United States - US - USA - USA - North America


United States Images
United States Factbook Data
Age structure
15-64 years: 63.4% (male 108,553,822/female 108,182,491)
65 years and over: 18.5% (2024 est.) (male 28,426,426/female 34,927,914)
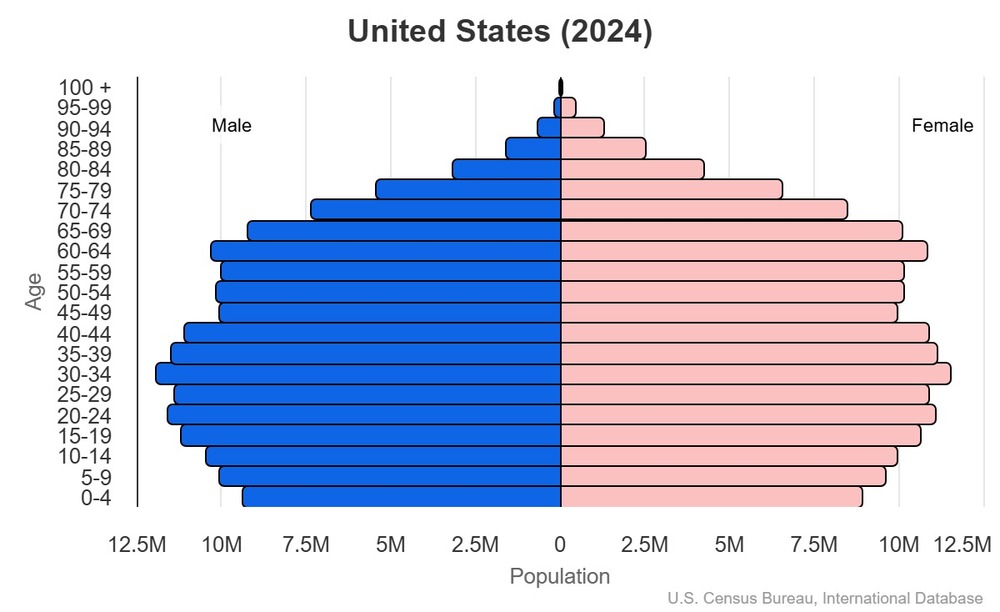
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
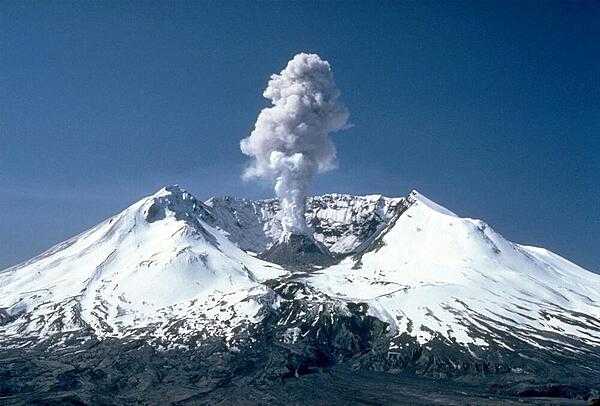
volcanism: volcanic activity in the Hawaiian Islands, Western Alaska, the Pacific Northwest, and in the Northern Mariana Islands; Mauna Loa (4,170 m) in Hawaii and Mount Rainier (4,392 m) in Washington have been deemed Decade Volcanoes by the International Association of Volcanology and Chemistry of the Earth's Interior, worthy of study due to their explosive history and close proximity to human populations; Pavlof (2,519 m) is the most active volcano in Alaska's Aleutian Arc and poses a significant threat to intercontinental air travel; St. Helens (2,549 m), famous for the devastating 1980 eruption, remains active today; other historically active volcanoes are mostly concentrated in the Aleutian arc and Hawaii, including (in Alaska) Aniakchak, Augustine, Chiginagak, Fourpeaked, Iliamna, Katmai, Kupreanof, Martin, Novarupta, Redoubt, Spurr, Wrangell, Trident, Ugashik-Peulik, Ukinrek Maars, Veniaminof, (in Hawaii) Haleakala, Kilauea, Loihi, (in the Northern Mariana Islands) Anatahan, (in the Pacific Northwest) Mount Baker, and Mount Hood; see note 2 under "Geography - note"
Area - comparative
Background
Thirteen of Britain's American colonies broke with the mother country in 1776 and were recognized as the new nation of the United States of America following the Treaty of Paris in 1783. During the 19th and 20th centuries, 37 new states were added as the nation expanded across the North American continent and acquired a number of overseas possessions. Two of the most traumatic experiences in the nation's history were the Civil War (1861-65), in which a northern Union of states defeated a secessionist Confederacy of 11 southern slave states, and the Great Depression of the 1930s, an economic downturn during which about a quarter of the labor force lost its jobs. Buoyed by victories in World Wars I and II and the end of the Cold War in 1991, the US remains the world's most powerful nation state. Since the end of World War II, the economy has achieved relatively steady growth, low unemployment, and rapid advances in technology.
