Laos - LA - LAO - LAO - East and Southeast Asia
Last updated: January 21, 2026

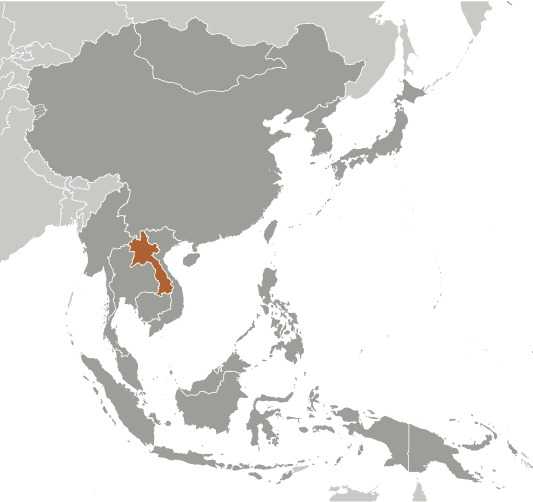
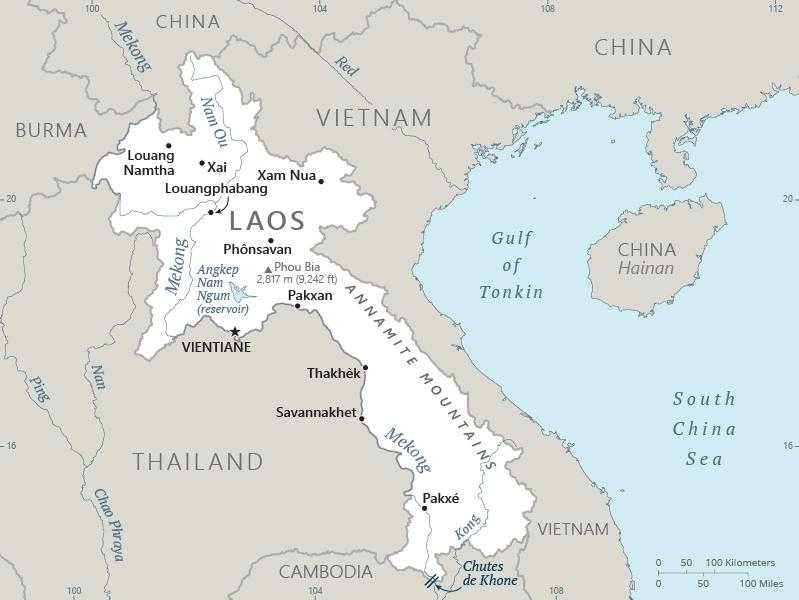
Laos Images
Laos Factbook Data
Diplomatic representation from the US
chief of mission: Ambassador Heather VARIAVA (since 5 February 2024)
embassy: Ban Somvang Tai, Thadeua Road, Km 9, Hatsayfong District, Vientiane
mailing address: 4350 Vientiane Place, Washington DC 20521-4350
telephone: [856] 21-48-7000
FAX: [856] 21-48-7040
email address and website:
CONSLAO@state.gov
https://la.usembassy.gov/
embassy: Ban Somvang Tai, Thadeua Road, Km 9, Hatsayfong District, Vientiane
mailing address: 4350 Vientiane Place, Washington DC 20521-4350
telephone: [856] 21-48-7000
FAX: [856] 21-48-7040
email address and website:
CONSLAO@state.gov
https://la.usembassy.gov/
Age structure
0-14 years: 30.1% (male 1,214,429/female 1,181,845)
15-64 years: 65% (male 2,573,668/female 2,599,957)
65 years and over: 4.8% (2024 est.) (male 178,223/female 205,434)
15-64 years: 65% (male 2,573,668/female 2,599,957)
65 years and over: 4.8% (2024 est.) (male 178,223/female 205,434)
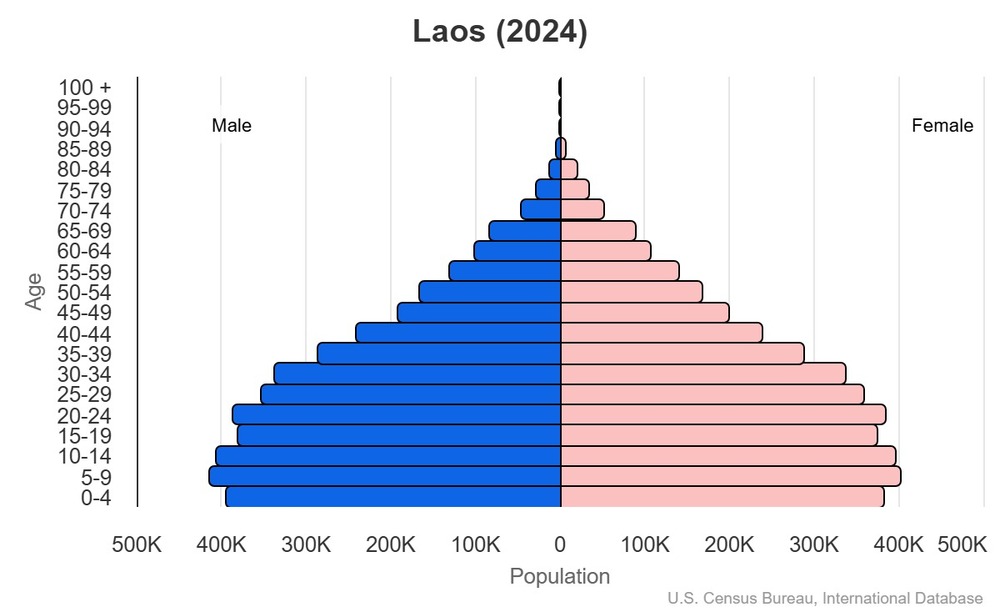
This is the population pyramid for Laos. A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page.
Geographic coordinates
18 00 N, 105 00 E
Sex ratio
at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
0-14 years: 1.03 male(s)/female
15-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.87 male(s)/female
total population: 1 male(s)/female (2024 est.)
Natural hazards
floods, droughts
Area - comparative
about twice the size of Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Utah
about twice the size of Pennsylvania; slightly larger than Utah
Military service age and obligation
18 years of age for voluntary military service; mandatory military service for men 18-35 with a minimum 18-month service obligation (2025)
Background
Modern-day Laos has its roots in the ancient Lao kingdom of Lan Xang, established in the 14th century under King FA NGUM. For 300 years, Lan Xang had influence reaching into present-day Cambodia and Thailand, as well as over all of what is now Laos. After centuries of gradual decline, Laos came under the domination of Siam (Thailand) from the late 18th century until the late 19th century, when it became part of French Indochina. The Franco-Siamese Treaty of 1907 defined the current