Samoa - WS - WSM - SAM - Australia and Oceania
Last updated: January 21, 2026
Samoa Images
Samoa Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: the US Ambassador to New Zealand is accredited to Samoa
embassy: 5th Floor, Accident Corporation Building, Matafele Apia
mailing address: 4400 Apia Place, Washington DC 20521-4400
telephone: [685] 21-436
FAX: [685] 22-030
email address and website:
ApiaConsular@state.gov
https://ws.usembassy.gov/
embassy: 5th Floor, Accident Corporation Building, Matafele Apia
mailing address: 4400 Apia Place, Washington DC 20521-4400
telephone: [685] 21-436
FAX: [685] 22-030
email address and website:
ApiaConsular@state.gov
https://ws.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
0-14 years: 26.9% (male 28,952/female 27,173)
15-64 years: 65.9% (male 70,225/female 67,427)
65 years and over: 7.2% (2024 est.) (male 6,743/female 8,333)
15-64 years: 65.9% (male 70,225/female 67,427)
65 years and over: 7.2% (2024 est.) (male 6,743/female 8,333)
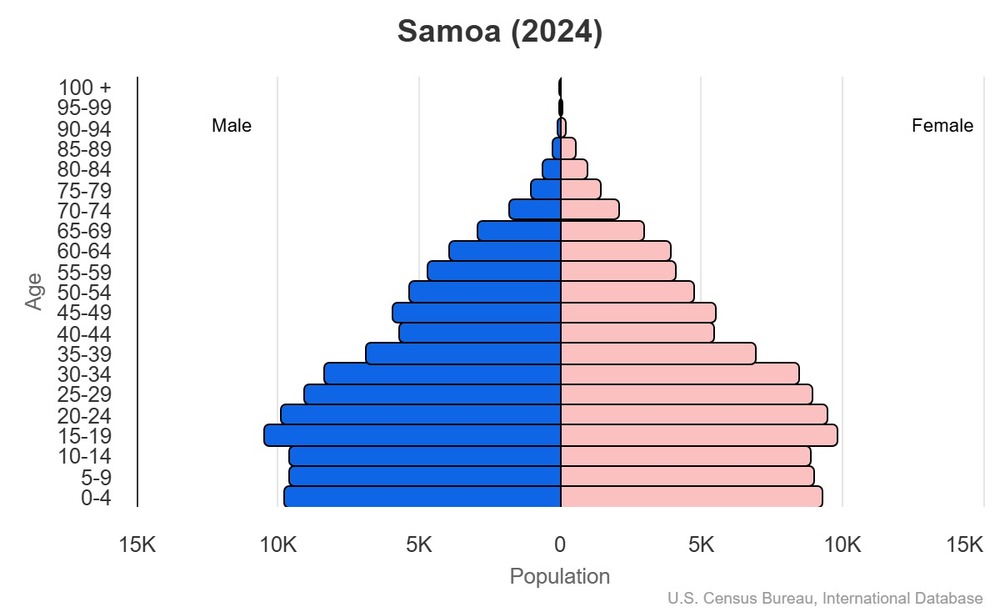
This is the population pyramid for Samoa. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
13 35 S, 172 20 W
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.07 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 1.03 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
occasional cyclones; active volcanism
volcanism: Savai'I Island (1,858 m) is historically active
volcanism: Savai'I Island (1,858 m) is historically active
Area - comparative
slightly smaller than Rhode Island
Background
The first Austronesian settlers arrived in Samoa around 1000 B.C., and early Samoans traded and intermarried with Fijian and Tongan nobility. The fa’amatai system of titles and nobility developed, which dominates Samoan politics to this day; all but two seats in the legislature are reserved for matai, or heads of families. A Dutch explorer was the first European to spot the islands in 1722. Christian missionaries arrived in the 1830s and were followed by an influx of American and European settlers and influence. By the 1880s, Germany, the UK, and the US had trading posts and claimed parts of the kingdom. In 1886, an eight-year civil war broke out, with rival matai factions fighting over royal succession and the three foreign powers providing support to the factions. Germany, the UK, and the US all sent warships to Apia in 1889 and came close to conflict, but a cyclone damaged or destroyed the ships of all three navies.
At the end of the civil war in 1894, Malietoa LAUPEPA was installed as king, but upon his death in 1898, a second civil war over succession broke out. When the war ended in 1899, the Western powers abolished the monarchy, giving the western Samoan islands to Germany and the eastern Samoan islands to the US. The UK abandoned claims in Samoa and received former German territory in the Solomon Islands.