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Hazardous Wastes, Marine Dumping-London Protocol
Military expenditures
3.2% of GDP (2024 est.)
3.1% of GDP (2023 est.)
3.2% of GDP (2022 est.)
3.5% of GDP (2021 est.)
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 30.4% (2023 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
note 1: the US Coast Guard is administered in peacetime by the Department of Homeland Security, but in wartime reports to the Navy
note 2: the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard are reserve components of their services and operate in part under state authority; the US military also maintains reserve forces for each branch
note 3: US law enforcement personnel include those of federal agencies, such as the Department of Homeland Security and Department of Justice, the 50 states, special jurisdictions, local sheriff’s offices, and municipal, county, regional, and tribal police departments
note 4: some US states have "state defense forces" (SDFs), which are military units that operate under the sole authority of state governments; SDFs are authorized by state and federal law and are under the command of the governor of each state; most are organized as ground units, but air and naval units also exist
Budget
expenditures: $6.857 trillion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
geographic coordinates: 38 53 N, 77 02 W
time difference: UTC-5 (during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins second Sunday in March; ends first Sunday in November; note - no DST for Hawaii and most of Arizona
time zone note: the 50 United States cover six time zones
etymology: named after George WASHINGTON (1732-1799), the first president of the United States
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
note: many consider Mount McKinley, the highest peak in the United States, to be the world’s coldest mountain because of its combination of high elevation and its subarctic location at 63 degrees north latitude; permanent snow and ice cover over 75 percent of the mountain, and enormous glaciers, up to 45 miles long and 3,700 feet thick, spider out from its base in every direction; it is home to some of the world’s coldest and most violent weather, where winds of over 150 miles per hour and temperatures of -93˚F have been recorded.
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed as a "joint resolution" by Congress, which requires a two-thirds majority vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate or by a constitutional convention called for by at least two thirds of the state legislatures; passage requires ratification by three fourths of the state legislatures or passage in state-held constitutional conventions as specified by Congress; the US president has no role in the constitutional amendment process
Dependent areas
note: from 18 July 1947 until 1 October 1994, the US administered the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands; it entered into a political relationship with all four political entities: the Northern Mariana Islands is a commonwealth in political union with the US (effective 3 November 1986); the Republic of the Marshall Islands signed a Compact of Free Association with the US (effective 21 October 1986); the Federated States of Micronesia signed a Compact of Free Association with the US (effective 3 November 1986); Palau concluded a Compact of Free Association with the US (effective 1 October 1994)
Exchange rates
Canadian dollars per US dollar: 1.369 (2024 est.), 1.35 (2023 est.), 1.302 (2022 est.), 1.254 (2021 est.), 1.341 (2020 est.)
Chinese yuan per US dollar: 0.783 (2024 est.), 7.084 (2023 est.), 6.737 (2022 est.), 6.449 (2021 est.), 6.901 (2020 est.)
euros per US dollar: 0.924 (2024 est.), 0.925 (2023 est.), 0.950 (2022 est.), 0.845 (2021 est.), 0.876 (2020 est.)