Lao border with Thailand. Following more than 15 years of civil war, the communist Pathet Lao took control of the government in 1975, ending a six-century-old monarchy and instituting a one party--the Lao People's Revolutionary Party--communist state. A gradual, limited return to private enterprise and the liberalization of foreign investment laws began in the late 1980s. Laos became a member of ASEAN in 1997 and the WTO in 2013.
In the 2010s, the country benefited from direct foreign investment, particularly in the natural resource and industry sectors. Construction of a number of large hydropower dams and expanding mining activities have also boosted the economy. Laos has retained its official commitment to communism and maintains close ties with its two communist neighbors, Vietnam and China, both of which continue to exert substantial political and economic influence on the country. China, for example, provided 70% of the funding for a $5.9 billion, 400-km railway line between the Chinese border and the capital Vientiane, which opened for operations in 2021. Laos financed the remaining 30% with loans from China. At the same time, Laos has expanded its economic reliance on the West and other Asian countries, such as Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Thailand. Nevertheless, despite steady economic growth for more than a decade, it remains one of Asia's poorest countries.
In the 2010s, the country benefited from direct foreign investment, particularly in the natural resource and industry sectors. Construction of a number of large hydropower dams and expanding mining activities have also boosted the economy. Laos has retained its official commitment to communism and maintains close ties with its two communist neighbors, Vietnam and China, both of which continue to exert substantial political and economic influence on the country. China, for example, provided 70% of the funding for a $5.9 billion, 400-km railway line between the Chinese border and the capital Vientiane, which opened for operations in 2021. Laos financed the remaining 30% with loans from China. At the same time, Laos has expanded its economic reliance on the West and other Asian countries, such as Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Thailand. Nevertheless, despite steady economic growth for more than a decade, it remains one of Asia's poorest countries.
