Philippines - PH - PHL - PHI - East and Southeast Asia

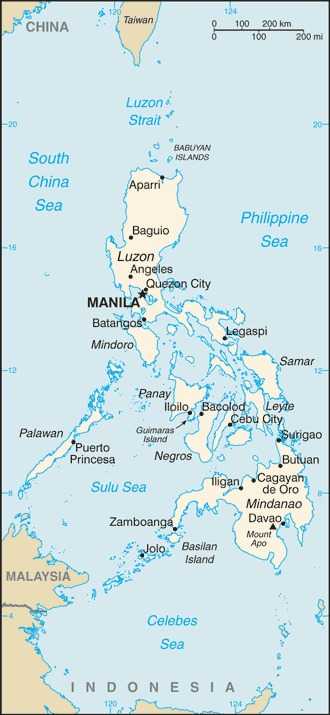
Philippines Images
Philippines Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: 1201 Roxas Boulevard, Manila 1000
mailing address: 8600 Manila Place, Washington DC 20521-8600
telephone: [63] (2) 5301-2000
FAX: [63] (2) 5301-2017
email address and website:
acsinfomanila@state.gov
https://ph.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
15-64 years: 64.3% (male 38,381,583/female 37,613,294)
65 years and over: 5.6% (2024 est.) (male 2,611,230/female 3,973,874)
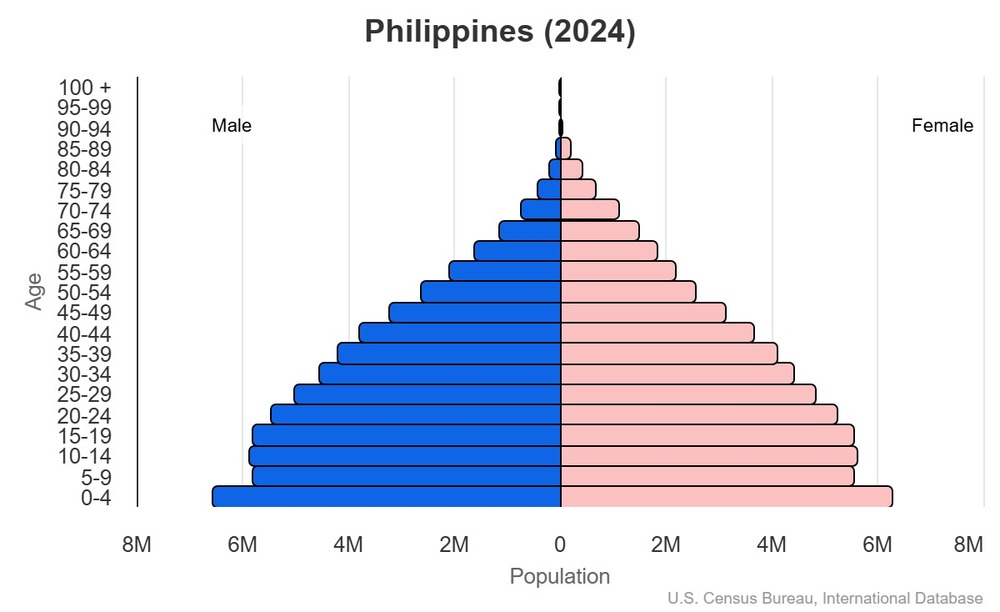
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.66 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
volcanism: significant volcanic activity; Taal (311 m) has been deemed a Decade Volcano by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to its explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Mayon (2,462 m), the country's most active volcano, erupted in 2009 and forced over 33,000 to be evacuated; other historically active volcanoes include Biliran, Babuyan Claro, Bulusan, Camiguin, Camiguin de Babuyanes, Didicas, Iraya, Jolo, Kanlaon, Makaturing, Musuan, Parker, Pinatubo, and Ragang; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Area - comparative
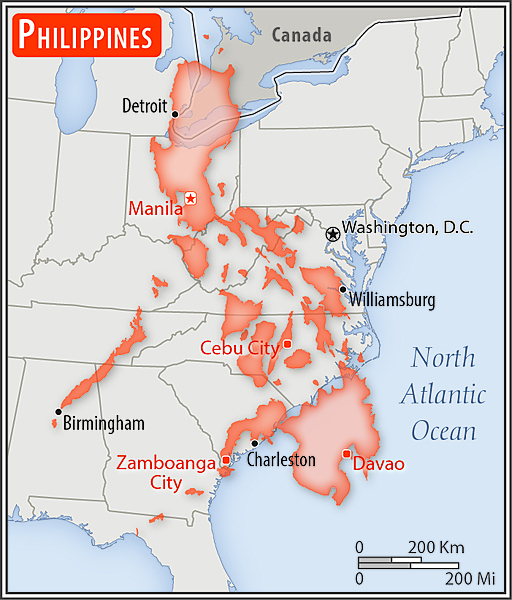
slightly less than twice the size of Georgia; slightly larger than Arizona
Background
The Philippine Islands became a Spanish colony during the 16th century; they were ceded to the US in 1898 following the Spanish-American War. Led by Emilio AGUINALDO, the Filipinos conducted an insurgency against US rule from 1899-1902, although some fighting continued in outlying islands as late as 1913. In 1935, the Philippines became a self-governing commonwealth. Manuel QUEZON was elected president and was tasked with preparing the country for independence after a 10-year transition. The islands fell under Japanese occupation during World War II, and US forces and Filipinos fought together during 1944-45 to regain control. On 4 July 1946 the Republic of the Philippines attained its independence.
Twenty-one years of authoritarian rule under Ferdinand MARCOS ended in 1986, when a "people power" movement in Manila ("EDSA 1") forced him into exile and installed Corazon AQUINO as president. Several coup attempts hampered her presidency, and progress on political stability and economic development faltered until Fidel RAMOS was elected president in 1992. The US closed its last military bases on the islands the same year. Joseph ESTRADA was elected president in 1998. His vice-president, Gloria MACAPAGAL-ARROYO, succeded him in 2001 after ESTRADA's stormy impeachment trial on corruption charges broke down and another "people power" movement ("EDSA 2") demanded his resignation. MACAPAGAL-ARROYO was elected president in 2004. Corruption allegations marred her presidency, but the Philippine economy was one of the few to avoid contraction after the 2008 global financial crisis. Benigno AQUINO III was elected as president in 2010, followed by Rodrigo DUTERTE in 2016. During his term, DUTERTE pursued a controversial drug war that garnered international criticism for alleged human rights abuses. Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. was elected president in 2022 with the largest popular vote in a presidential election since his father's ouster.
