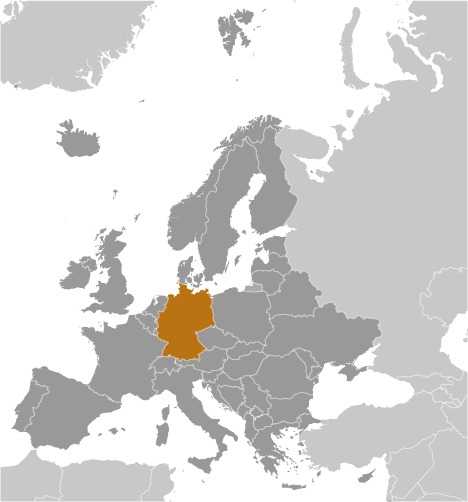
Germany - DE - DEU - GER - Europe

Germany Images
Germany Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
embassy: Pariser Platz 2, 10117 Berlin
Clayallee 170, 14191 Berlin (administrative services)
mailing address: 5090 Berlin Place, Washington DC 20521-5090
telephone: [49] (30) 8305-0
FAX: [49] (30) 8305-1215
email address and website:
BerlinPCO@state.gov
https://de.usembassy.gov/
consulate(s) general: Dusseldorf, Frankfurt am Main, Hamburg, Leipzig, Munich
Age structure
15-64 years: 62.5% (male 26,705,657/female 25,875,865)
65 years and over: 23.7% (2024 est.) (male 8,941,245/female 10,981,930)
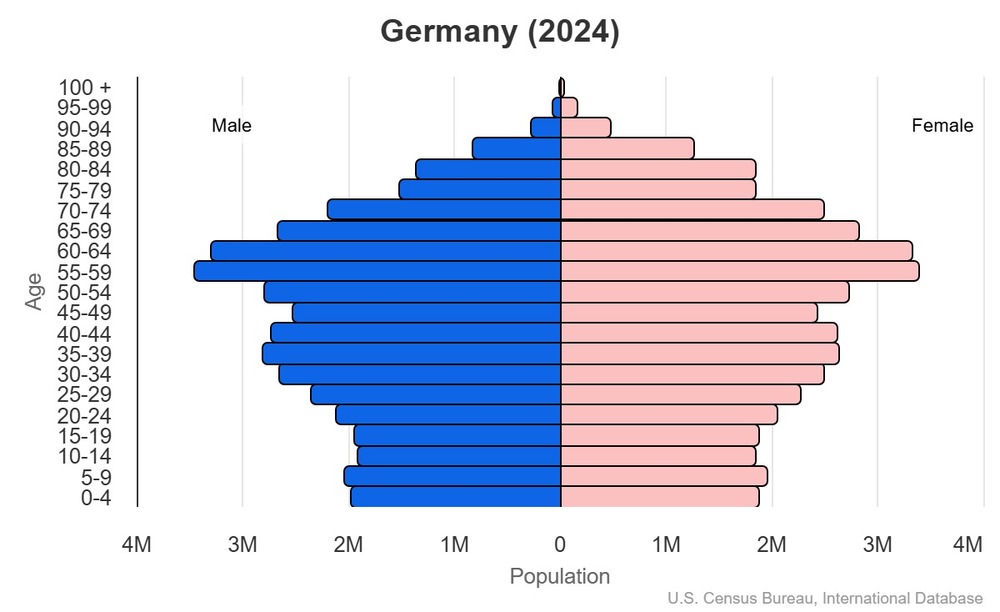
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
Sex ratio
0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.81 male(s)/female
total population: 0.98 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
Area - comparative
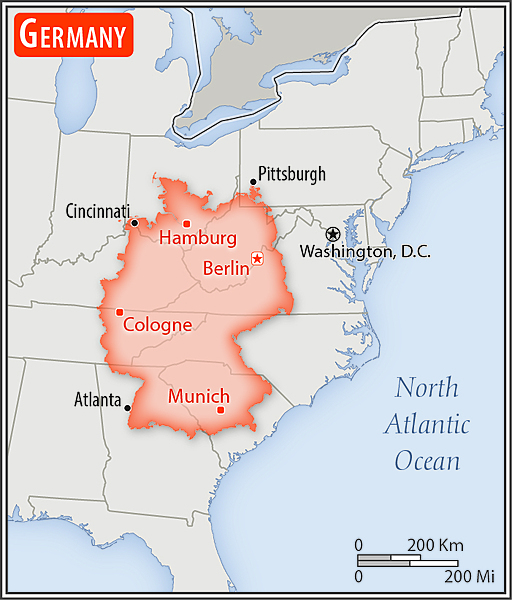
three times the size of Pennsylvania; slightly smaller than Montana
Military service age and obligation
note 1: conscription ended in 2011; in 2020, the German Government launched a new voluntary conscript initiative focused on homeland security tasks, with the volunteers serving for 7 months plus 5 months as reservists over a 6-year period
note 2: in December 2025, Germany passed a law reforming military service; from 2026, the new regulations require German males residing in Germany who have reached the age of 18 to complete a questionnaire, including questions about their willingness to serve; participation will remain voluntary for women
note 3: women have been eligible for voluntary service in all military branches and positions since 2001; in 2025, they accounted for more than 13% of the active-duty German military
Background
Environmental issues
International environmental agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