Environmental issues
unexploded ordnance; deforestation; soil erosion; loss of biodiversity; water pollution; limited access to potable water
International environmental agreements
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Climate Change-Paris Agreement, Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
Military expenditures
0.2% of GDP (2019 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2018 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2017 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2016 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2015 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2018 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2017 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2016 est.)
0.2% of GDP (2015 est.)
Population below poverty line
18.3% (2018 est.)
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
note: % of population with income below national poverty line
Household income or consumption by percentage share
lowest 10%: 3% (2018 est.)
highest 10%: 31.2% (2018 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
highest 10%: 31.2% (2018 est.)
note: % share of income accruing to lowest and highest 10% of population
Exports - commodities
electricity, fertilizers, gold, garments, paper (2023)
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five export commodities based on value in dollars
Exports - partners
China 39%, Thailand 34%, Australia 4%, USA 4%, Cambodia 2% (2023)
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
note: top five export partners based on percentage share of exports
Administrative divisions
17 provinces (khoueng, singular and plural) and 1 prefecture* (kampheng nakhon); Attapu, Bokeo, Bolikhamxay, Champasak, Houaphanh, Khammouan, Louangnamtha, Louangphabang (Luang Prabang), Oudomxai, Phongsali, Salavan, Savannakhet, Viangchan (Vientiane)*, Viangchan, Xaignabouli, Xaisomboun, Xekong, Xiangkhouang
Agricultural products
cassava, root vegetables, rice, sugarcane, vegetables, bananas, maize, rubber, coffee, watermelons (2023)
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
note: top ten agricultural products based on tonnage
Military and security forces
Lao People's Armed Forces (LPAF; aka Lao People's Army): Lao People's Army (LPA, includes Riverine Force), Lao People's Air Force (LPAF); Self-Defense Militia Forces (2025)
note: the Ministry of Public Security maintains internal security and is responsible for law enforcement; it oversees local, traffic, immigration, and security police, village police auxiliaries, and other armed police units
note: the Ministry of Public Security maintains internal security and is responsible for law enforcement; it oversees local, traffic, immigration, and security police, village police auxiliaries, and other armed police units
Budget
revenues: $2.288 billion (2022 est.)
expenditures: $2.259 billion (2022 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
expenditures: $2.259 billion (2022 est.)
note: central government revenues and expenses (excluding grants/extrabudgetary units/social security funds) converted to US dollars at average official exchange rate for year indicated
Capital
name: Vientiane (Viangchan)
geographic coordinates: 17 58 N, 102 36 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name Viangchan means "city of sandalwood" in Laotian; the standard spelling reflects French influence
geographic coordinates: 17 58 N, 102 36 E
time difference: UTC+7 (12 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
etymology: the name Viangchan means "city of sandalwood" in Laotian; the standard spelling reflects French influence
Imports - commodities
refined petroleum, cars, raw sugar, plastic products, trucks (2023)
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
note: top five import commodities based on value in dollars
Climate
tropical monsoon; rainy season (May to November); dry season (December to April)
Coastline
0 km (landlocked)
Constitution
history: previous 1947 (pre-independence); latest promulgated 13-15 August 1991
amendment process: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership and promulgation by the president of the republic
amendment process: proposed by the National Assembly; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership and promulgation by the president of the republic
Exchange rates
kips (LAK) per US dollar -
Exchange rates:
17,688.874 (2023 est.)
14,035.227 (2022 est.)
9,697.916 (2021 est.)
9,045.788 (2020 est.)
8,679.409 (2019 est.)
Exchange rates:
17,688.874 (2023 est.)
14,035.227 (2022 est.)
9,697.916 (2021 est.)
9,045.788 (2020 est.)
8,679.409 (2019 est.)