New Zealand occupied Samoa during World War I but was accused of negligence and opposed by many Samoans, particularly an organized political movement called the Mau (“Strongly Held View”) that advocated for independence. During the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic, about 20% of the population died. In 1929, New Zealand police shot into a crowd of peaceful Mau protestors, killing 11, in an event known as Black Sunday. In 1962, Samoa became the first Polynesian nation to reestablish its independence as Western Samoa but dropped the “Western” from its name in 1997. The Human Rights Protection Party dominated politics from 1982 until Prime Minister FIAME Naomi Mata'afa's Fa'atuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi (FAST) party gained a majority in elections in 2021.
At the end of the civil war in 1894, Malietoa LAUPEPA was installed as king, but upon his death in 1898, a second civil war over succession broke out. When the war ended in 1899, the Western powers abolished the monarchy, giving the western Samoan islands to Germany and the eastern Samoan islands to the US. The UK abandoned claims in Samoa and received former German territory in the Solomon Islands.
New Zealand occupied Samoa during World War I but was accused of negligence and opposed by many Samoans, particularly an organized political movement called the Mau (“Strongly Held View”) that advocated for independence. During the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic, about 20% of the population died. In 1929, New Zealand police shot into a crowd of peaceful Mau protestors, killing 11, in an event known as Black Sunday. In 1962, Samoa became the first Polynesian nation to reestablish its independence as Western Samoa but dropped the “Western” from its name in 1997. The Human Rights Protection Party dominated politics from 1982 until Prime Minister FIAME Naomi Mata'afa's Fa'atuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi (FAST) party gained a majority in elections in 2021.
Environmental issues
soil erosion; deforestation; invasive species; overfishing
International environmental agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Population below poverty line
21.9% (2018 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Exports - commodities
refined petroleum, integrated circuits, coconut oil, fish, insulated wire (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
India 26%, NZ 14%, USA 12%, American Samoa 10%, Australia 9% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
11 districts; A'ana, Aiga-i-le-Tai, Atua, Fa'asaleleaga, Gaga'emauga, Gagaifomauga, Palauli, Satupa'itea, Tuamasaga, Va'a-o-Fonoti, Vaisigano
Agricultural products
coconuts, bananas, taro, tropical fruits, pineapples, mangoes/guavas, papayas, root vegetables, milk, avocados (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
no regular military forces; Samoa Police Service (includes a maritime unit) (2025)
Budget
revenues: $371.764 million (2023 est.)
expenditures: $326.052 million (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
expenditures: $326.052 million (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
name: Apia
geographic coordinates: 13 49 S, 171 46 W
time difference: UTC+13 (18 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
geographic coordinates: 13 49 S, 171 46 W
time difference: UTC+13 (18 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, poultry, cars, plastic products, milk (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
tropical; rainy season (November to April), dry season (May to October)
Coastline
403 km
Constitution
history: several previous (pre-independence); latest 1 January 1962
amendment process: proposed as an act by the Legislative Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly membership in the third reading, provided at least 90 days have elapsed since the second reading, and assent of the chief of state; passage of amendments affecting constitutional articles on customary land or constitutional amendment procedures also requires at least two-thirds majority approval in a referendum
amendment process: proposed as an act by the Legislative Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly membership in the third reading, provided at least 90 days have elapsed since the second reading, and assent of the chief of state; passage of amendments affecting constitutional articles on customary land or constitutional amendment procedures also requires at least two-thirds majority approval in a referendum
Exchange rates
tala (SAT) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
2.754 (2024 est.)
2.738 (2023 est.)
2.689 (2022 est.)
2.556 (2021 est.)
2.665 (2020 est.)
Exchange rates:
2.754 (2024 est.)
2.738 (2023 est.)
2.689 (2022 est.)
2.556 (2021 est.)