Japanese yen per US dollar: 151.366 (2024 est.), 140.49 (2023 est.), 131.50 (2022 est.), 109.75 (2021 est.), 106.78 (2020 est.)
note 1: the following countries and territories use the US dollar officially as their legal tender: British Virgin Islands, Ecuador, El Salvador, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Palau, Timor Leste, Turks and Caicos, and islands of the Caribbean Netherlands (Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba)
note 2: the following countries and territories use the US dollar as official legal tender alongside local currency: Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, and Panama
Executive branch
head of government: President Donald J. TRUMP (since 20 January 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president, approved by the Senate
election/appointment process: president and vice president indirectly elected on the same ballot by the Electoral College of electors chosen from each state; president and vice president serve a 4-year term (eligible for a second term)
most recent election date: 5 November 2024
election results:
2024: Donald J. TRUMP elected president; electoral vote - Donald J. TRUMP (Republican Party) 312, Kamala HARRIS (Democratic Party) 226; percent of direct popular vote - Donald J. TRUMP 49.8%, Kamala HARRIS 48.3%, other 1.9%
2020: Joseph R. BIDEN, Jr. elected president; electoral vote - Joseph R. BIDEN, Jr. (Democratic Party) 306, Donald J. TRUMP (Republican Party) 232; percent of direct popular vote - Joseph R. BIDEN Jr. 51.3%, Donald J. TRUMP 46.9%, other 1.8%
expected date of next election: 7 November 2028
note: the president is both chief of state and head of government
Flag
meaning: the stars represent the 50 states, and the stripes represent the 13 original colonies; blue stands for loyalty, devotion, truth, justice, and friendship; red for courage, zeal, and fervency; white for purity and rectitude of conduct
note 1: sometimes referred to by its nickname of "Old Glory"
note 2: the design and colors have been the basis for a number of other flags, including Chile, Liberia, Malaysia, and Puerto Rico
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: president nominates and, with the advice and consent of the Senate, appoints Supreme Court justices; justices serve for life
subordinate courts: Courts of Appeal (includes the US Court of Appeal for the Federal District and 12 regional appeals courts); 94 federal district courts in 50 states and territories
note: the US court system consists of the federal court system and the state court systems; each court system is responsible for hearing certain types of cases, but neither is completely independent of the other, and the systems often interact
Land boundaries
border countries (2): Canada 8,891 km (including 2,475 km with Alaska); Mexico 3,111 km
note: US Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba is leased by the US and is part of Cuba; the base boundary is 28.5 km
Land use
arable land: 16.6% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 0.3% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 29.2% (2023 est.)
forest: 33.8% (2023 est.)