Flag
description: three horizontal bands of red (top), blue (double-width), and red, with a large white disk centered in the blue band
meaning: red stands for the blood shed for liberation, and blue for the Mekong River and prosperity; the white disk represents the full moon over the Mekong River and the unity of the people under the Lao People's Revolutionary Party, as well as the country's bright future
meaning: red stands for the blood shed for liberation, and blue for the Mekong River and prosperity; the white disk represents the full moon over the Mekong River and the unity of the people under the Lao People's Revolutionary Party, as well as the country's bright future
Illicit drugs
USG identification:
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country (2025)
major illicit drug-producing and/or drug-transit country (2025)
Independence
19 July 1949 (from France); 22 October 1953 (Franco-Lao Treaty recognizes full independence)
Industries
mining (copper, tin, gold, gypsum); timber, electric power, agricultural processing, rubber, construction, garments, cement, tourism
Judicial branch
highest court(s): People's Supreme Court (consists of the court president and organized into criminal, civil, administrative, commercial, family, and juvenile chambers, each with a vice president and several judges)
judge selection and term of office: president of People's Supreme Court appointed by the National Assembly upon the recommendation of the president of the republic for a 5-year term; vice presidents of the People's Supreme Court appointed by the president of the republic upon the recommendation of the National Assembly; appointment of chamber judges NA; tenure of court vice presidents and chamber judges NA
subordinate courts: appellate courts; provincial, municipal, district, and military courts
judge selection and term of office: president of People's Supreme Court appointed by the National Assembly upon the recommendation of the president of the republic for a 5-year term; vice presidents of the People's Supreme Court appointed by the president of the republic upon the recommendation of the National Assembly; appointment of chamber judges NA; tenure of court vice presidents and chamber judges NA
subordinate courts: appellate courts; provincial, municipal, district, and military courts
Land boundaries
total: 5,274 km
border countries (5): Burma 238 km; Cambodia 555 km; China 475 km; Thailand 1,845 km; Vietnam 2,161 km
border countries (5): Burma 238 km; Cambodia 555 km; China 475 km; Thailand 1,845 km; Vietnam 2,161 km
Land use
agricultural land: 9.9% (2023 est.)
arable land: 5.3% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.7% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 2.9% (2023 est.)
forest: 56.8% (2023 est.)
other: 33.3% (2023 est.)
arable land: 5.3% (2023 est.)
permanent crops: 1.7% (2023 est.)
permanent pasture: 2.9% (2023 est.)
forest: 56.8% (2023 est.)
other: 33.3% (2023 est.)
Legal system
civil law system similar in form to the French system
Legislative branch
legislature name: National Assembly (Sapha Heng Xat)
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 164 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 2/21/2021
parties elected and seats per party: Lao People's Revolutionary Party (LPRP) (158); Other (6)
percentage of women in chamber: 22%
expected date of next election: February 2026
legislative structure: unicameral
number of seats: 164 (all directly elected)
electoral system: plurality/majority
scope of elections: full renewal
term in office: 5 years
most recent election date: 2/21/2021
parties elected and seats per party: Lao People's Revolutionary Party (LPRP) (158); Other (6)
percentage of women in chamber: 22%
expected date of next election: February 2026
Literacy
total population: 75.6% (2023 est.)
male: 85.1% (2023 est.)
female: 66.7% (2023 est.)
male: 85.1% (2023 est.)
female: 66.7% (2023 est.)
Maritime claims
none (landlocked)
International organization participation
ADB, ARF, ASEAN, CP, EAS, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO (subscriber), ITU, MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
National holiday
Republic Day (National Day), 2 December (1975)
Nationality
noun: Lao(s) or Laotian(s)
adjective: Lao or Laotian
adjective: Lao or Laotian
Natural resources
timber, hydropower, gypsum, tin, gold, gemstones
Geography - note
landlocked; most of the country is mountainous and thickly forested; the Mekong River forms a large part of the western boundary with Thailand
Economic overview
lower middle-income, socialist Southeast Asian economy; one of the fastest growing economies; declining but still high poverty; natural resource rich; new anticorruption efforts; already high and growing public debt; service sector hit hard by COVID-19
Political parties
Lao People's Revolutionary Party or LPRP
note: other parties proscribed
note: other parties proscribed
Suffrage
18 years of age; universal
Terrain
mostly rugged mountains; some plains and plateaus
Government type
communist party-led state
Military - note
the LPAF’s primary missions are border and internal security, including counterinsurgency, counterterrorism, and counter-narcotics operations, as well as protecting the regime; its defense partners include Cambodia, China, Russia, and Vietnam (2025)
Country name
conventional long form: Lao People's Democratic Republic
conventional short form: Laos
local long form: Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao
local short form: Mueang Lao (unofficial)
abbreviation: Lao PDR
etymology: name means "Land of the Lao [people];" it derives from the name of the country's founder, Lao
conventional short form: Laos
local long form: Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao
local short form: Mueang Lao (unofficial)
abbreviation: Lao PDR
etymology: name means "Land of the Lao [people];" it derives from the name of the country's founder, Lao
Location
Southeastern Asia, northeast of Thailand, west of Vietnam
Map references
Southeast Asia
Irrigated land
4,410 sq km (2022)
Diplomatic representation in the US
chief of mission: Ambassador PHOUKHONG Sisoulath (since 5 September 2025)
chancery: 2222 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 332-6416
FAX: [1] (202) 332-4923
email address and website:
embasslao@gmail.com
https://laoembassy.com/
chancery: 2222 S Street NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 332-6416
FAX: [1] (202) 332-4923
email address and website:
embasslao@gmail.com
https://laoembassy.com/
Internet users
percent of population: 64% (2023 est.)