2% of GDP (2024 est.)
1.6% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.4% of GDP (2021 est.)
Population below poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
highest 10%: 25% (2020 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
note: Bayern, Sachsen, and Thueringen refer to themselves as free states (Freistaaten, singular - Freistaat), while Bremen calls itself a Free Hanseatic City (Freie Hansestadt) and Hamburg considers itself a Free and Hanseatic City (Freie und Hansestadt)
Agricultural products
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
note: responsibility for internal and border security is shared by the police forces of the 16 states, the Federal Criminal Police Office, and the Federal Police; the states’ police forces report to their respective interior ministries while the Federal Police forces report to the Federal Ministry of the Interior
Budget
expenditures: $1.369 trillion (2023 est.)
note: central government revenues (excluding grants) and expenditures converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
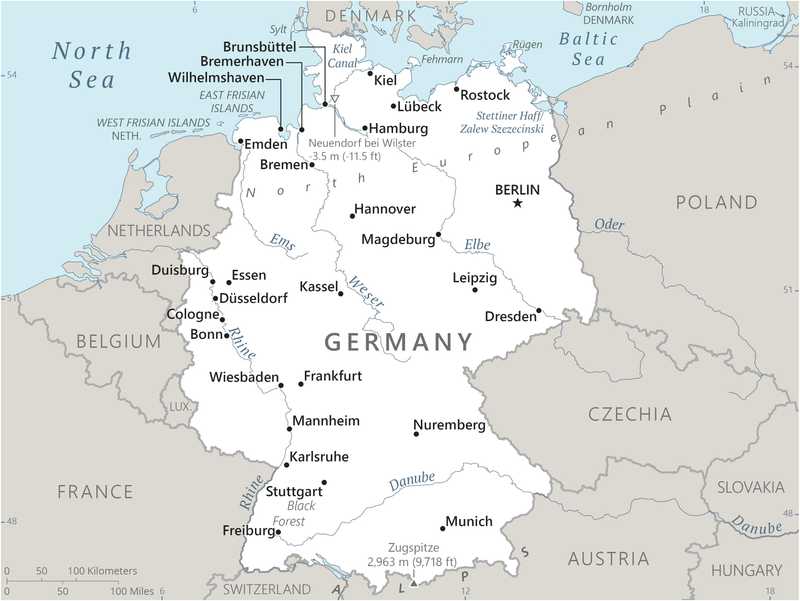
Capital
geographic coordinates: 52 31 N, 13 24 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October
etymology: the origin of the name is unclear but may be related to the Old Slavic (Polabian) word berl or birl, meaning "swamp" and referring to the original settlement site by the Spree River
Imports - commodities
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
Coastline
Constitution
amendment process: proposed by Parliament; passage and enactment into law require two-thirds majority vote by both the Bundesrat (upper house) and the Bundestag (lower house) of Parliament; articles including those on basic human rights and freedoms cannot be amended
Exchange rates
Exchange rates:
0.924 (2024 est.)