other: 18.7% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: bicameral
note: in addition to the regular members of the House of Representatives there are 6 non-voting delegates elected from the District of Columbia and the US territories of American Samoa, Guam, Puerto Rico, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Virgin Islands; these are single seat constituencies directly elected by simple majority vote to serve a 2-year term (except for the resident commissioner of Puerto Rico who serves a 4-year term); the delegate can vote when serving on a committee and when the House meets as the Committee of the Whole House, but not when legislation is submitted for a “full floor” House vote; election of delegates last held on 8 November 2022 (next to be held on 3 November 2024)
Maritime claims
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: not specified
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: American
Natural resources
note: the US has the world's largest coal reserves with 491 billion short tons accounting for 27% of the world's total
Geography - note
note 2: the western US coast and the southern coast of Alaska lie along the Ring of Fire, which is a belt bordering the Pacific Ocean that contains about 75% of the world's volcanoes and up to 90% of the world's earthquakes
note 3: the Aleutian Islands are a chain of volcanic islands that divide the Bering Sea (north) from the main Pacific Ocean (south); they extend about 1,800 km (1,118 mi) westward from the Alaskan Peninsula; the archipelago consists of 14 larger islands, 55 smaller islands, and hundreds of islets; there are 41 active volcanoes on the islands, which together form a large northern section of the Ring of Fire
note 4: Mammoth Cave, in west-central Kentucky, is the world's longest known cave system with more than 650 km (405 miles) of surveyed passageways, which is nearly twice as long as the second-longest cave system, the Sac Actun underwater cave in Mexico (see "Geography - note" under Mexico)
note 5: Kazumura Cave on the island of Hawaii is the world's longest and deepest lava-tube cave; it has been surveyed at 66 km (41 mi) long and 1,102 m (3,614 ft) deep
note 6: Bracken Cave outside San Antonio, Texas is the world's largest bat cave and the summer home to the largest colony of bats in the world; an estimated 20 million Mexican free-tailed bats roost in the cave from March to October, making it the world's largest known concentration of mammals
Economic overview
world’s largest economy by nominal GDP; largest importer and second-largest exporter; home to leading financial exchanges and global reserve currency; high and growing public debt; inflation moderating but remains above pre-pandemic levels
Political parties
Constitution Party
Democratic Party
Green Party
Libertarian Party
Republican Party
Vermont Progressive Party
Railways
standard gauge: 293,564.2 km (2014) 1.435-m gauge
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: United States
abbreviation: US or USA
etymology: the name America was first used in 1507 and is derived from the first name of Amerigo VESPUCCI (1454-1512), an Italian explorer, navigator, and cartographer; the name United States first appeared in a document subtitle during the discussions that led to the Declaration of Independence in 1776
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 21,737 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 15 years (2022 est.)
female: 17 years (2022 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.96% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 100% of population (2022 est.)
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 0% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: Francis Scott KEY/John Stafford SMITH
history: adopted 1931; during the War of 1812, Francis Scott KEY witnessed the successful American defense of Baltimore's Fort McHenry against a British naval bombardment, later writing a poem about it that would become the US national anthem; the lyrics were set to the tune of "The Anacreontic Song;" there are four verses, but only the first verse is sung
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 13.4% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 21.6% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.1% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 10.9% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -14% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: yes
dual citizenship recognized: no, but the US government acknowledges such situtations exist; US citizens are not encouraged to seek dual citizenship since it limits protection by the US
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 99.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 98.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 99.6% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 1.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0.4% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
note: a separate listing for Hispanic is not included because the US Census Bureau considers Hispanic to mean persons of Spanish/Hispanic/Latino origin including those of Mexican, Cuban, Puerto Rican, Dominican Republic, Spanish, and Central or South American origin living in the US who may be of any race or ethnic group (White, Black, Asian, etc.); an estimated 18.7% of the total US population is Hispanic as of 2020
Religions
Languages
note: data represent the language spoken at home; English is the official national language as of March 2025, but English previously had official status in 32 of the 50 states; Hawaiian is an official language in the state of Hawaii, and 20 indigenous languages are official in Alaska
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
lowest point: Death Valley (lowest point in North America) -86 m
mean elevation: 760 m
note 1: Mount McKinley is one of the most striking features on the entire planet; at 20,310 feet, it is the crowning peak of the Alaska Range and the highest mountain on North America; it towers three and one-half vertical miles above its base, making it a mile taller from base to summit than Mt. Everest; McKinley's base sits at about 2,000 feet above sea level and rises over three and one-half miles to its 20,310 foot summit; Everest begins on a 14,000-foot high plain, then summits at 29,028 feet
note 2: the peak of Mauna Kea (4,207 m above sea level) on the island of Hawaii rises about 10,200 m above the Pacific Ocean floor; by this measurement, it is the world's tallest mountain -- higher than Mount Everest (8,850 m), which is recognized as the tallest mountain above sea level