Internet country code
.la
GDP (official exchange rate)
$16.503 billion (2024 est.)
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
note: data in current dollars at official exchange rate
Trafficking in persons
tier rating: Tier 3 — Laos does not fully meet the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking and is not making significant efforts to do so, therefore, Laos was downgraded to Tier 3; for more details, go to: https://www.state.gov/reports/2025-trafficking-in-persons-report/laos/
Total renewable water resources
333.5 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education)
total: 9 years (2023 est.)
male: 9 years (2023 est.)
female: 9 years (2023 est.)
male: 9 years (2023 est.)
female: 9 years (2023 est.)
Urbanization
urban population: 38.2% of total population (2023)
rate of urbanization: 2.99% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
rate of urbanization: 2.99% annual rate of change (2020-25 est.)
Broadcast media
6 TV stations operating out of Vientiane, with half state-operated and half commercial; 17 provincial stations, with nearly all programming relayed via satellite from the state-operated stations in Vientiane; multi-channel satellite and cable TV systems provide access to a wide range of foreign stations; state-controlled radio with state-operated Lao National Radio (LNR) broadcasting on 5 frequencies; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are accessible
Drinking water source
improved:
urban: 97.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 78.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 85.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 21.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 14.5% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 97.1% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 78.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 85.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 2.9% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 21.5% of population (2022 est.)
total: 14.5% of population (2022 est.)
National anthem(s)
title: "Pheng Xat Lao" (Hymn of the Lao People)
lyrics/music: SISANA Sisane/THONGDY Sounthonevichit
history: music adopted 1945, lyrics adopted 1975; the anthem's lyrics were changed after the communist revolution that overthrew the monarchy in 1975
lyrics/music: SISANA Sisane/THONGDY Sounthonevichit
history: music adopted 1945, lyrics adopted 1975; the anthem's lyrics were changed after the communist revolution that overthrew the monarchy in 1975
This is an audio of the National Anthem for Laos. The national anthem is generally a patriotic musical composition - usually in the form of a song or hymn of praise - that evokes and eulogizes the history, traditions, or struggles of a nation or its people. National anthems can be officially recognized as a national song by a country's constitution or by an enacted law, or simply by tradition. Although most anthems contain lyrics, some do not.
Major urban areas - population
721,000 VIENTIANE (capital) (2023)
International law organization participation
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
Physician density
0.33 physicians/1,000 population (2022)
Hospital bed density
1.3 beds/1,000 population (2021 est.)
National symbol(s)
elephant
GDP - composition, by end use
household consumption: 65.7% (2016 est.)
government consumption: 14% (2016 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 29% (2016 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 33.2% (2016 est.)
imports of goods and services: -41.9% (2016 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
government consumption: 14% (2016 est.)
investment in fixed capital: 29% (2016 est.)
investment in inventories: 0% (2016 est.)
exports of goods and services: 33.2% (2016 est.)
imports of goods and services: -41.9% (2016 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to rounding or gaps in data collection
Citizenship
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Laos
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Laos
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
Population distribution
most densely populated area is in and around the capital city of Vientiane; large communities are primarily found along the Mekong River along the southwestern border; overall density is considered one of the lowest in Southeast Asia
Electricity access
electrification - total population: 100% (2022 est.)