2.665 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: TUIMALEALI'IFANO Va’aletoa Sualauvi II (since 21 July 2017)
head of government: Prime Minister LA'AULIALEMALIETOA La'auli Leuatea Schmidt (since 16 September 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the chief of state on the advice of the prime minister
election/appointment process: chief of state indirectly elected by the Legislative Assembly to serve a 5-year term (2-term limit); following legislative elections, the chief of state usually appoints the leader of the majority party as prime minister, with the approval of the Legislative Assembly
most recent election date: 23 August 2022
election results: TUIMALEALI'IFANO Va’aletoa Sualauvi II (independent) unanimously reelected by the Legislative Assembly
expected date of next election: 2026
head of government: Prime Minister LA'AULIALEMALIETOA La'auli Leuatea Schmidt (since 16 September 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the chief of state on the advice of the prime minister
election/appointment process: chief of state indirectly elected by the Legislative Assembly to serve a 5-year term (2-term limit); following legislative elections, the chief of state usually appoints the leader of the majority party as prime minister, with the approval of the Legislative Assembly
most recent election date: 23 August 2022
election results: TUIMALEALI'IFANO Va’aletoa Sualauvi II (independent) unanimously reelected by the Legislative Assembly
expected date of next election: 2026
Flag
description: red with a blue rectangle in the upper-left quadrant; on the rectangle are five five-pointed white stars that represent the Southern Cross constellation
meaning: red stands for courage, blue for freedom, and white for purity
note: similar to the flag of Taiwan
meaning: red stands for courage, blue for freedom, and white for purity
note: similar to the flag of Taiwan
Independence
1 January 1962 (from New Zealand-administered UN trusteeship)
Industries
food processing, building materials, auto parts
Judicial branch
highest court(s): Court of Appeal (consists of the chief justice and 2 Supreme Court judges and meets once or twice a year); Supreme Court (consists of the chief justice and several judges)
judge selection and term of office: chief justice appointed by the chief of state on the advice of the prime minister; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the Judicial Service Commission, a 3-member body chaired by the chief justice and includes the attorney general and an appointee of the Minister of Justice; judges normally serve until retirement at age 68
subordinate courts: District Court; Magistrates' Courts; Land and Titles Courts; village chief councils
judge selection and term of office: chief justice appointed by the chief of state on the advice of the prime minister; other Supreme Court judges appointed by the Judicial Service Commission, a 3-member body chaired by the chief justice and includes the attorney general and an appointee of the Minister of Justice; judges normally serve until retirement at age 68
subordinate courts: District Court; Magistrates' Courts; Land and Titles Courts; village chief councils
Land boundaries
total: 0 km
Land use
agricultural land: 17.6% (2023 est.)
arable land: 3.9% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 11.4% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 2.3% (2023 est.)
forest: 57.8% (2023 est.)
other: 24.6% (2023 est.)
arable land: 3.9% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 11.4% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 2.3% (2023 est.)
forest: 57.8% (2023 est.)
other: 24.6% (2023 est.)
Legal system
mixed system of English common law and customary law; judicial review of legislative acts involving fundamental citizen rights
Legislative branch
legislature name: Legislative Assembly (Fono)
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 51 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/29/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Faatuatua ile Atua Samoa ua Tasi (FAST) (32); Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP) (22), Sāmoa Uniting Party (SUP) (3), Independents (4)
percentage of women in chamber: 9.8%
expected date of next election: August 2030
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 51 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 8/29/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Faatuatua ile Atua Samoa ua Tasi (FAST) (32); Human Rights Protection Party (HRPP) (22), Sāmoa Uniting Party (SUP) (3), Independents (4)
percentage of women in chamber: 9.8%
expected date of next election: August 2030
Literacy
total population: 98% (2019 est.)
male: 98.3% (2019 est.)
female: 97.7% (2019 est.)
male: 98.3% (2019 est.)
female: 97.7% (2019 est.)
Maritime claims
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
International organization participation
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Independence Day Celebration, 1 June (1962)
note: 1 January 1962 is the date of independence from the New Zealand-administered UN trusteeship, but it is observed in June
note: 1 January 1962 is the date of independence from the New Zealand-administered UN trusteeship, but it is observed in June
Nationality
noun: Samoan(s)
adjective: Samoan
adjective: Samoan
Natural resources
hardwood forests, fish, hydropower
Geography - note
occupies an almost central position within Polynesia
Economic overview
ower middle-income Pacific island economy; enormous fishing and agriculture industries; significant remittances; growing offshore financial hub; recently hosted Pacific Games to drive tourism and infrastructure growth
Political parties
Fa'atuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi or FAST
Human Rights Protection Party or HRPP
Sāmoa Uniting Party (SUP)
Tautua Samoa Party or TSP
Human Rights Protection Party or HRPP
Sāmoa Uniting Party (SUP)
Tautua Samoa Party or TSP
Suffrage
21 years of age; universal
Terrain
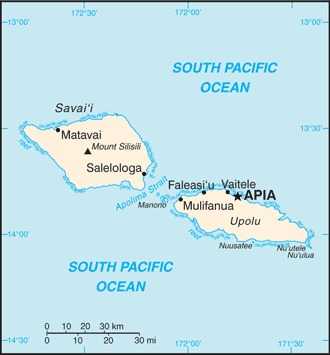
two main islands (Savaii, Upolu) and several smaller islands and uninhabited islets; narrow coastal plain with volcanic, rugged mountains in interior
Government type
parliamentary republic
Military - note
informal defense ties exist with New Zealand, which pledged to afford assistance to Samoa in the conduct of its international relations under the 1962 Treaty of Friendship; New Zealand naval vessels patrol Samoan waters