Health expenditure
24.7% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military - note
the US military has a global presence; the separate services operate jointly under 11 regional or functionally based joint service "combatant" commands: Africa Command; Central Command, Cyber Command, European Command, Indo-Pacific Command, Northern Command, Southern Command, Space Command, Special Operations Command, Strategic Command, and Transportation Command
Congress officially created the US military in September 1789; the US Army was established in June 1775 as the Continental Army; after the declaration of independence in July 1776, the Continental Army and the militia in the service of Congress became known collectively as the Army of the United States; when Congress ordered the Continental Army to disband in 1784, it retained a small number of personnel that would form the nucleus of the 1st American Regiment for national service formed later that year; both the US Navy and the US Marines were also established in 1775, but the Navy fell into disuse after the Revolutionary War, and was reestablished by Congress in 1794; the first US military unit devoted exclusively to aviation began operations in 1913 as part of the US Army; the Army Air Corps (AAC) was the US military service dedicated to aerial warfare between 1926 and 1941; the AAC became the US Army Air Forces in 1941 and remained as a combat arm of the Army until the establishment of the US Air Force in 1947 (2025)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 209.7 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 176.2 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 14.8% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 1.9% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
Major aquifers
Major lakes (area sq km)
note - Great Lakes* area shown as US waters
salt water lake(s): Great Salt – 4,360 sq km; Pontchartrain – 1,620 sq km; Selawik – 1,400 sq km; Salton Sea – 950 sq km
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Pacific Ocean drainage: Yukon* (847,620 sq km, US only 23,820 sq km); Colorado (703,148 sq km); Columbia* (657,501 sq km, US only 554,501 sq km)
note: watersheds shared with Canada shown with *
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Yellowstone National Park (n); Grand Canyon National Park (n); Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site (c); Independence Hall (c); Statue of Liberty (c); Yosemite National Park (n); Papahānaumokuākea (m); Monumental Earthworks of Poverty Point (c); The 20th-Century Architecture of Frank Lloyd Wright (c); Mesa Verde National Park (c); Mammoth Cave National Park (n); Monticello and the University of Virginia in Charlottesville (c); Olympic National Park (n); Everglades National Park (n); Kluane / Wrangell-St. Elias / Glacier Bay / Tatshenshini-Alsek (n); Redwood National and State Parks (n); Great Smoky Mountains National Park (n); La Fortaleza and San Juan National Historic Site in Puerto Rico (c); Chaco Culture (c); Hawaii Volcanoes National Park (n); Taos Pueblo (c); Carlsbad Caverns National Park (n); Waterton Glacier International Peace Park (n); Moravian Church Settlements (c); San Antonio Missions (c); Hopewell Ceremonial Earthworks (c)
Coal
consumption: 495.156 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 92.28 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 3.825 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 247.883 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
nuclear: 18.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 5.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 9.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 5.6% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
geothermal: 0.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 1.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 920.47 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
exports: 215.48 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 82.917 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 13.402 trillion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 20.307 million bbl/day (2024 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 38.212 billion barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
0% of GDP (2023 est.)
0% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Nuclear energy
Net capacity of operational nuclear reactors: 96.95GW (2025 est.)
Percent of total electricity production: 18.5% (2023 est.)
Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down: 41 (2025)
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
note: the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO; established in 1961) is responsible for designing, building, launching, and maintaining intelligence satellites; the US Space Command (USSPACECOM; established in 2019) is one of 11 unified combatant commands within the Department of Defense and is responsible for military operations in outer space, specifically all operations over 100 kilometers or 62 miles above mean sea level); the US Space Force (USSF; established 2019) is a branch of the US Armed Forces
Ports
large: 21
medium: 38
small: 132
very small: 475
ports with oil terminals: 204
key ports: Baltimore, Boston, Brooklyn, Buffalo, Chester, Cleveland, Detroit, Galveston, Houston, Los Angeles, Louisiana Offshore Oil Port (LOOP), Mobile, New Orleans, New York City, Norfolk, Oakland, Philadelphia, Portland, San Francisco, Seattle, Tri-City Port
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 435 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 2 years
most recent election date: 11/5/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Republican Party (220); Democratic Party (215)
percentage of women in chamber: 28.9%
expected date of next election: November 2026
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 100 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: partial renewal
term in office: 6 years
most recent election date: 11/5/2024
parties elected and seats per party: Republican Party (15); Democratic Party (19)
percentage of women in chamber: 26%
expected date of next election: November 2026
National color(s)
Particulate matter emissions
Methane emissions
agriculture: 9,063.9 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 4,974 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 758.6 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 10.4% (2024 est.)
female: 8.3% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 37.8 years
female: 40 years
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$773.426 billion (2023 est.)
