Uganda - UG - UGA - UGA - Africa

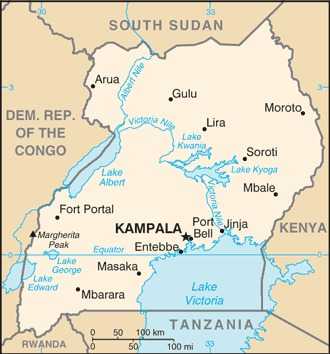
Uganda Images
Uganda Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: 1577 Ggaba Road, Kampala
mailing address: 2190 Kampala Place, Washington DC 20521-2190
telephone: [256] (0) 312-306-001
FAX: [256] (0) 414-259-794
email address and website:
KampalaWebContact@state.gov
https://ug.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
15-64 years: 50.6% (male 11,788,483/female 13,131,051)
65 years and over: 2.4% (2024 est.) (male 504,332/female 683,498)
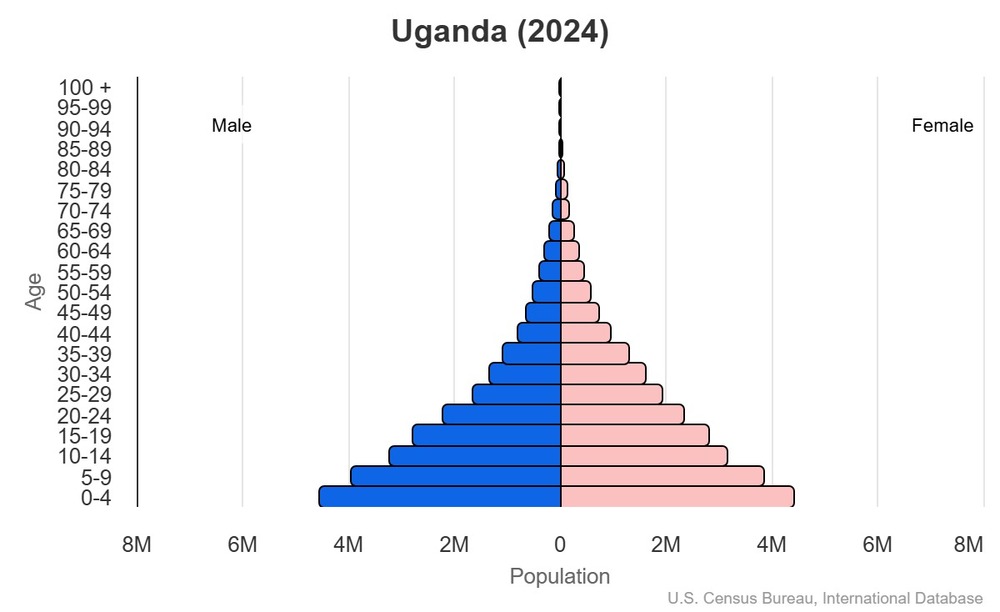
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.9 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.74 male(s)/female
total population: 0.95 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
Area - comparative
slightly more than two times the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Oregon
Military service age and obligation
Background
An ancient crossroads for various migrations, Uganda has as many as 65 ethnic groups that speak languages from three of Africa’s four major linguistic families. As early as 1200, fertile soils and regular rainfall in the south fostered the formation of several large, centralized kingdoms, including Buganda, from which the country derives its name. Muslim traders from Egypt reached northern Uganda in the 1820s, and Swahili merchants from the Indian Ocean coast arrived in the south by the 1840s. The area attracted the attention of British explorers seeking the source of the Nile River in the 1860s, and this influence expanded in subsequent decades with the arrival of Christian missionaries and trade agreements; Uganda was declared a British protectorate in 1894. Buganda and other southern kingdoms negotiated agreements with Britain to secure privileges and a level of autonomy that were rare during the colonial period in Africa. Uganda's colonial boundaries grouped together a wide range of ethnic groups with different political systems and cultures, and the disparities between how Britain governed southern and northern areas compounded these differences, complicating efforts to establish a cohesive independent country.