0.925 (2023 est.)
0.95 (2022 est.)
0.845 (2021 est.)
0.876 (2020 est.)
Executive branch
head of government: Chancellor Friedrich MERZ (since 6 May 2025)
cabinet: Cabinet or Bundesminister (Federal Ministers) recommended by the chancellor, appointed by the president
election/appointment process: president indirectly elected by a Federal Convention consisting of all members of the Federal Parliament (Bundestag) and an equivalent number of delegates indirectly elected by the state parliaments; president serves a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); following the most recent Federal Parliament election, the party or coalition with the most representatives usually elects the chancellor, who is appointed by the president to serve a renewable 4-year term
most recent election date: president: 13 February 2022
chancellor: 6 May 2025
election results:
2025: Friedrich MERZ (CDU) elected chancellor in second round; Federal Parliament vote - 325 to 289
2022: Frank-Walter STEINMEIER reelected president; Federal Convention vote count - Frank-Walter STEINMEIER (SPD) 1,045, Max OTTE (CDU) 140, Gerhard TRABERT (The Left) 96, Stefanie GEBAUER (Free Voters) 58, abstentions 86
expected date of next election: president: February 2027
Flag
history: the colors can be traced back to the medieval banner of the Holy Roman Emperor -- a black eagle with red claws and beak on a gold field
Illicit drugs
major precursor-chemical producer (2025)
Independence
Industries
iron, steel, coal, cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, automobiles, food and beverages, shipbuilding, textiles
Judicial branch
judge selection and term of office: Federal Court of Justice judges selected by the Judges Election Committee, which consists of the Secretaries of Justice from each of the 16 federated states and 16 members appointed by the Federal Parliament; judges appointed by the president; judges serve until mandatory retirement at age 65; half of Federal Constitutional Court judges are elected by the House of Representatives and half by the Senate; judges appointed for 12-year terms with mandatory retirement at age 68
subordinate courts: Federal Administrative Court; Federal Finance Court; Federal Labor Court; Federal Social Court; each of the 16 federated states or Land has its own constitutional court and a hierarchy of ordinary (civil, criminal, family) and specialized (administrative, finance, labor, social) courts; two English-speaking commercial courts opened in 2020 in the state of Baden-Wuerttemberg -- the Stuttgart Commercial Court and the Mannheim Commercial Court
Land boundaries
border countries (9): Austria 801 km; Belgium 133 km; Czechia 704 km; Denmark 140 km; France 418 km; Luxembourg 128 km; Netherlands 575 km; Poland 447 km; Switzerland 348 km
Land use
arable land: 33.4% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 0.6% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 13.5% (2023 est.)
forest: 32.8% (2023 est.)
other: 15% (2023 est.)
Legal system
Legislative branch
note: due to Germany's recognition of the concepts of "overhang" (when a party's share of the nationwide votes would entitle it to fewer seats than the number of individual constituency seats won in an election under Germany's mixed member proportional system) and "leveling" (whereby additional seats are elected to supplement the members directly elected by each constituency in order to ensure that each party's share of the total seats is roughly proportional to the party's overall shares of votes at the national level), the 20th Bundestag is the largest to date
Maritime claims
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200-m depth or to the depth of exploitation
International organization participation
National holiday
Nationality
adjective: German
Natural resources
Geography - note
Economic overview
leading export-driven, core EU and eurozone economy; key automotive, chemical, engineering, finance, and green energy industries; growth stalled by energy crisis and declining exports; tight labor market with falling working-age population; fiscal rebalancing with phaseout of energy price supports
Political parties
Alternative for Germany or AfD
Christian Democratic Union or CDU
Christian Social Union or CSU
Free Democratic Party or FDP
Free Voters or FW
The Left or Die Linke
Social Democratic Party or SPD
Railways
15 km 0.900-mm gauge, 24 km 0.750-mm gauge (2015)
Suffrage
Terrain
Government type
Country name
conventional short form: Germany
local long form: Bundesrepublik Deutschland
local short form: Deutschland
former: German Reich
etymology: the origin of the name is unclear; it may come from Celtic words meaning "neighboring people," or it may derive from Germanic words meaning either "spear man" or "head man;" the native designation "Deutsch" comes from the Old High German "diutisc" meaning "national"
Location
Map references
Irrigated land
Diplomatic representation in the US
chancery: 4645 Reservoir Road NW, Washington, DC 20007
telephone: [1] (202) 298-4000
FAX: [1] (202) 298-4261
email address and website:
info@washington.diplo.de
https://www.germany.info/us-en
consulate(s) general: Atlanta, Boston, Chicago, Houston, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, San Francisco
Internet users
Internet country code
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 100 (2023 est.)
