Kosovo - XK - UNK - KOS - Europe

Kosovo Images
Kosovo Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: Arberia/Dragodan, Rr. 4 KORRIKU Nr. 25, Pristina
mailing address: 9520 Pristina Place, Washington DC 20521-9520
telephone: [383] 38-59-59-3000
FAX: [383] 38-604-890
email address and website:
PristinaACS@state.gov
https://xk.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
15-64 years: 68.9% (male 712,403/female 649,932)
65 years and over: 8.4% (2024 est.) (male 72,579/female 92,865)
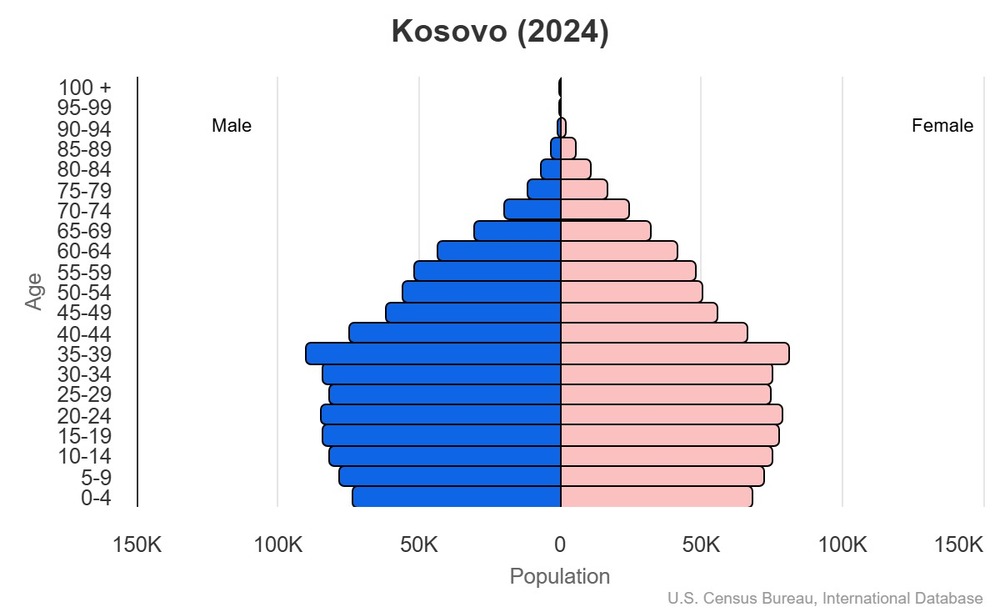
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.08 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.1 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.78 male(s)/female
total population: 1.06 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Area - comparative
slightly larger than Delaware
Background
The Ottoman Empire took control of Kosovo in 1389 after defeating Serbian forces. Large numbers of Turks and Albanians moved to the region, and by the end of the 19th century, Albanians had replaced Serbs as the majority ethnic group in Kosovo. Serbia reacquired control of Kosovo during the First Balkan War of 1912, and after World War II, Kosovo became an autonomous province of Serbia in the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY). Increasing Albanian nationalism in the 1980s led to riots and calls for Kosovo's independence, but in 1989, Belgrade -- which has in turn served as the capital of Serbia and Yugoslavia -- revoked Kosovo's autonomous status. When the SFRY broke up in 1991, Kosovo Albanian leaders organized an independence referendum, and Belgrade's repressive response led to an insurgency. Kosovo remained part of Serbia, which joined with Montenegro to declare a new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) in 1992.
In 1998, Belgrade launched a brutal counterinsurgency campaign, with some 800,000 ethnic Albanians expelled from their homes in Kosovo. After international mediation failed, a NATO military operation began in March 1999 and forced Belgrade to withdraw its forces from Kosovo. UN Security Council Resolution 1244 (1999) placed Kosovo under the temporary control of the UN Interim Administration Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK). Negotiations in 2006-07 ended without agreement between Serbia and Kosovo, though the UN issued a comprehensive report that endorsed independence. On 17 February 2008, the Kosovo Assembly declared Kosovo independent.
Serbia continues to reject Kosovo's independence, but the two countries began EU-facilitated discussions in 2013 to normalize relations, which resulted in several agreements. Additional agreements were reached in 2015 and 2023, but implementation remains incomplete. In 2022, Kosovo formally applied for membership in the EU, which is contingent on fulfillment of accession criteria, and the Council of Europe. Kosovo is also seeking UN and NATO memberships.
Environmental issues
Military expenditures
1.3% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.1% of GDP (2021 est.)