Samoa has a "shiprider" agreement with the US, which allows local maritime law enforcement officers to embark on US Coast Guard (USCG) and US Navy (USN) vessels, including to board and search vessels suspected of violating laws or regulations within Somoa's designated exclusive economic zone (EEZ) or on the high seas; "shiprider" agreements also enable USCG personnel and USN vessels with embarked USCG law enforcement personnel to work with host nations to protect critical regional resources (2025)
Samoa has a "shiprider" agreement with the US, which allows local maritime law enforcement officers to embark on US Coast Guard (USCG) and US Navy (USN) vessels, including to board and search vessels suspected of violating laws or regulations within Somoa's designated exclusive economic zone (EEZ) or on the high seas; "shiprider" agreements also enable USCG personnel and USN vessels with embarked USCG law enforcement personnel to work with host nations to protect critical regional resources (2025)
Country name
conventional long form: Independent State of Samoa
conventional short form: Samoa
local long form: Malo Sa'oloto Tuto'atasi o Samoa
local short form: Samoa
former: Western Samoa
etymology: the name's meaning and origin are unclear; some assert that it can mean "place of the moa bird" of Polynesian mythology, or it could be a local chieftain's name
conventional short form: Samoa
local long form: Malo Sa'oloto Tuto'atasi o Samoa
local short form: Samoa
former: Western Samoa
etymology: the name's meaning and origin are unclear; some assert that it can mean "place of the moa bird" of Polynesian mythology, or it could be a local chieftain's name
Location
Oceania, group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Hawaii and New Zealand
Map references
Oceania
Irrigated land
0 sq km (2022)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Pa’olelei LUTERU (since 7 July 2021); note - also Permanent Representative to the UN
chancery: 685 Third Avenue, 44th Street, 11th Floor, Suite 1102, New York, NY 10017
telephone: [1] (212) 599-6196
FAX: [1] (212) 599-0797
email address and website:
samoa@samoanymission.ws
About | Samoa Permanent Mission to the United Nations
consulate(s) general: Pago Pago (American Samoa)
chancery: 685 Third Avenue, 44th Street, 11th Floor, Suite 1102, New York, NY 10017
telephone: [1] (212) 599-6196
FAX: [1] (212) 599-0797
email address and website:
samoa@samoanymission.ws
About | Samoa Permanent Mission to the United Nations
consulate(s) general: Pago Pago (American Samoa)
Internet users
percent of population: 58% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.ws
GDP (official exchange rate)
$1.068 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Urbanization
urban population: 17.5% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: -0.03% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
rate of urbanization: -0.03% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
state-owned TV station privatized in 2008; 4 privately owned TV stations; about a half-dozen privately owned radio stations and one state-owned; TV and radio broadcasts of several stations from American Samoa are available (2019)
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 98.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 99% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 1.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 1% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 98.8% of population (2022 est.)
total: 99% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 1.2% of population (2022 est.)
total: 1% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "O le Fu'a o le Sa'olotoga o Samoa" (The Banner of Freedom)
lyrics/music: Sauni Liga KURESA
history: adopted 1962; also known as "Samoa Tula'i" (Samoa Arise)
lyrics/music: Sauni Liga KURESA
history: adopted 1962; also known as "Samoa Tula'i" (Samoa Arise)
Major urban areas - population
36,000 APIA (capital) (2018)
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
Physician density
0.56 physicians/1,000 population (2021)
National symbol(s)
Southern Cross constellation (five five-pointed stars)
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 80.8% (2024 est.)
government consumption: 18.2% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 30.5% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 2.3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 29.3% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -53.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 18.2% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 30.5% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 2.3% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 29.3% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -53.8% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Samoa
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Samoa
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Population distribution
about three quarters of the population lives on the island of Upolu
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 98.3% (2022 est.)
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 97.9%
electrification - urban areas: 100%
electrification - rural areas: 97.9%
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
5W
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 99.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 98.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 99% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 1.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 1% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 99.7% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 98.9% of population (2022 est.)
total: 99% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0.3% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 1.1% of population (2022 est.)
total: 1% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Samoan 96%, Samoan/New Zealander 2%, other 1.9% (2011 est.)
note: data represent the population by country of citizenship
note: data represent the population by country of citizenship
Religions
Protestant 54.9% (Congregationalist 29%, Methodist 12.4%, Assembly of God 6.8%, Seventh Day Adventist 4.4%, other Protestant 2.3%), Roman Catholic 18.8%, Church of Jesus Christ 16.9%, Worship Centre 2.8%, other Christian 3.6%, other 2.9% (includes Baha'i, Muslim), none 0.2% (2016 est.)