$706.644 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: central government debt as a % of GDP
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
3.7% (2023 est.)
3.7% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 777.302 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 2.258 billion metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 1.76 billion metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 9,147,593 sq km
water: 685,924 sq km
note: includes only the 50 states and District of Columbia, no overseas territories
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$24.977 trillion (2023 est.)
$24.276 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 5.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 4.7 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
4.1% (2023 est.)
8% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$905.378 billion (2023 est.)
-$1.012 trillion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$74,200 (2023 est.)
$72,700 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 38 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 27.7% (2025 est.)
female: 16.7% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 4.085 trillion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 19.87 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 38.874 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 191.104 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 4, container ship 60, general cargo 96, oil tanker 68, other 3,305
note - oceangoing self-propelled, cargo-carrying vessels of 1,000 gross tons and above
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$3.857 trillion (2023 est.)
$3.984 trillion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$3.072 trillion (2023 est.)
$3.039 trillion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 26 (2023 est.)
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 3.97 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 1.67 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 3.29 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 78.7 years
female: 83.1 years
Real GDP growth rate
2.9% (2023 est.)
2.5% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 17.3% (2024 est.)
services: 79.7% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
11.3% national budget (2021 est.)
Population growth rate
Space program overview
Key space-program milestones
1961-1963 - Project Gemini (longer-duration manned flights in preparation for Moon landings)
1963-1971 - Project Apollo Moon landings (world's first manned landing on the Moon, 1969)
1964 - launched first successful Mars probe (Mariner)
1965-1979 - operated Skylab space station
1977 - began launching Voyager probes to Jupiter, Saturn, and beyond the solar system
1980s-2011 - operated Space Shuttle program (world’s first re-usable space orbiters)
1990 - launched Hubble Space Telescope
1993 - began participating in International Space Station project
2003 - launched surface rover vehicles (Spirit and Opportunity) to Mars
2011 - launched orbital probe (Juno) to Jupiter
2016 - launched OSIRIS-REx mission to retrieve asteroid sample (landed on asteroid Bennu in 2020 and returned with sample in 2023)
2017 - initiated Artemis lunar landing project
2019 - initiated Gateway lunar orbital station project
2021 - launched James Webb Space Telescope (ESA contributed launch vehicle and launch site); surface rover vehicle (Perseverance) with robot helicopter (Ingenuity) successfully landed on surface of Mars
2024 - successfully placed a commercial lander on the Moon and launched probe (Europa Clipper) to study Jupiter's Europa moon
Military service age and obligation
note 1: the US military has been all-volunteer since 1973, but an act of Congress can reinstate the draft in case of a national emergency; males aged 18-25 must register with Selective Service
note 2: all military occupations and positions open to women; women comprised 17.7% of the total US regular military personnel as of 2023
note 3: non-citizens living permanently and legally in the US may join as enlisted personnel; they must have permission to work in the US, a high school diploma, and speak, read, and write English fluently; under the Compact of Free Association, citizens of the Federated States of Micronesia, the Republic of Palau, and the Republic of the Marshall Islands may volunteer
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 26.8 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 29.2 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 3.4 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 167,543,554
female: 170,472,705
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 113 (2024 est.)
































































