1% of GDP (2020 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 32.9% (2021 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
Administrative divisions
Agricultural products
Military and security forces
note: the Kosovo Police are under the Ministry of Internal Affairs
Budget
expenditures: $2.547 billion (2020 est.)
Capital
geographic coordinates: 42 40 N, 21 10 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the town takes its name from the river; the origin of the river's name is unclear but could come from a pre-Slavic language
Imports - commodities
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by the government, by the president of the republic, or by one fourth of Assembly deputies; passage requires two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly, including two-thirds majority vote of deputies representing non-majority communities, followed by a favorable Constitutional Court assessment
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
0.924 (2024 est.)
0.925 (2023 est.)
0.951 (2022 est.)
0.845 (2021 est.)
0.877 (2020 est.)
note: Kosovo, which is neither an EU member state nor a party to a formal EU monetary agreement, uses the euro as its de facto currency
Executive branch
head of government: Acting Prime Minister Albin KURTI (since 15 April 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet elected by the Assembly
election/appointment process: president indirectly elected for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term) by at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly; if a candidate does not reach this threshold in the first two ballots, the candidate winning a simple majority vote in the third ballot is elected; prime minister indirectly elected by the Assembly
most recent election date: 3-4 April 2021
election results:
2021: Vjosa OSMANI-Sadriu elected president in third ballot; Assembly vote - Vjosa OSMANI-Sadriu (Guxo!) 71 votes; Albin KURTI (LVV) elected prime minister; Assembly vote - 67 for, 30 against
2017: Ramush HARADINAJ (AAK) elected prime minister; Assembly vote - 61 for, 1 abstention, 0 against (opposition boycott)
2016: Hashim THACI elected president in third ballot; Assembly vote - Hashim THACI (PDK) 71 votes
expected date of next election: 2026
note: Prime Minister Albin KURTI resigned on 15 April 2025; a replacement has not yet been selected
Flag
meaning: each star represents one of the major ethnic groups of Kosovo: Albanians, Serbs, Turks, Gorani, Roma, and Bosniaks
note: one of two national flags that uses a map as a design element; the flag of Cyprus is the other
Independence
Industries
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges nominated by the Kosovo Judicial Council, a 13-member independent body staffed by judges and lay members, and also responsible for overall administration of Kosovo's judicial system; judges appointed by the president of the Republic of Kosovo; judges appointed until mandatory retirement age; Constitutional Court judges nominated by the Kosovo Assembly and appointed by the president of the republic to serve single, 9-year terms
subordinate courts: Court of Appeals (organized into 4 departments: General, Serious Crime, Commercial Matters, and Administrative Matters); Basic Court (located in 7 municipalities, each with several branches)
note: in 2015, the Kosovo Assembly approved a constitutional amendment that established the Kosovo Relocated Specialist Judicial Institution, also referred to as the Kosovo Specialist Chambers or "Special Court"; the court, located at the Hague in the Netherlands, began operating in 2016 and has jurisdiction to try crimes against humanity, war crimes, and other crimes under Kosovo law that occurred in the 1998-2000 period
Land boundaries
border countries (4): Albania 112 km; North Macedonia 160 km; Montenegro 76 km; Serbia 366 km
Land use
arable land: 27.4% (2018 est.)
permanent crops: 1.9% (2018 est.)
permanent pasture: 23.5% (2018 est.)
forest: 41.7% (2018 est.)
other: 5.5% (2018 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 120 (all directly elected)
electoral system: proportional representation
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 4 years
most recent election date: 2/14/2021
parties elected and seats per party: Self-Determination Movement (LVV) (58), Democratic Party of Kosovo (PDK) (19), Democratic League of Kosovo (LDK) (15), Serb List (10), Alliance for the Future of Kosovo (AAK) (8), other (10)
percentage of women in chamber: 34%
expected date of next election: 2025
note: 20 seats reserved for ethnic minorities -- 10 for Serbs and 10 for other minorities
Maritime claims
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: Kosovan
note: Kosovo, a neutral term, is sometimes also used as a noun or adjective as in Kosovo Albanian, Kosovo Serb, Kosovo minority, or Kosovo citizen
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
Political parties
Ashkali Party for Integration or PAI
Civic Initiative for Freedom, Justice, and Survival
Democratic League of Kosovo or LDK
Democratic Party of Kosovo or PDK
New Democratic Initiative of Kosovo or IRDK
New Democratic Party or NDS
Progressive Movement of Kosovar Roma or LPRK
Romani Initiative
Self-Determination Movement (Lëvizja Vetevendosje or Vetevendosie) or LVV or VV
Serb List or SL
Social Democratic Union or SDU
Turkish Democratic Party of Kosovo or KDTP
Unique Gorani Party or JGP
Vakat Coalition or VAKAT
Railways
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Kosovo
local long form: Republika e Kosoves (Albanian)/ Republika Kosovo (Serbian)
local short form: Kosove (Albanian)/ Kosovo (Serbian)
etymology: name may derive from the Serbian word kos, meaning "blackbird," or from a personal name
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 3612 Massachusetts Ave NW, Washington, D.C. 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 450-2130
FAX: [1] (202) 735-0609
email address and website:
embassy.usa@rks-gov.net
U.S. Embassies of the Republic of Kosovo (ambasadat.net)
consulate(s) general: New York
consulate(s): Des Moines (IA)
Internet country code
note: assigned as a temporary code under UN Security Council resolution 1244/99
Refugees and internally displaced persons
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: no lyrics/Mendi MENGJIQI
history: adopted 2008; Kosovo chose not to include lyrics in its anthem to avoid offending the country's minority ethnic groups
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
National symbol(s)
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 12.3% (2024 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 33.8% (2024 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2024 est.)