Languages
Samoan (Polynesian) (official) 91.1%, Samoan/English 6.7%, English (official) 0.5%, other 0.2%, unspecified 1.6% (2006 est.)
Imports - partners
NZ 20%, Singapore 19%, China 17%, Australia 10%, Fiji 9% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Elevation
highest point: Mount Silisili 1,857 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
Health expenditure
6.8% of GDP (2021)
15.2% of national budget (2022 est.)
15.2% of national budget (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 27,400 tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 57.6% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 57.6% (2022 est.)
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 0.9% (2020)
women married by age 18: 7.4% (2020)
men married by age 18: 2% (2020)
women married by age 18: 7.4% (2020)
men married by age 18: 2% (2020)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 59.7% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 15.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 18.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 6.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 15.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 18.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 6.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 2,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.12 (2025 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
62% (2020 est.)
Remittances
26.4% of GDP (2024 est.)
28.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
33.6% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
28.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
33.6% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Ports
total ports: 1 (2024)
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 0
very small: 1
ports with oil terminals: 1
key ports: Apia
large: 0
medium: 0
small: 0
very small: 1
ports with oil terminals: 1
key ports: Apia
National color(s)
red, white, blue
Particulate matter emissions
7.8 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Labor force
57,200 (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 11.9% (2024 est.)
male: 7.4% (2024 est.)
female: 20.9% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 7.4% (2024 est.)
female: 20.9% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
-6.57 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 27.8 years (2025 est.)
male: 27 years
female: 27.8 years
male: 27 years
female: 27.8 years
Debt - external
$269.974 million (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
101 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$507.74 million (2024 est.)
$447.09 million (2023 est.)
$321.163 million (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$447.09 million (2023 est.)
$321.163 million (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Total fertility rate
2.29 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Unemployment rate
4.6% (2024 est.)
5% (2023 est.)
5.1% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
5% (2023 est.)
5.1% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
335,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 335,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 335,000 metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 2,831 sq km
land: 2,821 sq km
water: 10 sq km
land: 2,821 sq km
water: 10 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
26.7% (of GDP) (2023 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$1.503 billion (2024 est.)
$1.374 billion (2023 est.)
$1.258 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$1.374 billion (2023 est.)
$1.258 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
4 (2025)
Infant mortality rate
total: 17.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 20.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 13.6 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 20.9 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 13.6 deaths/1,000 live births
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
2.2% (2024 est.)
7.9% (2023 est.)
11% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
7.9% (2023 est.)
11% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$64.616 million (2024 est.)
$40.177 million (2023 est.)
-$74.039 million (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
$40.177 million (2023 est.)
-$74.039 million (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$6,900 (2024 est.)
$6,300 (2023 est.)
$5,800 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$6,300 (2023 est.)
$5,800 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 2,000 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (2022 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 20.5% (2025 est.)
male: 28.6% (2025 est.)
female: 12.3% (2025 est.)
male: 28.6% (2025 est.)
female: 12.3% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
47.3% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
23.476 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Death rate
5.41 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
18.53 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 54,000 kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 141.846 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 17.284 million kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 141.846 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 17.284 million kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 13 (2023)
by type: general cargo 3, oil tanker 1, other 9
by type: general cargo 3, oil tanker 1, other 9
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
3.4% (2019 est.)
Imports
$575.749 million (2024 est.)
$560.776 million (2023 est.)
$512.021 million (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$560.776 million (2023 est.)
$512.021 million (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$369.73 million (2024 est.)
$346.187 million (2023 est.)
$175.377 million (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$346.187 million (2023 est.)
$175.377 million (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 2.18 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.17 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 2.01 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 0.17 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 75.7 years (2024 est.)
male: 72.8 years
female: 78.7 years
male: 72.8 years
female: 78.7 years
Real GDP growth rate
9.4% (2024 est.)
9.2% (2023 est.)
-5.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
9.2% (2023 est.)
-5.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
4.2% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 11% (2024 est.)
industry: 10.9% (2024 est.)
services: 72.5% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 10.9% (2024 est.)
services: 72.5% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
5.5% of GDP (2024 est.)
11.7% national budget (2025 est.)
11.7% national budget (2025 est.)
Population growth rate
0.66% (2025 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 51.6 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 40.2 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 11.4 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.8 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 40.2 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 11.4 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.8 (2025 est.)
Population
total: 210,223 (2025 est.)
male: 106,542
female: 103,681
male: 106,542
female: 103,681
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 134,000 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 62 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 62 (2022 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 4,570 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2022 est.)