For decades, the country has been challenged by armed ethnic separatists, communist rebels, and Islamic terrorist groups, particularly in the southern islands and remote areas of Luzon.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
1.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 31.6% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
provinces: Abra, Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Aklan, Albay, Antique, Apayao, Aurora, Basilan, Bataan, Batanes, Batangas, Biliran, Benguet, Bohol, Bukidnon, Bulacan, Cagayan, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, Camiguin, Capiz, Catanduanes, Cavite, Cebu, Cotabato, Davao del Norte, Davao del Sur, Davao de Oro, Davao Occidental, Davao Oriental, Dinagat Islands, Eastern Samar, Guimaras, Ifugao, Ilocos Norte, Ilocos Sur, Iloilo, Isabela, Kalinga, Laguna, Lanao del Norte, Lanao del Sur, La Union, Leyte, Maguindanao, Marinduque, Masbate, Mindoro Occidental, Mindoro Oriental, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, Mountain, Negros Occidental, Negros Oriental, Northern Samar, Nueva Ecija, Nueva Vizcaya, Palawan, Pampanga, Pangasinan, Quezon, Quirino, Rizal, Romblon, Samar, Sarangani, Siquijor, Sorsogon, South Cotabato, Southern Leyte, Sultan Kudarat, Sulu, Surigao del Norte, Surigao del Sur, Tarlac, Tawi-Tawi, Zambales, Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugay
chartered cities: Angeles, Bacolod, Baguio, Butuan, Cagayan de Oro, Caloocan, Cebu, Cotabato, Dagupan, Davao, General Santos, Iligan, Iloilo, Lapu-Lapu, Las Pinas, Lucena, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Mandaue, Manila, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Naga, Navotas, Olongapo, Ormoc, Paranaque, Pasay, Pasig, Puerto Princesa, Quezon, San Juan, Santiago, Tacloban, Taguig, Valenzuela, Zamboanga
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Department of Transportation: Philippine Coast Guard (PCG); Department of the Interior: Philippine National Police Force (PNP) (2025)
note 1: the PCG is an armed and uniformed service that would be attached to the AFP during a conflict
note 2: the Philippine Government also arms and supports civilian militias; the AFP controls the Civilian Armed Force Geographical Units, while the Civilian Volunteer Organizations fall under PNP command
Budget
expenditures: $93.871 billion (2022 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenditures (excluding grants and social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 14 36 N, 120 58 E
time difference: UTC+8 (13 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: derives from the Tagalog word may, meaning "there is," and nila, the local name for a shrub in the indigo family