exports of goods and services: 41.9% (2024 est.)
imports of goods and services: -72.3% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Kosovo
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years
Population distribution
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Ethnic groups
note: these estimates may under-represent Serb, Romani, and some other ethnic minorities because they are based on the 2011 Kosovo national census, which excluded northern Kosovo (a largely Serb-inhabited region) and was partially boycotted by Serb and Romani communities in southern Kosovo
Religions
note: these estimates may under-represent Serb, Romani, and some other ethnic minorities because they are based on the 2011 Kosovo national census, which excluded northern Kosovo (a largely Serb-inhabited region) and was partially boycotted by Serb and Romani communities in southern Kosovo
Languages
major-language sample(s): Libri i fakteve boterore, burimi i pazevendesueshem per informacione elementare (Albanian)
Knjiga svetskih činjenica, neophodan izvor osnovnih informacija. (Serbian)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
note: these estimates may under-represent Serb, Romani, and other ethnic minority languages because they are based on the 2011 Kosovo national census, which excluded northern Kosovo (a largely Serb-inhabited region) and was partially boycotted by Serb and Romani communities in southern Kosovo
Imports - partners
Elevation
lowest point: Drini i Bardhe/Beli Drim (located on the border with Albania) 297 m
mean elevation: 450 m
Physician density
Military service age and obligation
(2024)
Military - note
in 2019, Kosovo approved legislation that began a process to transition the KSF by 2028 into a professional military (the Kosovo Armed Forces) led by a General Staff and comprised of a Land Force, a National Guard, a Logistics Command, and a Doctrine and Training Command; it would have a strength of up to 5,000 with about 3,000 reserves; at the same time, the KSF’s mission was expanded to include traditional military functions, such as territorial defense and international peacekeeping; the KSF’s first international mission was the deployment of a small force to Kuwait in 2021
the NATO-led KFOR has operated in the country as a peace support force since 1999; in addition to assisting in the development of the KSF, KFOR is responsible for providing a safe and secure environment and ensuring freedom of movement for all citizens; as of 2025, it had approximately 4,700 troops from more than 30 countries (2025)
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 33 (2024 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 12.1 (2024 est.)
potential support ratio: 8.2 (2024 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Internet users
Waste and recycling
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Major watersheds (area sq km)
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales: Medieval Monuments in Kosovo
Coal
consumption: 6.931 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 13,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 20,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 1.564 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
solar: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 6.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 6.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Petroleum
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
17.2% of GDP (2022 est.)
18% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
National color(s)
National coat of arms

Labor force
note: includes those estimated to be employed in the gray economy
Debt - external
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$1.245 billion (2023 est.)
$1.248 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Population
male: 1,017,992
female: 959,101
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 5.005 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 2.439 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 10,887 sq km
water: 0 sq km
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$23.962 billion (2023 est.)
$23.025 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 98 (2022 est.)
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
4.9% (2023 est.)
11.6% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
-$983.283 million (2022 est.)
-$818.351 million (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$14,200 (2023 est.)
$13,000 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Energy consumption per capita
Electricity
consumption: 6.571 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 2.442 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 3.449 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 789.167 million kWh (2023 est.)
Imports
$6.661 billion (2022 est.)
$6.128 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$3.579 billion (2022 est.)
$3.138 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 7 (2022 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 71 years
female: 75.5 years
Real GDP growth rate
4.1% (2023 est.)
4.3% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 26.2% (2024 est.)
services: 45.7% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Gross reproduction rate
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 31.7 years
female: 32.4 years
Total fertility rate
Infant mortality rate
male: 24.2 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 21.5 deaths/1,000 live births