Civil aircraft registration country code prefix
RDPL
Sanitation facility access
improved:
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 72% of population (2022 est.)
total: 82.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 28% of population (2022 est.)
total: 17.5% of population (2022 est.)
urban: 100% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 72% of population (2022 est.)
total: 82.5% of population (2022 est.)
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population (2022 est.)
rural: 28% of population (2022 est.)
total: 17.5% of population (2022 est.)
Ethnic groups
Lao 53.2%, Khmou 11%, Hmong 9.2%, Phouthay 3.4%, Tai 3.1%, Makong 2.5%, Katong 2.2%, Lue 2%, Akha 1.8%, other 11.6% (2015 est.)
note: the Laos Government officially recognizes 49 ethnic groups, but the total number of ethnic groups is estimated to be well over 200
note: the Laos Government officially recognizes 49 ethnic groups, but the total number of ethnic groups is estimated to be well over 200
Religions
Buddhist 64.7%, Christian 1.7%, none 31.4%, other/not stated 2.1% (2015 est.)
Languages
Lao (official), French, English, various ethnic languages
major-language sample(s):
ແຫລ່ງທີ່ຂາດບໍ່ໄດ້ສຳລັບຂໍ້ມູນຕົ້ນຕໍ່” (Lao)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
major-language sample(s):
ແຫລ່ງທີ່ຂາດບໍ່ໄດ້ສຳລັບຂໍ້ມູນຕົ້ນຕໍ່” (Lao)
The World Factbook, the indispensable source for basic information.
Lao audio sample
Imports - partners
Thailand 58%, China 36%, Japan 1%, Singapore 1%, Germany 1% (2023)
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
note: top five import partners based on percentage share of imports
Refugees and internally displaced persons
IDPs: 1,274 (2024 est.)
Elevation
highest point: Phu Bia 2,817 m
lowest point: Mekong River 70 m
mean elevation: 710 m
lowest point: Mekong River 70 m
mean elevation: 710 m
Health expenditure
2.7% of GDP (2021)
4.3% of national budget (2022 est.)
4.3% of national budget (2022 est.)
Military and security service personnel strengths
information limited and varied; estimated 30,000 active Armed Forces; estimated 100,000 Self-Defense Militia Forces (2025)
Military equipment inventories and acquisitions
the LPAF is armed with Chinese, Russian, and Soviet-era equipment and weapons (2025)
Total water withdrawal
municipal: 130 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 170 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 7.05 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
industrial: 170 million cubic meters (2022 est.)
agricultural: 7.05 billion cubic meters (2022 est.)
Waste and recycling
municipal solid waste generated annually: 351,900 tons (2024 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 15.1% (2022 est.)
percent of municipal solid waste recycled: 15.1% (2022 est.)
Average household expenditures
on food: 50.5% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 7.8% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
on alcohol and tobacco: 7.8% of household expenditures (2023 est.)
Major watersheds (area sq km)
Pacific Ocean drainage: Mekong (805,604 sq km)
Major rivers (by length in km)
Mènam Khong (Mekong) (shared with China [s], Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam [m]) - 4,350 km
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
note: [s] after country name indicates river source; [m] after country name indicates river mouth
National heritage
total World Heritage Sites: 3 (all cultural)
selected World Heritage Site locales: Town of Luangphrabang; Vat Phou and Associated Ancient Settlements; Megalithic Jar Sites in Xiengkhuang - Plain of Jars
selected World Heritage Site locales: Town of Luangphrabang; Vat Phou and Associated Ancient Settlements; Megalithic Jar Sites in Xiengkhuang - Plain of Jars
Child marriage
women married by age 15: 7.1% (2017)
women married by age 18: 32.7% (2017)
men married by age 18: 10.8% (2017)
women married by age 18: 32.7% (2017)
men married by age 18: 10.8% (2017)
Coal
production: 16.629 million metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 15.944 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.065 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 22,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 62 million metric tons (2023 est.)
consumption: 15.944 million metric tons (2023 est.)
exports: 1.065 million metric tons (2023 est.)
imports: 22,000 metric tons (2023 est.)
proven reserves: 62 million metric tons (2023 est.)
Electricity generation sources
fossil fuels: 23.3% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 76.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
solar: 0.2% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
hydroelectricity: 76.5% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
biomass and waste: 0.1% of total installed capacity (2023 est.)
Petroleum
refined petroleum consumption: 25,000 bbl/day (2023 est.)