stateless persons: 28,813 (2024 est.)
GDP (official exchange rate)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Total renewable water resources
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
male: 17 years (2023 est.)
female: 17 years (2023 est.)
Urbanization
rate of urbanization: 0.13% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
Drinking water source
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 100% of population (2022 est.)
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 0% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
lyrics/music: August Heinrich HOFFMANN VON FALLERSLEBEN/Franz Joseph HAYDN
history: first adopted 1922; the anthem, also known as "Deutschlandlied" (Song of Germany), was originally adopted for its connection to the March 1848 liberal revolution; the Nazis later appropriated the first verse -- specifically the phrase "Deutschland, Deutschland ueber alles" (Germany, Germany above all) -- to promote nationalism, and the anthem was banned after 1945; in 1952, West Germany adopted the third verse as its national anthem; in 1990, it became the national anthem for the reunited Germany
Major urban areas - population
International law organization participation
Physician density
Hospital bed density
National symbol(s)
Mother's mean age at first birth
GDP - composition, by end use
government consumption: 21.2% (2023 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 21.5% (2023 est.)
investment in inventories: 0.2% (2023 est.)
exports of goods and services: 43.4% (2023 est.)
imports of goods and services: -39.4% (2023 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a German citizen or a resident alien who has lived in Germany at least 8 years
dual citizenship recognized: yes, but requires prior permission from government
residency requirement for naturalization: 8 years
Population distribution
Electricity access
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
Sanitation facility access
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 100% of population (2022 est.)
total: 100% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 0% of population (2022 est.)
total: 0% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
note: data represent population by nationality
Religions
Languages
major-language sample(s):
Das World Factbook, die unverzichtbare Quelle für grundlegende Informationen. (German)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Imports - partners
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Military - note
the Bundeswehr was established in 1955; at the height of the Cold War in the 1980s, it had nearly 600,000 personnel, over 7,000 tanks, and 1,000 combat aircraft; in addition, over 400,000 soldiers from other NATO countries—including about 200,000 US military personnel—were stationed in West Germany; in the years following the collapse of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, the Bundeswehr shrank by more than 60% in size (over 90% in tanks and about 80% in aircraft), while funding fell from nearly 3% of GDP and over 4% of government spending in the mid-1980s to 1.2% and 1.6% respectively; by the 2010s, the Bundeswehr’s ability to fulfill its regional security commitments had deteriorated; the Russian annexation of Crimea in 2014 and full-scale assault on Ukraine in 2022 led to renewed emphasis on Germany’s leadership role in European defense and NATO and efforts to boost funding for the Bundeswehr to improve readiness, modernize, and expand (2025)
Elevation
lowest point: Neuendorf bei Wilster -3.5 m
mean elevation: 263 m
Health expenditure
20.5% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
Military deployments
note: the German military also has air and naval contingents deployed to support NATO missions
Terrorist group(s)
note: details about the history, aims, leadership, organization, areas of operation, tactics, targets, weapons, size, and sources of support of the group(s) appear(s) in the Terrorism reference guide
Total water withdrawal
industrial: 14.005 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 1.075 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 49.8% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on alcohol and tobacco: 3.1% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Major lakes (area sq km)
salt water lake(s): Stettiner Haff/Zalew Szczecinski (shared with Poland) - 900 sq km
Major rivers (by length in km)
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
selected World Heritage Site locales:
Museumsinsel (Museum Island), Berlin (c); Palaces and Parks of Potsdam and Berlin (c); Speyer Cathedral (c); Aachen Cathedral (c); Bauhaus and its Sites in Weimar, Dessau, and Bernau (c); Caves and Ice Age Art in the Swabian Jura (c); Roman Monuments, Cathedral of St. Peter, and Church of Our Lady in Trier (c); Hanseatic City of Lübeck (c); Old Town of Regensburg with Stadtamhof (c); Würzburg Residence with the Court Gardens and Residence Square (c); Pilgrimage Church of Wies (c); Castles of Augustusburg and Falkenlust at Brühl (c); St Mary's Cathedral and St Michael's Church at Hildesheim (c); Abbey and Altenmünster of Lorsch (c); Maulbronn Monastery Complex (c); Collegiate Church, Castle and Old Town of Quedlinburg (c); Cologne Cathedral (c); Castle Church in Wittenberg (c); Classical Weimar (c); Wartburg Castle (c); Garden Kingdom of Dessau-Wörlitz (c); Monastic Island of Reichenau (c); Berlin Modernism Housing Estates (c); Prehistoric Pile Dwellings around the Alps (c); Moravian Church Settlements (c); Speicherstadt and Kontorhaus District with Chilehaus (c); The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier, an Outstanding Contribution to the Modern Movement (c); Archaeological Border complex of Hedeby and the Danevirke (c); Naumburg Cathedral (c); Mathildenhöhe Darmstadt (c); ShUM Sites of Speyer, Worms and Mainz (c); The Great Spa Towns of Europe (c); Jewish-Medieval Heritage of Erfurt (c); Schwerin Residence Ensemble (c); The Palaces of King Ludwig II of Bavaria: Neuschwanstein, Linderhof, Schachen and Herrenchiemsee (c); The Palaces of King Ludwig II of Bavaria: Neuschwanstein, Linderhof, Schachen and Herrenchiemsee (c)
Coal
consumption: 140.994 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.68 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 32.933 million metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 35.4 billion metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
nuclear: 1.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 11.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
wind: 25.9% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 3.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 9.4% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Natural gas
consumption: 82.371 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
imports: 74.989 billion cubic meters (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 23.39 billion cubic meters (2021 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 2.062 million bbl/day (2024 est.)
crude oil estimated reserves: 115.2 million barrels (2021 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
Remittances
0.5% of GDP (2023 est.)
0.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Nuclear energy
Number of nuclear reactors permanently shut down: 33 (2025)
Space program overview
Space launch site(s)
Space agency/agencies
note: DLR's predecessor organization, the German Test and Research Institute for Aviation and Space Flight, was established in 1969; the Federal Republic of Germany was allowed to research space flight after gaining sovereignty in 1955
Geoparks
global geoparks and regional networks: Bergstraße-Odenwald ; Harz, Braunschweiger Land; Swabian Alb; TERRA.vita; Vulkaneifel; Thuringia Inselsberg -Drei Gleichen; Muskauer Faltenbogen / Łuk Mużakowa (includes Poland); Ries (2023)
Ports
large: 5
medium: 4
small: 11
very small: 15
ports with oil terminals: 12
key ports: Brake, Bremen, Bremerhaven, Cuxhaven, Emden, Hamburg, Kiel, Lubeck, Rostock
Legislative branch - lower chamber
number of seats: 630 (all directly elected)
electoral system: mixed system
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 4 years
most recent election date: 2/23/2025
parties elected and seats per party: Christian Democratic Union (CDU) (164); Alternative for Germany (AfD) (152); Social Democratic Party (SPD) (120); Green Party (85); Left Party (Die Linke) (64); Christian Social Union of Bavaria (CSU) (44); Other (1)
percentage of women in chamber: 32.4%
expected date of next election: February 2029
note 1: total seats can vary each electoral term; currently includes 4 seats for independent members; approximately one-half of members directly elected in multi-seat constituencies by proportional representation vote and approximately one-half directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote; members' terms vary depending on the states they represent
note 2: the 20th Bundestag is the largest to date, due to Germany's recognition of "overhang" (when a party's share of the nationwide votes would entitle it to fewer seats than the number of individual constituency seats won in an election) and "leveling" (when additional seats are elected to supplement the members directly elected in order to ensure that each party's share of the total seats is roughly proportional to its overall share of votes at the national level)
Legislative branch - upper chamber
number of seats: 69 (all appointed)
parties elected and seats per party: SPD 23; CDU 17; Green Party 15; Left Party 4; CSU 3; FW 3; FDP 2; other 2