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by Congress if supported by three fourths of the membership, by a constitutional convention called by Congress, or by public petition; passage by either of the three proposal methods requires a majority vote in a national referendum
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
57.291 (2024 est.)
55.63 (2023 est.)
54.478 (2022 est.)
49.255 (2021 est.)
49.624 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: President Ferdinand "BongBong" MARCOS, Jr. (since 30 June 2022)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president with the consent of the Commission of Appointments, an independent body of 25 Congressional members that includes the Senate president (ex officio chairman) and is appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president and vice president directly elected on separate ballots by simple-majority popular vote for a single 6-year term
most recent election date: 9 May 2022
election results:
2022: Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. elected president; percent of vote - Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. (PFP) 58.7%, Leni ROBREDO (independent) 27.9%, Manny PACQUIAO (PROMDI) 6.8%, other 6.6%; Sara DUTERTE-Carpio elected vice president; percent of vote Sara DUTERTE-Carpio (Lakas-CMD) 61.5%, Francis PANGILINAN (LP) 17.8%, Tito SOTTO 15.8%, other 4.9%
2016: Rodrigo DUTERTE elected president; percent of vote - Rodrigo DUTERTE (PDP-Laban) 39%, Manuel "Mar" ROXAS (LP) 23.5%, Grace POE (independent) 21.4%, Jejomar BINAY (UNA) 12.7%, Miriam Defensor SANTIAGO (PRP) 3.4%; Leni ROBREDO elected vice president; percent of vote Leni ROBREDO (LP) 35.1%, Ferdinand MARCOS, Jr. (independent) 34.5%, Alan CAYETANO 14.4%, Francis ESCUDERO (independent) 12%, other 4%
expected date of next election: 9 May 2028
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
meaning: blue stands for peace and justice, red for courage, and the triangle for equality; the rays represent the first eight provinces that sought independence from Spain, and the stars represent the country's three parts: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao
history: the design dates to 1897
note: in wartime, the flag is flown upside-down with the red band at the top
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council, a constitutionally created, 6-member body that recommends Supreme Court nominees; justices serve until age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; Sandiganbayan (special court for corruption cases of government officials); Court of Tax Appeals; regional, metropolitan, and municipal trial courts; sharia courts
Land boundaries
Land use
arable land: 18.7% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 18.9% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 5% (2023 est.)
forest: 24.7% (2023 est.)
other: 32.7% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
Literacy
male: 98.4% (2020 est.)
female: 97% (2022 est.)