Gross reproduction rate
1.07 (2025 est.)
Currently married women (ages 15-49)
61.6% (2017 est.)
Remittances
1.8% of GDP (2023 est.)
1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
1.5% of GDP (2022 est.)
1.2% of GDP (2021 est.)
note: personal transfers and compensation between resident and non-resident individuals/households/entities
Railways
total: 422 km (2023)
standard gauge: 422 km (2023) 1.435-m gauge (422 km overhead electrification)
standard gauge: 422 km (2023) 1.435-m gauge (422 km overhead electrification)
National color(s)
red, white, blue
Particulate matter emissions
20.5 micrograms per cubic meter (2019 est.)
Labor force
3.585 million (2024 est.)
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
note: number of people ages 15 or older who are employed or seeking work
Youth unemployment rate (ages 15-24)
total: 2.2% (2024 est.)
male: 2.4% (2024 est.)
female: 2.1% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
male: 2.4% (2024 est.)
female: 2.1% (2024 est.)
note: % of labor force ages 15-24 seeking employment
Net migration rate
-0.93 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Median age
total: 25.8 years (2025 est.)
male: 25 years
female: 25.7 years
male: 25 years
female: 25.7 years
Debt - external
$9.619 billion (2023 est.)
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
note: present value of external debt in current US dollars
Maternal mortality ratio
112 deaths/100,000 live births (2023 est.)
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold
$1.77 billion (2023 est.)
$1.576 billion (2022 est.)
$1.951 billion (2021 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
$1.576 billion (2022 est.)
$1.951 billion (2021 est.)
note: holdings of gold (year-end prices)/foreign exchange/special drawing rights in current dollars
Total fertility rate
2.19 children born/woman (2025 est.)
Unemployment rate
1.3% (2024 est.)
1.2% (2023 est.)
1.3% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
1.2% (2023 est.)
1.3% (2022 est.)
note: % of labor force seeking employment
Carbon dioxide emissions
23.412 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 19.652 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 3.76 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from coal and metallurgical coke: 19.652 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
from petroleum and other liquids: 3.76 million metric tonnes of CO2 (2023 est.)
Area
total : 236,800 sq km
land: 230,800 sq km
water: 6,000 sq km
land: 230,800 sq km
water: 6,000 sq km
Taxes and other revenues
12.1% (of GDP) (2022 est.)
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
note: central government tax revenue as a % of GDP
Real GDP (purchasing power parity)
$66.905 billion (2024 est.)
$64.173 billion (2023 est.)
$61.856 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$64.173 billion (2023 est.)
$61.856 billion (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Airports
20 (2025)
Infant mortality rate
total: 34.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2025 est.)
male: 39.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 31.6 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 39.1 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 31.6 deaths/1,000 live births
Gini Index coefficient - distribution of family income
38.8 (2018 est.)
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
note: index (0-100) of income distribution; higher values represent greater inequality
Inflation rate (consumer prices)
23.1% (2024 est.)
31.2% (2023 est.)
23% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
31.2% (2023 est.)
23% (2022 est.)
note: annual % change based on consumer prices
Current account balance
$404.523 million (2023 est.)
-$458.754 million (2022 est.)
$431.636 million (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
-$458.754 million (2022 est.)
$431.636 million (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - net trade and primary/secondary income in current dollars
Real GDP per capita
$8,600 (2024 est.)
$8,400 (2023 est.)
$8,200 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
$8,400 (2023 est.)
$8,200 (2022 est.)
note: data in 2021 dollars
Broadband - fixed subscriptions
total: 183,000 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2022 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 2 (2022 est.)
Tobacco use
total: 24.1% (2025 est.)
male: 41% (2025 est.)
female: 7.2% (2025 est.)
male: 41% (2025 est.)
female: 7.2% (2025 est.)
Obesity - adult prevalence rate
5.3% (2016)
Energy consumption per capita
34.463 million Btu/person (2023 est.)
Death rate
6.07 deaths/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Birth rate
19.22 births/1,000 population (2025 est.)
Electricity
installed generating capacity: 12.738 million kW (2023 est.)
consumption: 12.803 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 38 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 955.095 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.447 billion kWh (2023 est.)
consumption: 12.803 billion kWh (2023 est.)
exports: 38 billion kWh (2023 est.)
imports: 955.095 million kWh (2023 est.)
transmission/distribution losses: 2.447 billion kWh (2023 est.)