percentage of women in chamber: 34.8%
National color(s)
National coat of arms

Particulate matter emissions
Key space-program milestones
1973 - participated with other European states, particularly France and the UK, in development of Ariane satellite launch vehicle
1978 - first German in space on Soviet Salyut space station
1980s-1990s - participated in US Space Shuttle program, including providing astronauts
1999 - launched a space-based X-ray telescope (ABRAXIS) on Russian rocket
2005 - began development of reusable space plane/shuttle/transporter
2019 - launched first space-based X-ray telescope (eROSITA) capable of imaging the entire sky (joint project with Russia)
2023 - signed US-led Artemis Accords for the exploration of space and the Moon; adopted a new national space strategy
Methane emissions
agriculture: 1,197.8 kt (2019-2021 est.)
waste: 459 kt (2019-2021 est.)
other: 110 kt (2019-2021 est.)
Labor force
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
male: 7.4% (2024 est.)
female: 5.9% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
Median age
male: 45.5 years
female: 48.3 years
Maternal mortality ratio
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$322.7 billion (2023 est.)
$293.914 billion (2022 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Public debt
note: general government gross debt is defined in the Maastricht Treaty as consolidated general government gross debt at nominal value, outstanding at the end of the year in the following categories of government liabilities (as defined in ESA95): currency and deposits (AF.2), securities other than shares excluding financial derivatives (AF.3, excluding AF.34), and loans (AF.4); the general government sector comprises the sub-sectors of central government, state government, local government and social security funds; the series are presented as a percentage of GDP and in millions of euros; GDP used as a denominator is the gross domestic product at current market prices; data expressed in national currency are converted into euro using end-of-year exchange rates provided by the European Central Bank
Total fertility rate
Unemployment rate
3.1% (2023 est.)
3.2% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
from coal and metallurgical coke: 163.407 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 277.688 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from consumed natural gas: 159.097 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
land: 348,672 sq km
water: 8,350 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$5.26 trillion (2023 est.)
$5.274 trillion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
Infant mortality rate
male: 3.5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 2.7 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
5.9% (2023 est.)
6.9% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$251.479 billion (2023 est.)
$161.759 billion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$62,700 (2023 est.)
$62,900 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2023 est.)
Tobacco use
male: 19.4% (2025 est.)
female: 15% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
Energy consumption per capita
Death rate
Birth rate
Electricity
consumption: 519.691 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 60.316 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 69.353 billion kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 25.774 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
by type: bulk carrier 1, container ship 69, general cargo 82, oil tanker 32, other 411
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
Imports
$1.781 trillion (2023 est.)
$1.808 trillion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$1.958 trillion (2023 est.)
$1.917 trillion (2022 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Heliports
Alcohol consumption per capita
beer: 5.57 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 3.02 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 1.97 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
male: 79.6 years
female: 84.4 years
Real GDP growth rate
-0.3% (2023 est.)
1.4% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
industry: 25.8% (2024 est.)
services: 63.9% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
10.7% national budget (2022 est.)
Population growth rate
Dependency ratios
youth dependency ratio: 22.4 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 38.9 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 2.6 (2025 est.)
Population
male: 41,517,301
female: 42,494,983
Telephones - mobile cellular
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 129 (2024 est.)
Telephones - fixed lines
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 45 (2024 est.)


