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: to the depth of exploitation
International organization participation
National holiday
note: 12 June 1898 was the date of independence from Spain; 4 July 1946 was the date of independence from the US
Nationality
adjective: Philippine
Natural resources
Geography - note
note 2: the Philippines is one of the countries along the Ring of Fire, which is a belt bordering the Pacific Ocean that contains about 75% of the world's volcanoes and up to 90% of the world's earthquakes
note 3: the Philippines sits on the Pacific typhoon belt, and an average of 9 typhoons make landfall on the islands each year, with about 5 being destructive; the country is the most exposed in the world to tropical storms
Economic overview
Political parties
Alliance for Change (Hugpong ng Pagbabago or HNP)
Katipunan ng Nagkakaisang Pilipino (KANP)
Lakas ng EDSA-Christian Muslim Democrats or Lakas-CMD
Liberal Party or LP
Nacionalista Party or NP
Nationalist People's Coalition or NPC
National Unity Party or NUP
Partido Demokratiko Pilipino-Lakas ng Bayan or PDP-Laban
Partido Federal ng Pilipinas or PFP
Railways
standard gauge: 49 km (2017) 1.435-m gauge
narrow gauge: 28 km (2017) 1.067-m gauge
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Philippines
local long form: Republika ng Pilipinas
local short form: Pilipinas
etymology: named in honor of King PHILLIP II of Spain by Spanish explorer Ruy LOPEZ de VILLALOBOS, who visited the islands in 1543
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 1600 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036
telephone: [1] (202) 467-9300
FAX: [1] (202) 328-7614
email address and website:
info@phembassy-us.org
The Embassy of the Republic of the Philippines in Washington D.C. (philippineembassy-dc.org)
consulate(s) general: Chicago, Honolulu, Houston, Los Angeles, New York, San Francisco, Tamuning (Guam)
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 1,158,643 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 30 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 12 years (2021 est.)
female: 13 years (2021 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 2.04% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 97.8% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 92.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.9% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.2% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 7.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.1% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: collectively/Julian FELIPE
history: music adopted 1898 and lyrics adopted 1956; only sung in Tagalog
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 25-49
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 14.5% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 23.6% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.1% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 25.8% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -40.1% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Philippines
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 98%
electrification - rural areas: 91.1%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 96.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 92.7% of population (2022 est.)
total: 94.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 3.5% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 7.3% of population (2022 est.)
total: 5.5% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
Ang World Factbook, ang mapagkukunan ng kailangang impormasyon. (Tagalog)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: data represent percentage of households; unspecified Filipino (based on Tagalog) and English are official languagesTaga; eight major dialects - Tagalog, Cebuano, Ilocano, Hiligaynon or Ilonggo, Bicol, Waray, Pampango, and Pangasinan
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Philippine Sea 0 m
mean elevation: 442 m
Physician density
Health expenditure
9% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
maritime security is also a priority; the AFP's naval forces conduct naval interdiction missions in support of security operations on the southern islands, including joint maritime patrols with Indonesia and Malaysia; rising tensions with China over disputed waters and land features in the South China Sea since 2012 have spurred the AFP to place more emphasis on blue-water naval capabilities, including acquiring larger warships such as guided missile frigates, corvettes, offshore patrol vessels, and landing platform dock (LPD) amphibious assault ships
the Philippine military was formally organized during the American colonial period as the Philippine Army; they were established by the National Defense Act of 1935 and comprised of both Filipinos and Americans; the US and Philippines agreed to a mutual defense treaty in 1951; based on agreements signed in 2014 and 2023, the Philippine Government allows the rotational presence of US military forces, aircraft, and ships at up to nine bases in the Philippines; also in 2023, the US agreed to assist in modernizing Philippine defense capabilities, deepen interoperability, enhance bilateral planning and information-sharing, and combat transnational and nonconventional threats (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
People - note
Terrorist group(s)
note 1: ISIS-EA factions include Daulah Islamiya-Lanao (aka Maute Group), Daulah Islamiya-Maguindanao, Daulah Islamiya-Socsargen, ISIS-aligned elements of the Abu Sayyaf Group (ASG), ISIS-aligned elements of the Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters (BIFF), and rogue elements of the Moro Islamic Liberation Front (MILF)
note 2: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 13.602 billion cubic meters (2022)
agricultural: 67.937 billion cubic meters (2022)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 49.9% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.9% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Baroque Churches of the Philippines (c); Tubbataha Reefs Natural Park (n); Rice Terraces of the Philippine Cordilleras (c); Historic Vigan (c); Puerto-Princesa Subterranean River National Park (n); Mount Hamiguitan Range Wildlife Sanctuary (n)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 9.4% (2022)
Coal
consumption: 42.859 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 8.151 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 36.542 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 361 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 1.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
geothermal: 9.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 3.12 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 794.289 million cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 98.543 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 457,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 138.5 million barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
8.9% of GDP (2023 est.)