Merchant marine
total: 1 (2023)
by type: general cargo 1
by type: general cargo 1
Children under the age of 5 years underweight
24.3% (2023 est.)
Imports
$8.596 billion (2023 est.)
$7.983 billion (2022 est.)
$6.527 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
$7.983 billion (2022 est.)
$6.527 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - imports of goods and services in current dollars
Exports
$9.698 billion (2023 est.)
$8.604 billion (2022 est.)
$7.82 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
$8.604 billion (2022 est.)
$7.82 billion (2021 est.)
note: balance of payments - exports of goods and services in current dollars
Alcohol consumption per capita
total: 8.15 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.62 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.07 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 4.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
beer: 3.62 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
wine: 0.07 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
spirits: 4.46 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
other alcohols: 0 liters of pure alcohol (2019 est.)
Life expectancy at birth
total population: 69 years (2024 est.)
male: 67.4 years
female: 70.7 years
male: 67.4 years
female: 70.7 years
Real GDP growth rate
4.3% (2024 est.)
3.7% (2023 est.)
2.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
3.7% (2023 est.)
2.7% (2022 est.)
note: annual GDP % growth based on constant local currency
Industrial production growth rate
3.9% (2024 est.)
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
note: annual % change in industrial value added based on constant local currency
GDP - composition, by sector of origin
agriculture: 16.8% (2024 est.)
industry: 29% (2024 est.)
services: 43.5% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
industry: 29% (2024 est.)
services: 43.5% (2024 est.)
note: figures may not total 100% due to non-allocated consumption not captured in sector-reported data
Education expenditure
1.2% of GDP (2023 est.)
8.2% national budget (2024 est.)
8.2% national budget (2024 est.)
Population growth rate
1.22% (2025 est.)
Executive branch
chief of state: President THONGLOUN Sisoulith (since 22 March 2021)
head of government: Prime Minister SONEXAY (also spelled SONXAI) Siphandon (since 30 December 2022)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president and approved by the National Assembly
election/appointment process: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term (no term limits); prime minister nominated by the president, elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term
most recent election date: 22 March 2021
election results:
2021: THONGLOUN Sisoulith (LPRP) elected president; National Assembly vote - 161-1; PHANKHAM Viphavanh (LPRP) elected prime minister; National Assembly vote - 158-3
2016: BOUNNHANG Vorachit (LPRP) elected president; percent of National Assembly vote - NA; THONGLOUN Sisoulith (LPRP) elected prime minister; percent of National Assembly vote - NA
expected date of next election: March 2026
note: President THONGLOUN Sisoulith is also general secretary of the Lao People's Revolutionary Party
head of government: Prime Minister SONEXAY (also spelled SONXAI) Siphandon (since 30 December 2022)
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president and approved by the National Assembly
election/appointment process: president and vice president indirectly elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term (no term limits); prime minister nominated by the president, elected by the National Assembly for a 5-year term
most recent election date: 22 March 2021
election results:
2021: THONGLOUN Sisoulith (LPRP) elected president; National Assembly vote - 161-1; PHANKHAM Viphavanh (LPRP) elected prime minister; National Assembly vote - 158-3
2016: BOUNNHANG Vorachit (LPRP) elected president; percent of National Assembly vote - NA; THONGLOUN Sisoulith (LPRP) elected prime minister; percent of National Assembly vote - NA
expected date of next election: March 2026
note: President THONGLOUN Sisoulith is also general secretary of the Lao People's Revolutionary Party
Telephones - mobile cellular
total subscriptions: 4.96 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 65 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 65 (2023 est.)
Dependency ratios
total dependency ratio: 52.9 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 45.3 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 7.6 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 13.1 (2025 est.)
youth dependency ratio: 45.3 (2025 est.)
elderly dependency ratio: 7.6 (2025 est.)
potential support ratio: 13.1 (2025 est.)
Population
total: 8,052,913 (2025 est.)
male: 4,016,077
female: 4,036,836
male: 4,016,077
female: 4,036,836
Telephones - fixed lines
total subscriptions: 1.23 million (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 16 (2023 est.)
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 16 (2023 est.)






