chamber: 14.1%
expected date of next election: May 2029
number of seats: 163 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 12/11/2020
parties elected and seats per party: Isika Rehetra Miaraka Amin’i Andry Rajoelina (IRMAR) (84); Firaisankina (22); Independents (50); Other (7)
percentage of women in chamber: 14.1%
expected date of next election: May 2029
National color(s)
red, green, white
Particulate matter emissions
16.7 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Labor force
16.519 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 5.4% (2024 est.)
male: 5.3% (2024 est.)
female: 5.4% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 5.3% (2024 est.)
female: 5.4% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
-0.08 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 20.5 years (2025 est.)
male: 21.1 years
female: 21.5 years
male: 21.1 years
female: 21.5 years
Debt - external
$3.548 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
445 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$2.785 billion (2024 est.)
$2.632 billion (2023 est.)
$2.16 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$2.632 billion (2023 est.)
$2.16 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Total fertility rate
3.47 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Unemployment rate
3.1% (2024 est.)
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.2% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.2% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
3.936 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 1.057 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 2.879 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 1.057 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 2.879 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 587,041 sq km
land: 581,540 sq km
water: 5,501 sq km
land: 581,540 sq km
water: 5,501 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
9.6% (of GDP) (2023 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$52.968 billion (2024 est.)
$50.833 billion (2023 est.)
$48.782 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$50.833 billion (2023 est.)
$48.782 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
93 (2025)
Infant mortality rate
total: 38.4 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 40.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 34 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 40.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 34 deaths/1,000 live births
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
9.9% (2023 est.)
8.2% (2022 est.)
5.8% (2021 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
8.2% (2022 est.)
5.8% (2021 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$829.376 million (2022 est.)
-$721.953 million (2021 est.)
-$623.653 million (2020 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
-$721.953 million (2021 est.)
-$623.653 million (2020 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$1,700 (2024 est.)
$1,600 (2023 est.)
$1,600 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$1,600 (2023 est.)
$1,600 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 34,000 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Tobacco use
total: 24.1% (2025 est.)
male: 40.2% (2025 est.)
female: 8.2% (2025 est.)
male: 40.2% (2025 est.)
female: 8.2% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
5.3% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
1.816 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Death rate
5.95 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
27.54 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 759,000 kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 2.506 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 139 million kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 2.506 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 139 million kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 29 (2023)
by type: general cargo 16, oil tanker 2, other 11
by type: general cargo 16, oil tanker 2, other 11
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
22.6% (2021 est.)
Imports
$6.041 billion (2022 est.)
$4.769 billion (2021 est.)
$3.718 billion (2020 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$4.769 billion (2021 est.)
$3.718 billion (2020 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$4.689 billion (2022 est.)
$3.362 billion (2021 est.)
$2.589 billion (2020 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$3.362 billion (2021 est.)
$2.589 billion (2020 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 0.89 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.5 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.07 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.32 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 0.5 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.07 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.32 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 68.8 years (2024 est.)
male: 67.3 years
female: 70.3 years
male: 67.3 years
female: 70.3 years
Real GDP growth rate
4.2% (2024 est.)
4.2% (2023 est.)
4.2% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
4.2% (2023 est.)
4.2% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
3.7% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 22.5% (2024 est.)
industry: 22.8% (2024 est.)
services: 46.4% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 22.8% (2024 est.)
services: 46.4% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
3% of GDP (2023 est.)
18% national budget (2019 est.)
18% national budget (2019 est.)
Population growth rate
2.15% (2025 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: Michael RANDRIANIRINA (Col.)
head of government: Prime Minister Herintsalama RAJAONARIVELO (since 22 October 2025)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister
election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); prime minister nominated by the National Assembly, appointed by the president
most recent election date: 16 November 2023
election results:
2023: Andry RAJOELINA reelected president in first round; percent of vote - Andry RAJOELINA (TGV) 59.0%, Siteny Thierry RANDRIANASOLONIAIKO 14.4%, Marc RAVALOMANANA (TIM) 12.1%, other 14.5%
expected date of next election: November 2028
note: on 14 October 2025 Col. Michael Randrianirina, commander of an elite unit of the country’s armed forces, announced the formation of a transitional government made up of civilians, which would rule for two years; the constitution, the country’s top court, and the electoral commission were suspended, and a referendum will be held to formulate a new constitution; the lower house of Parliament was not suspended and impeached former-President Andry RAJOELINA
head of government: Prime Minister Herintsalama RAJAONARIVELO (since 22 October 2025)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the prime minister
election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); prime minister nominated by the National Assembly, appointed by the president
most recent election date: 16 November 2023
election results:
2023: Andry RAJOELINA reelected president in first round; percent of vote - Andry RAJOELINA (TGV) 59.0%, Siteny Thierry RANDRIANASOLONIAIKO 14.4%, Marc RAVALOMANANA (TIM) 12.1%, other 14.5%
expected date of next election: November 2028
note: on 14 October 2025 Col. Michael Randrianirina, commander of an elite unit of the country’s armed forces, announced the formation of a transitional government made up of civilians, which would rule for two years; the constitution, the country’s top court, and the electoral commission were suspended, and a referendum will be held to formulate a new constitution; the lower house of Parliament was not suspended and impeached former-President Andry RAJOELINA
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 23.5 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 76 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 76 (2023 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 73.4 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 66.9 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 6.5 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 15.3 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 66.9 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 6.5 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 15.3 (2025 est.)
Legislative branch - upper chamber
chamber name: Senate (Antenimierandoholona)
number of seats: 18 (12 indirectly elected; 6 appointed)
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 5/29/2024
parties elected and seats per party: IRMAR (10); MALAGASY MIARA-MIAINGA (2)
percentage of women in chamber: 11.1%
expected date of next election: 31 December 2026
number of seats: 18 (12 indirectly elected; 6 appointed)
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 5/29/2024
parties elected and seats per party: IRMAR (10); MALAGASY MIARA-MIAINGA (2)
percentage of women in chamber: 11.1%
expected date of next election: 31 December 2026
Population
total: 31,345,040 (2025 est.)
male: 15,647,362
female: 15,697,678
male: 15,647,362
female: 15,697,678
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 3,410 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