9.4% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Space program overview
Space agency/agencies
Geoparks
global geoparks and regional networks: Bohol Island (2023)
Ports
large: 2
medium: 4
small: 8
very small: 56
ports with oil terminals: 22
key ports: Batangas City, Cagayan de Oro, Cebu, Manila, San Fernando Harbor, Subic Bay
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 317 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 3 years
most recent election date: 5/12/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Lakas-CMD party (103), National Unity Party (NUP) (32), Nationalist People's Coalition (NPC) 31, Partido Federal ng Pilipinas (PFP) (27), Nacionalista Party (NP) (22), Liberal Party (LP) (6), others (28), independents (11)
percentage of women in chamber: 28.3%
expected date of next election: May 2028
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 24 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: partial renewal
term in office: 6 years
most recent election date: 5/12/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Nationalist People's Coalition (NPC) (2); Nacionalista Party (NP) (3); Partido Demokratiko Pilipino-Laban (PDP-Laban) (2); Lakas- CMD party (1); Katipunan ng Nagkakaisang Pilipino (KANP) (1); Liberal Party (1); Independents (2)
percentage of women in chamber: 20.8%
expected date of next election: May 2028
National coat of arms

National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Methane emissions
agriculture: 1,662.2 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 452.7 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 39.1 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Key space-program milestones
1996 - acquired first communications satellite (Agila-1) from Indonesia after it was already in orbit
2014 - initiated a scientific remote sensing (RS) microsatellite development program in collaboration with Japan, resulting in first RS microsatellite (Diwata-1) being deployed from the International Space Station (ISS) in 2016
2018 - first domestically designed and built scientific/technology-demonstrator cube satellite (Maya-1) deployed from ISS; second RS microsatellite (Diwata-2) developed with assistance from and launched by Japan
2023 - signed agreement with the ESA and EU to expand cooperation on Earth observation/RS data sharing
2025 - signed US-led Artemis Accords for space exploration
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 5.6% (2024 est.)
female: 8.3% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 25.1 years
female: 26.3 years
Debt - external
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$103.742 billion (2023 est.)
$96.04 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
2.3% (2023 est.)
2.6% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 88.581 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 61.597 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 6.05 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 298,170 sq km
water: 1,830 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.137 trillion (2023 est.)
$1.078 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 24.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 19.6 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
6% (2023 est.)
5.8% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$12.387 billion (2023 est.)
-$18.261 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$9,900 (2023 est.)
$9,500 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 34.4% (2025 est.)
female: 3.7% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 100.824 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 10.693 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 52, container ship 43, general cargo 955, oil tanker 207, other 946
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$151.441 billion (2023 est.)
$152.638 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$103.588 billion (2023 est.)
$98.832 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 1.47 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.03 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 3.34 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 67.3 years
female: 74.5 years
Real GDP growth rate
5.5% (2023 est.)
7.6% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 27.7% (2024 est.)
services: 63.2% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
15.2% national budget (2025 est.)
Population growth rate
Military service age and obligation
note: as of 2023, women made up about 8% of the active military; women have attended the Philippine Military Academy and trained as combat soldiers since 1993
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 39.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 8.6 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 11.6 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 56,846,416
female: 56,058,042
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 115 (2024 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 4 (2024 est.)