Uganda gained independence in 1962 with one of the more developed economies and one of the strongest education systems in Sub-Saharan Africa, but it descended within a few years into political turmoil and internal conflict that lasted more than two decades. In 1966, Prime Minister Milton OBOTE suspended the constitution and violently deposed President Edward MUTESA, who was also the king of Buganda. Idi AMIN seized power in 1971 through a military coup and led the country into economic ruin and rampant mass atrocities that killed as many as 500,000 civilians. AMIN’s annexation of Tanzanian territory in 1979 provoked Tanzania to invade Uganda, depose AMIN, and install a coalition government. In the aftermath, Uganda continued to experience atrocities, looting, and political instability and had four different heads of state between 1979 and 1980. OBOTE regained the presidency in 1980 through a controversial election that sparked renewed guerrilla warfare, killing as an estimated 300,000 civilians. Gen. Tito OKELLO seized power in a coup in 1985, but his rule was short-lived, with Yoweri MUSEVENI becoming president in 1986 after his insurgency captured the capital. MUSEVENI is widely credited with restoring relative stability and economic growth to Uganda but has resisted calls to leave office. In 2017, parliament removed presidential age limits, making it possible for MUSEVENI to remain in office for life.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification
Military expenditures
2.2% of GDP (2022 est.)
2.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
2.5% of GDP (2020 est.)
1.7% of GDP (2019 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 34.5% (2019 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Ministry of Internal Affairs: Uganda Police Force (2025)
note 1: the Special Forces Command is a separate branch within the UPDF; it evolved from the former Presidential Guard Brigade and has continued to retain presidential protection duties in addition to its traditional missions, such as counterinsurgency
note 2: the Uganda Police Force includes air, field, territorial, and marine units, as well as a presidential guard force
note 3: in 2018, President MUSEVENI created a volunteer force of Local Defense Units under the military to beef up local security in designated parts of the country
Budget
expenditures: $10.043 billion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 0 19 N, 32 33 E
time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name is said to come from an African antelope, the impala
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership in the second and third readings; proposals affecting "entrenched clauses," including the sovereignty of the people, supremacy of the constitution, human rights and freedoms, the democratic and multiparty form of government, presidential term of office, independence of the judiciary, and the institutions of traditional or cultural leaders, also requires passage by referendum, ratification by at least two-thirds majority vote of district council members in at least two thirds of Uganda's districts, and assent of the president of the republic
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
3,757.263 (2024 est.)
3,726.14 (2023 est.)
3,689.817 (2022 est.)
3,587.052 (2021 est.)
3,718.249 (2020 est.)
Flag
meaning: black stands for the African people, yellow for sunshine and vitality, and red for African brotherhood
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the president of the republic in consultation with the Judicial Service Commission, an 8-member independent advisory body, and approved by the National Assembly; justices serve until mandatory retirement at age 70
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal (also acts as the Constitutional Court); High Court (includes 12 High Court Circuits and 8 High Court Divisions); Industrial Court; Chief Magistrate Grade One and Grade Two Courts throughout the country; qadhis courts; local council courts; family and children courts
Land boundaries
border countries (5): Democratic Republic of the Congo 877 km; Kenya 814 km; Rwanda 172 km; South Sudan 475 km; Tanzania 391 km
Land use
arable land: 34.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 11% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 26.5% (2023 est.)
forest: 12.1% (2023 est.)
other: 16% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Literacy
male: 78.5% (2016 est.)
female: 61% (2016 est.)
Maritime claims
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Ugandan
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Forum for Democratic Change or FDC
Justice Forum or JEEMA
National Resistance Movement or NRM
National Unity Platform
People's Progressive Party or PPP
Uganda People's Congress or UPC
Railways
narrow gauge: 1,244 km (2014) 1.000-m gauge
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Uganda
etymology: the name is derived from the Swahili word u, meaning "land" or "country," and the Ganda people; the origin of the Ganda name is unclear
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 5911 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20011
telephone: [1] (202) 726-7100
FAX: [1] (202) 726-1727
email address and website:
washington@mofa.go.ug
https://washington.mofa.go.ug/
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 22,209 (2024 est.)
stateless persons: 10,284 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 10 years (2016 est.)
female: 9 years (2016 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 5.41% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 80.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 51.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 59.3% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 19.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 48.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 40.7% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: George Wilberforce KAKOMOA
history: adopted 1962; one of the shortest national anthems in the world
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
note: data represents median age at first birth among women 20-49
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 10% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 21.5% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.8% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 16.9% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -24.6% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent or grandparent must be a native-born citizen of Uganda
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: an aggregate of 20 years and continuously for the last 2 years prior to applying for citizenship
Population distribution
Electricity access
electrification - urban areas: 72%
electrification - rural areas: 35.9%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 67.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 27.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 38.2% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 32.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 72.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 61.8% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Religions
Languages
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Albert Nile 614 m
Health expenditure
4.9% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the military traces its history back to the formation of the Uganda Rifles in 1895 under the British colonial government; the Uganda Rifles were merged with the Central Africa Regiment and the East Africa Rifles to form the King’s African Rifles (KAR) in 1902, which participated in both world wars, as well as the Mau Mau rebellion in Kenya (1952-1960); in 1962, the Ugandan battalion of the KAR was transformed into the country's first military force, the Uganda Rifles, which was subsequently renamed the Uganda Army; the UPDF was established in 1995 from the former rebel National Resistance Army following the enactment of the 1995 Constitution of Uganda (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 50 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 259 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 24.1% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major lakes (area sq km)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Bwindi Impenetrable National Park (n); Rwenzori Mountains National Park (n); Tombs of Buganda Kings at Kasubi (c)
Child marriage
women married by age 18: 34% (2016)
men married by age 18: 5.5% (2016)
Coal
exports: 100 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 19 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 799.999 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 2.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 86.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 8.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
Petroleum
crude oil estimated reserves: 2.5 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
2.7% of GDP (2022 est.)
2.9% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 3.5% (2024 est.)
female: 5.5% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 15.5 years
female: 17.1 years
Debt - external
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$3.721 billion (2017 est.)
$3.098 billion (2016 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
2.8% (2023 est.)
2.9% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: -398 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 6.354 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 197,100 sq km
water: 43,938 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$135.803 billion (2023 est.)
$128.923 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 31.8 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 25.1 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.4% (2023 est.)
7.2% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$4.064 billion (2022 est.)
-$3.605 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$2,800 (2023 est.)
$2,700 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1
Tobacco use
male: 7.8% (2025 est.)
female: 1.5% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 4.254 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 400.349 million kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 23.289 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 1.116 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$11.079 billion (2022 est.)
$10.62 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$6.116 billion (2022 est.)
$6.231 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 0.85 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.5 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 5.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 67.5 years
female: 72 years
Real GDP growth rate
5.3% (2023 est.)
4.6% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 24.9% (2024 est.)
services: 43.1% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
8.5% national budget (2022 est.)
Population growth rate
Executive branch
head of government: Prime Minister Robinah NABBANJA (since 14 June 2021)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president from among elected members of Parliament or persons who qualify to be elected as members of Parliament
election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 5-year term (no term limits)
most recent election date: 15 January 2026
election results:
2026: Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI reelected president in the first round; percent of vote - Yoweri Kaguta MUSEVENI (NRM) 71.7%, Robert Kyagulanyi SSENTAMU (aka Bobi WINE) (NUP) 24.7%, Other 3.6%
expected date of next election: 2031
Legislative branch
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 529 (499 directly elected; 30 indirectly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 1/14/2021 to 1/18/2021
parties elected and seats per party: National Resistance Movement (NRM) (336); National Unity Platform (NUP) (57); Forum for Democratic Change (FDC) (32); Independents (74); Other (30)
percentage of women in chamber: 34.1%
expected date of next election: 1/15/2026 to 2/6/2026
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 92.1 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 4.8 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 20.8 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 24,835,513
female: 26,028,337
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 83 (2024 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: (2023 est.) less than 1





